Low estrogen negatively affects more than just a woman's physical health. A variety of signs and symptoms can weaken her emotional well-being, too, causing a bout of life-degrading turmoil. Therefore, when the imbalance is suspected and diagnosed, it is crucial to pursue increasing estrogen immediately before temporarily low levels turn into a constant estrogen deficiency.
Continue reading to learn more about how to stop the hormonal imbalance by increasing estrogen levels naturally and through conventional methods.
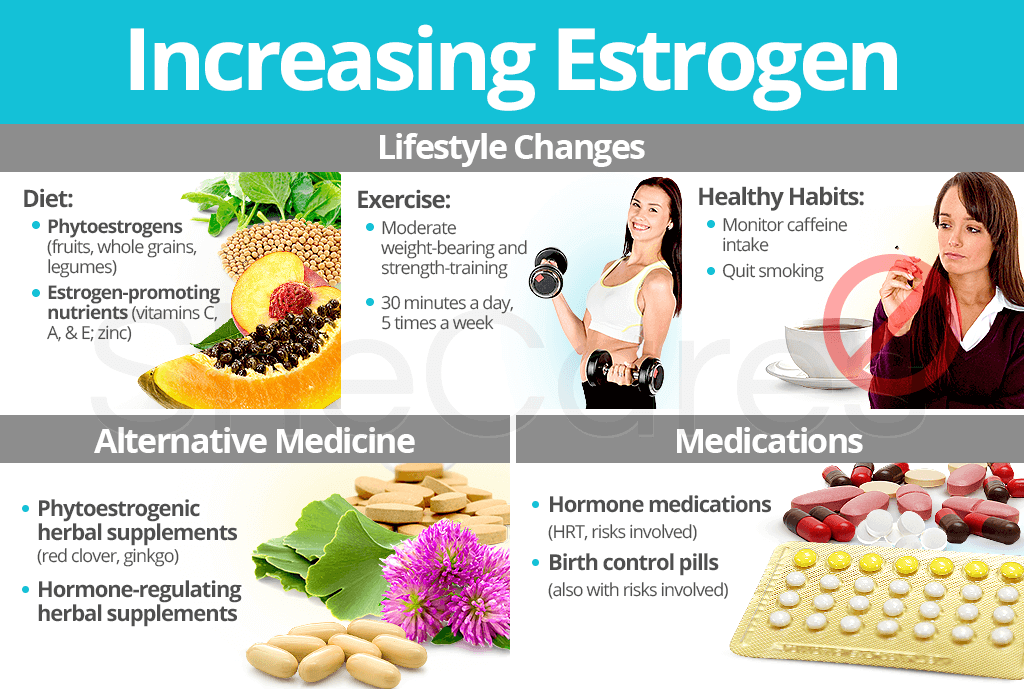
Lifestyle Changes to Increase Estrogen

Lifestyle changes can greatly improve endocrine system functions by encouraging hormonal balance, especially in regards to increasing estrogen naturally.
Diet
For overall nutrition, it is beneficial to consume a colorful variety of unprocessed foods in balanced amounts. Try to avoid saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and excessive sodium. When specifically making an effort to increase estrogen levels naturally, add the following to a wholesome diet:
- Food with phytoestrogens. Phytoestrogens are estrogens found within plants that weakly mimic the ability of endogenous estrogens by attaching to site receptors. Women trying to naturally increase estrogen often turn to these plant-based estrogens for relief:
Fruits
cherries, apples, papaya, pomegranates, plums, strawberries, peaches, tomatoes
Whole grains
barley, oats, wheat, brown rice
Vegetables
sprouts, eggplants, celery, yams, carrots, alfalfa, parsley
Legumes
soybeans, lentils, black-eyed peas, garbanzo beans, split peas
Nuts and seeds
sesame seeds, flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, almonds, walnuts
- Foods with estrogen-promoting nutrients. The following list of vitamins and minerals are acclaimed for helping raise estrogen levels naturally. Many of these also help prevent adrenal fatigue, which can further disrupt overall hormonal balance:
Exercise
While exercise does promote whole body wellness, women trying to increase estrogen levels naturally with routine exercise should do so in moderation.
A condition known as exercise-induced amenorrhea occurs when excessive exercise causes decreased estrogen levels. To increase estrogen levels, choose moderate, weight-bearing and strength-training exercises at least 30 minutes a day, five times a week to maintain an ideal body weight and fat percentage of at least 17 percent. Options include walking, jogging, dancing, playing tennis, and weight training.
Healthy habits
Keeping up with healthy habits is also key to naturally raising estrogen levels.
- Monitor caffeine intake. Research shows those of Caucasian descent who consumed at least 200 milligrams of caffeine daily had slightly lower estrogen levels than those who consumed less. Results were opposite for women of Asian and African descent.
- Quit smoking. Recent studies have proven that women who smoke have lower free estradiol levels than do nonsmokers.
All of these lifestyle changes may have a positive effect. However, the following help directly increase estrogen.
Alternative Medicine to Increase Estrogen

Using alternative approaches involves little to no risk and can be an extremely effective way in increasing estrogen naturally. Two of the most common alternative medicines are phytoestrogenic herbal supplements and hormone-regulating herbal supplements.
Phytoestrogenic herbal supplements
These supplements, made from black cohosh, red clover, dong quai, and other herbs, herbs contain phytoestrogens that can help stimulate hormonal balance in the body. They should be considered different from a phytoestrogenic diet as supplemental doses are often higher than those obtained from dietary sources.
Hormone-regulating herbal supplements
These supplements, including Macafem, stimulate the body's natural hormone production by nourishing the pituitary and endocrine glands, helping the body produce hormones more efficiently. This results in the balance of estrogen as well as other important hormones, such as progesterone. These supplements can be considered the safest and most natural way to support natural hormone production.
Read more about which estrogen foods and supplements help increase estrogen levels.
Medications to Increase Estrogen
Interventions involving pharmaceutical options often implicate the highest risk at the highest costs. Most common drugs to increase estrogen levels include hormone medications and birth control pills.
Hormone medications
Many women who are undergoing the menopausal transition or are estrogen deficient will often opt to receive hormone medications in the form of hormone replacement therapy, HRT.
Although HRT is generally effective with quick results, it can have dire side effects. Studies have shown that estrogen therapy can increase the risk of blood clots, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and more.
Birth control pills
Other prescription medications, such as birth control pills, can increase estrogen in the body to ultimately regulate hormones. Just like HRT, birth control pills carry inevitable side effects, which sometimes may not arise until after discontinuing use.
All in all, increasing estrogen levels naturally starts with a wholesome diet that is composed of phytoestrogenic foods and estrogen-promoting nutrients and continues with moderate exercise and healthy habits, such as avoiding excess caffeine intake and quitting smoking. From there, various herbal supplements can assist in ultimately bringing about hormonal balance.
Continue reading about estrogen foods and supplements for more extensive information on raising estrogen levels naturally to combat symptoms once and for all.
Sources
- Baron, J.A. et al. (1995). The effect of cigarette smoking on adrenal cortical hormones. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 272(1), 151-155. Retrieved August 22, 2017, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7815328
- Corwin, R.L. et al. (2006). Dietary Saturated Fat Intake Is Inversely Associated with Bone Density in Humans: Analysis of NHANES III. Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 159-165. Retrieved July 11, 2017, from http://jn.nutrition.org/content/136/1/159.full
- Gill, J. (2000). The Effects of Moderate Alcohol Consumption on Female Hormone Levels and Reproductive Function. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 35(5), 417-423. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/35.5.417
- Martin, R. & Gerstung, J. (2005). The Estrogen Alternative: A Guide to Natural Hormonal Balance. Vermont: Healing Arts Press. Available from Google Books.
- Meraglia, T. (2015). The Hormone Secret. New York: Atria Paperback. Available from Google Books.
- National Institutes of Health. (2012). NIH Study shows caffeine consumption linked to estrogen changes | Estrogen and Progestin (Hormone Replacement Therapy). Retrieved August 22, 2017, from https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-study-shows-caffeine-consumption-linked-estrogen-changes | https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a601041.html
- National Women's Health Network. (2015). Herbs and Phytoestrogens. Retrieved August 23, 2017, from https://www.nwhn.org/herbs-and-phytoestrogens/
- Patisaul, H.B. & Jefferson, W. (2010). The pros and cons of phytoestrogens. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 31(4), 400-419. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.03.003
- Pölkki, M. & Rantala, M.J. (2009). Smoking Affects Womens' Sex Hormone-Regulated Body Form. American Public Health Association, 99(8), 1350. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2009.163485
- Rapuri, P.B. et al. (2001). Caffeine intake increases the rate of bone loss in elderly women and interacts with vitamin D receptor genotypes 1,2,3,4. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 74(5), 694-700. Retrieved July 11, 2017, from http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/74/5/694.full
- Tallia, A.F. et al. (Eds.). (2017). Swanson's Family Medicine Review E-Book. Pennsylvania: Elsevier. Available from Google Books.
- Tansavatdi, K. et al. (2004). The effects of smoking on estradiol metabolism. Minerva Ginecologica, 56(1), 105-14. Retrieved July 11, 2017, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14973414