What is Estrogen?
Estrogen, also known as oestrogen, is the term for any group of chemically similar hormones that promote the development and maintenance of female characteristics of the body.
Types of Estrogen
Although natural estrogen hormones are collectively referred to simply as “estrogen,” there are three different hormones that make up the compound steroid estrogen: estrone, estradiol, and estriol.
Synthetically produced estrogens or those naturally occurring in plants have just as much of an impact on health as endogenous steroidal estrogens.
Click on the following link to learn more about estrogen and the different types of this ubiquitously famous "female" hormone.
Estrogen Production
Estrogen Glands
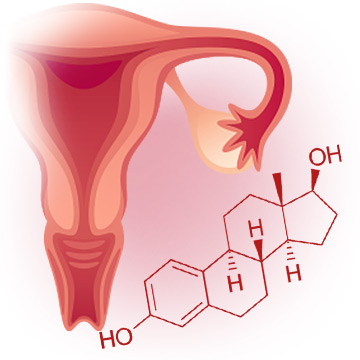
It is true that the majority of estrogen - estradiol – is produced in the ovaries. However, the quantity and type of estrogen hormone produced depends greatly upon the reproductive stage in which a woman finds herself.
Aside from the ovaries, estrogen in women is produced in an assortment of glands, such as adipose tissue and adrenal glands as well as in the placenta during pregnancy.
Estrogen Receptors
After being transported throughout the body to various receptors, estrogens find a target cell to penetrate and enter to directly influence the cell's behavior, which positively or negatively affects a woman's health.
Click on the following link to discover more about estrogen production for a better appreciation of the hormone's holistic role within the body.
Estrogen Function
Natural estrogen is essential to a woman's physical and psychological well-being, affecting everything from appearance to reproductive ability.
Estrogen Roles
However, aside from its principal reproductive roles, estrogen carries out a range of other tasks that include:
- Protecting against heart disease
- Preserving bone density
- Sustaining mood levels
- Preserving skin tension
- And more critical functions
Estrogen Effects

Also, estrogen affects an array of organs and body systems, including the urinary tract; hair; mucous membranes; reproductive tract; heart and blood vessels; brain; pelvic muscles; breasts; and bones.
To learn more about estrogen's continuous contribution to women's overall health, continue reading about estrogen roles and effects throughout the body.
Estrogen Fluctuations through Life
From menarche to postmenopause, estrogen hormones play an instrumental role in women's livelihoods. Click on the following link to learn more about estrogen fluctuations through life, or continue reading about pivotal life moments that garner certain hormonal fluctuations.
Estrogen and Pregnancy
Estrogen is one of the most important hormones needed to make conception possible for a woman. Principally, the hormone grows and matures the uterine lining in preparation for nourishing an embryo. Upon conception, natural estrogen continues to cause changes until after birth. Learn all about estrogen and pregnancy.
Estrogen and Menopause
The physical changes of perimenopause are rooted in hormonal fluctuations, specifically variations in the level of circulating estrogen. The quantity and quality of follicles diminishes once a woman reaches her 40s, causing fewer ovulations and, consequently, lower progesterone levels to counteract the effects of estrogen. Read all about estrogen and menopause.
Estrogen and Postmenopause
Postmenopause is the time after menopause has been declared. From this date onward, women do not ovulate nor menstruate since ovaries stop reproductive functions. Blood estrogen levels drop dramatically as the hormone's production sites change, causing severe symptoms if not managed properly. Learn all about estrogen and postmenopause.
Estrogen Levels
Due to natural estrogen's vast involvement in driving the health of almost every single body system, it is critical for women to maintain normal estrogen levels.
During adulthood, normal estrogen levels will range from 30 - 400 pg/mL. The steady rise and fall of estrogen levels happens within the menstrual cycle on a monthly basis. Moreover, during key times in a woman's reproductive life, the hormone adapts to more specific roles. Click on the following link to read more about healthy estrogen levels.
Low Estrogen Levels
The majority of women will experience abnormal drops of natural estrogen at some point in their reproductive lives, and these drops can be caused by a variety of factors. Low levels of estrogen in women can be caused by natural incidences, lifestyle factors, induced causes, and other conditions. Read more about low estrogen levels and causes that could be leading to unbearable symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Estrogen
Likewise, some women may not automatically recognize that the underlying cause of their symptoms are low estrogen levels as symptoms can be varied and subtle. Symptoms and signs of low estrogen affect not only the reproductive system, but also other body systems and organs. Learn more about the signs and symptoms of low estrogen levels before the imbalance becomes a more serious health condition.
High Estrogen Levels

Just as estrogen hormone levels can drop below normal, the opposite is also true, in which estrogen levels rise above the normal range. Having too much estrogen can be due to periods of reproductive significance - such as pregnancy - as well as lifestyle factors, such as poor diet and stress. They can also be caused by treatments, medications, environmental exposures, and other conditions. Read more about the causes of high estrogen levels for heightened awareness on how to avoid an estrogen imbalance.
Signs and Symptoms of High Estrogen
Irregular periods, weight gain, carbohydrate cravings, and irritability are just a few of the many symptoms of high estrogen that can develop. These symptoms eventually evolve into more serious health conditions if not properly managed. Learn more about the signs and symptoms of high estrogen as well as what the imbalance can turn into if left untreated.
Estrogen Deficiency
Estrogen deficiency – or hypoestrogenism – is a consistent lack or decreased levels of estrogen that have adverse effects on the female body. It is distinct from temporary low estrogen levels, which can occur when estrogen levels are periodically below normal.
A permanent state of low estrogen levels, outside the hormone's regular fluctuation, often occurs from certain genetic factors as well as from undergoing reproductive health surgeries or taking some medications. There are several risk factors that make women more susceptible to this hormonal imbalance as well.Learn all about the causes, signs, and symptoms of estrogen deficiency.
Estrogen Dominance
Conversely, there is the hormonal imbalance known as estrogen dominance. Estrogen dominance is not solely defined as high estrogen hormone levels. It occurs when a woman has normal or excessive estrogen levels, but with little or no progesterone to balance out its effects.
Because the endocrine system is very sensitive and is affected by a range of factors, identifying the cause is instrumental with improving hormonal health. Just like estrogen deficiency, estrogen dominance can also be caused a number of health conditions, use of certain medications, and more. Discover more about estrogen dominance and the condition's causes, signs, and symptoms.
Estrogen Tests
In general, estrogen tests are used to help investigate menstrual abnormalities, such as amenorrhea, the absence of menstruation, and menorrhagia, excessive menstrual bleeding.
Common Estrogen Tests
A blood test measures estradiol, estriol, and estrone levels found in blood serum or blood plasma content. It is often considered the most conventional of the tests.
Another common estrogen test is the urine test, which is most commonly used to measure the level of estriol in pregnant women.
Advanced Estrogen Tests
One of the more advanced estrogen tests includes saliva testing. Many researchers argue this test is the most accurate because it measures bioavailable hormones delivered to cell receptors. This can be important when monitoring hormone therapy effectiveness.
Discover more about estrogen tests, including when to take each for optimal results, by clicking on the preceding link.
Lowering Estrogen Levels
Lifestyle changes in regards to diet as well as exercise and healthy habits are fundamental musts for indirectly lowering estrogen levels. Moreover, alternative treatments - such as phytoestrogenic herbal supplements, vitamins, and hormone-regulating herbal supplements - and pharmaceutical options help directly lower estrogen levels. Learn more about how to lower estrogen levels before the progression into estrogen dominance.
Estrogen Blockers
An estrogen blocker is any substance that keeps cells from producing or using estrogen in cases of estrogen dominance. Natural estrogen blockers, such as certain foods and herbs, have been used for centuries to lower estrogen levels and include aromatase inhibitors, which work by blocking the activity of the enzyme aromatase.
Pharmaceutical estrogen blockers are a relatively recent invention. They not only work as aromatase inhibitors, but also as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), which bind to estrogen receptors and prevent natural estrogen from binding. Read more about different varieties and types of estrogen blockers.
Increasing Estrogen Levels

Once a hormonal imbalance is diagnosed, there are methods women can use to increase natural estrogen levels. Lifestyle changes that indirectly increase estrogen levels include an estrogen-friendly diet, moderate exercise, and healthy habits. Also, conscientious consumption of phytoestrogens, alternative medicine, and several pharmaceutical options can directly increase estrogen levels. Find out how to increase estrogen levels and rid oneself of the hormonal slump.
Estrogen Medications & Products
Alternative approaches offer little to no risk and treat the hormonal imbalance directly at its source. They include phytoestrogenic supplements - like black cohosh and red clover - as well as hormone-regulating supplements that naturally nourish endocrine glands, such as Macafem. However, hormonal imbalance symptoms may be so severe that more complex treatment is necessary, such as HRT (with risks involved). Discover more about the various estrogen medications and products that can be taken to finally stabilize hormones.
Estrogen Foods & Supplements
Natural sources of estrogen are derived from are hundreds of plants that contain phytoestrogens. When consumed in ample amounts, plant-based estrogens can assist to balance hormonal levels. The same can be said for medicinal herbs high in phytoestrogens. Learn more about estrogen foods and supplements as well as the benefit of consuming an estrogen diet to induce hormonal balance.
Sources
- American Association for Clinical Chemistry. (2014). Estrogens. Retrieved June 20, 2018, from https://labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/estrogen/tab/test/
- Balunas, M.J. et al. (2008). Natural Products as Aromatase Inhibitors. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 8(6), 646-682. Retrieved June 20, 2018, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3074486/
- Conrad, C. (2005). A Woman's Guide to Natural Hormones. New York: Penguin Group. Available from Google Books.
- National Women's Health Network. (n.d.). Herbs and Phytoestrogens. Retrieved July 12, 2017, from https://www.nwhn.org/herbs-and-phytoestrogens/
- National Women's Health Resource Center, Inc. (2017). Estrogen. Retrieved June 20, 2018, from http://www.healthywomen.org/condition/estrogen
- National Institute of Health. (2017). Hormone Replacement Therapy. Retrieved July 20, 2017, from https://medlineplus.gov/hormonereplacementtherapy.html
- The North American Menopause Society. (2010). Changes in Hormone Levels. Retrieved June 20, 2018, from https://www.menopause.org/for-women/sexual-health-menopause-online/changes-at-midlife/changes-in-hormone-levels
- Tulane University. (2014). Phytoestrogens. Retrieved July 19, 2017, from http://e.hormone.tulane.edu/learning/phytoestrogens.html
- University of Rochester Medical Center. (2017). Estrogen's Effects on the Female Body | Health Encyclopedia: Estradiol (Blood). Retrieved June 20, 2018, from https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=85&ContentID=P00559 | https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=estradiol
- Women in Balance Institute: National University of Natural Medicine. (n.d.). Hormones 101 | Hormone Testing & Diagnostic Resources. Retrieved June 20, 2018, from http://womeninbalance.org/about-hormone-imbalance/hormones-101/ | https://womeninbalance.org/physician-resources/hormone-testing-diagnostic-resources/