What is Fertility Preservation?
Fertility preservation methods aim at saving or protecting eggs or ovarian tissue for future use.
There are several reasons for why women might want to preserve their fertility, which typically fall into one of two categories:
Medical fertility preservation. Women with certain health conditions, such as endometriosis or lupus, might want to preserve their fertility before their disease progresses and compromises their ability to conceive. Also, those undergoing radiation or chemotherapy for cancer might choose fertility preservation for the duration of the treatment to prevent damage to their reproductive organs.
Social fertility preservation. Women might also wish to undergo social fertility preservation to delay pregnancy for later for non-medical reasons, such as personal preference, life situation, career goals, finances, or relationship status.
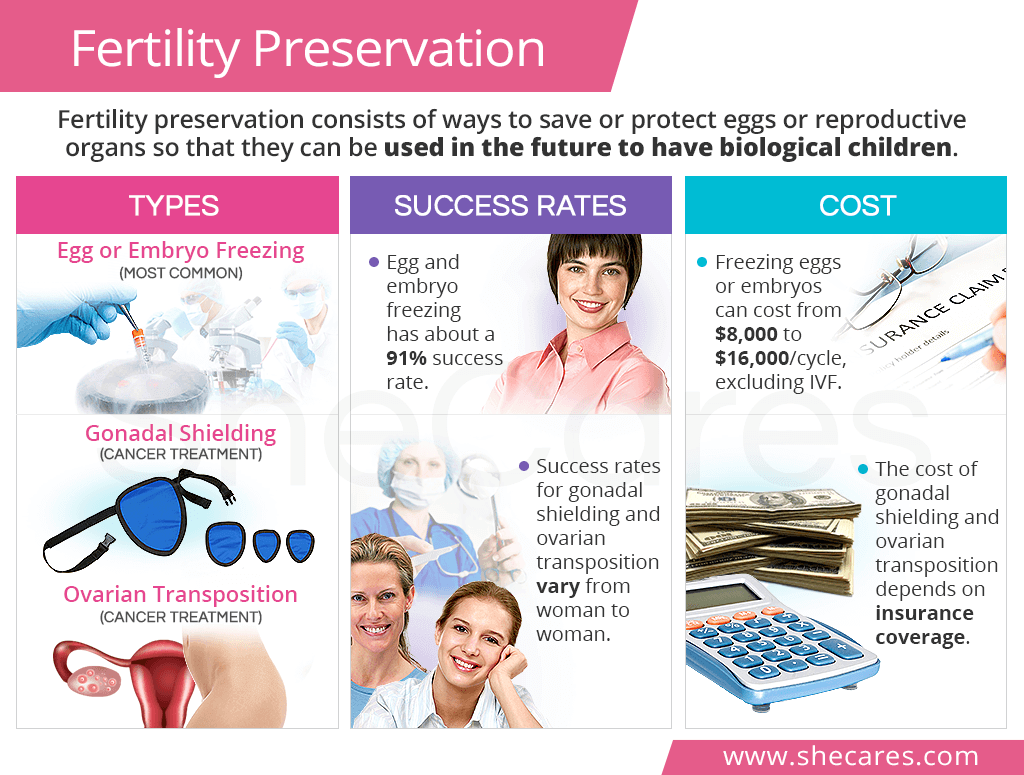
Types of Fertility Preservation
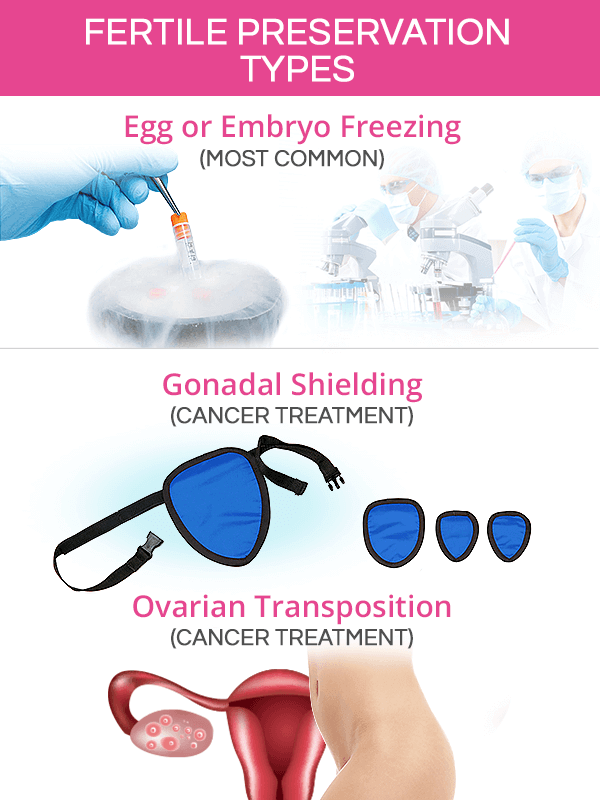
To date, there are three approved methods of preserving fertility, including egg freezing, gonadal shielding, and ovarian transposition. There are several others that are still being researched.
Egg Freezing
Freezing eggs, medically knows as cryopreservation, is available to women who have already reached puberty. Female eggs can be frozen in two ways:
Embryo cryopreservation is the most common method to preserve fertility. It consists of surgical removal of the eggs from the ovaries, followed by their in vitro fertilization and freezing. Once frozen, eggs are stored until a woman decides it is time for pregnancy. This method can be used for both medical and social reasons, and it is most appropriate for women who either have a partner or want to use a sperm donor.
Oocyte cryopreservation. Most of the steps in this method of fertility preservation are the same as in embryo freezing; however, in this case, the eggs are not fertilized prior to being stored. Once harvested, they are frozen and stored unfertilized. Oocyte cryopreservation might be most suitable for women who don't have a partner or don't want to use a donor as well as for those with religious or ethical objections against freezing embryos.
Moreover, ovarian tissue freezing, during which a part of the ovarian cortical tissue containing undeveloped eggs is frozen to be re-implanted in the future, shows promising results for female fertility preservation. However, more research is needed as it is still considered an experimental procedure.
Gonadal Shielding
Another method preserving fertility for medical reasons is called gonadal shielding, which is mainly oriented towards cancer patients about to undergo radiation therapy. It is can also be applicable for pre-pubertal girls with cancer in order to protect their fertility in the future.
Gonads are reproductive organs, like the ovaries in women or testes in men. Since radiation treatment applied to the pelvic area has been found to negatively affect fertility by damaging the ovaries or lowering ovarian reserve, gonadal shielding involves protecting reproductive organs with a lead shield to block the exposure.
Ovarian Transposition
An alternative way to protect ovarian function from the effects of radiation therapy is through ovarian transposition.
This fertility preservation method consists of surgically moving the ovaries away from the area where the rays will be applied. Most commonly, they are moved to the abdomen. In women past puberty, the ovaries and fallopian tubes are typically detached from the uterus; whereas, in pre-pubertal girls, they can be moved intact.
Once radiation therapy is completed, women with detached fallopian tubes cannot get pregnant naturally. Instead, the eggs can be retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized in vitro.
Fertility Preservation Success Rates
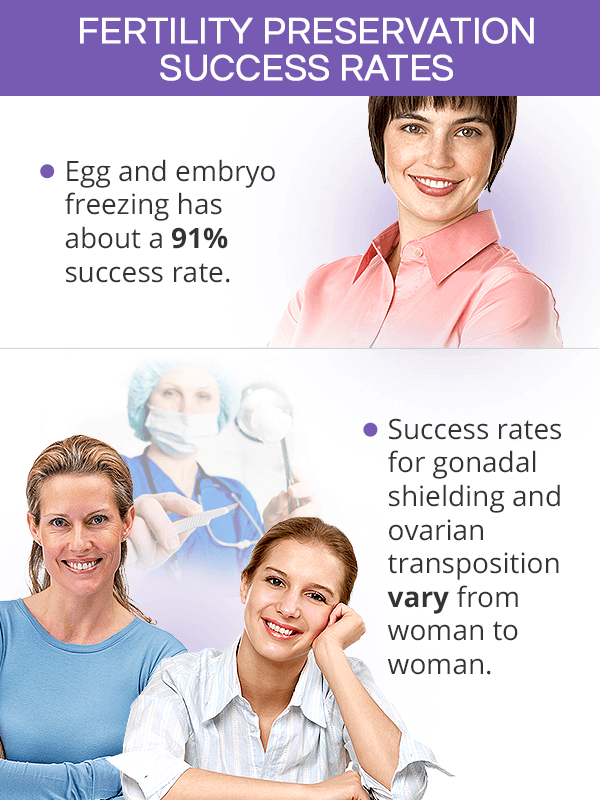
The effectiveness of various female fertility preservation procedures depends on numerous factors, including a woman's age and health status, and reliable statistics might not be available.
Egg Freezing
Embryo cryopreservation has the highest rates of success from among all available fertility preservation methods. Oocyte freezing has slightly lower effectiveness, but still high.
There are two available freezing methods: slow freezing, which has a 55-61% egg survival rate, and a vitrification method with about a 91% success rate. However, the chance of the embryo to implant in the uterine wall and grow into a healthy pregnancy depends on a woman's age at the time of their retrieval.
Because the number and quality of eggs decreases with age, women freezing their eggs before the age of 35 have the highest chance of success. Older women have higher risks of miscarriage and might need several egg harvesting cycles.
Gonadal Shielding
Success rates for gonadal shielding depend on various factors, such as the type and location of cancer, dose and duration of radiation therapy, among others.
The practice gonadal shielding is controversial among doctors as some studies have shown that various shielding techniques might either be ineffective or actually increase the dose of radiation applied to the reproductive organs. Caution in choosing experienced and knowledgeable fertility preservation specialists is, therefore, of the essence.
Ovarian Transposition
Ovarian transposition is generally considered a safe and effective method of preserving ovarian function and fertility, although more specific success rates are not available. One study has shown that women can benefit from this fertility preservation method the most until the age of 35. Its effectiveness among older women varies greatly.
Moreover, because the uterus cannot be moved away from the target area, it might receive some radiation, which - in turn - might alter its reproductive functions. In some cases, ovaries still received scatter radiation even if they are relocated. Moreover, ovarian preservation might only be effective when local pelvic radiation is applied in comparison to total body radiation.
Fertility Preservation Cost
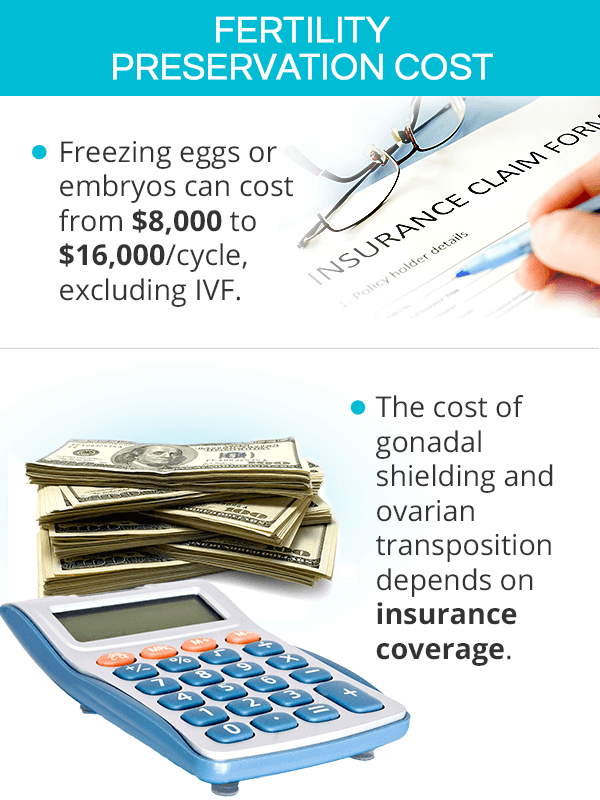
Female fertility preservation is generally very expensive. Most insurance plans do not provide coverage, while some might cover the costs partially, if the procedures are medically necessitated.
Egg freezing is the most expensive approach. Egg preservation cost can range from $8,000 to $16,000 per cycle. Annual storage fees range from $300 to $500, while the cost of IVF once pregnancy is desired can fall around $10,000 per cycle, excluding medications.
Gonadal shielding is typically part of medical equipment at the medical facility where radiation therapy is performed. Some insurance companies cover the whole cost of the cancer treatment.
Ovarian transposition's cost depends on whether it was performed as an open or a laparoscopic procedure. Oftentimes, insurance companies participate in covering the costs. The price of IVF following ovarian transposition is an additional cost, which can add up $10,000 or more, not including hormonal stimulation.
Key Takeaways
Fertility preservation methods allow women to secure their chances of having biological children in the future if they cannot or do not want to have them at the moment due to health conditions, cancer treatment, or personal choice. There are three ways to preserve fertility, including egg freezing, either fertilized (embryo cryopreservation) or unfertilized (oocyte cryopreservation); gonadal shielding from the effects of radiation; and ovarian transposition to protect ovarian function. Most pregnancies following fertility preservation, except for gonadal shielding, are achieved through in vitro fertilization with embryo freezing being the most effective and most expensive option.
Sources
- Alliance for Fertility Preservation. (2018). About Fertility Preservation. Retrieved November 2, 2018 from http://www.allianceforfertilitypreservation.org/
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. (2013). Fertility Preservation. Retrieved May 31, 2016, from http://www.cancer.net/research-and-advocacy/asco-care-and-treatment-recommendations-patients/fertility-preservation
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (n.d.). Fertility Preservation. Retrieved November 2, 2018 from https://www.asrm.org/topics/topics-index/fertility-preservation/
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Fertility Preservation. Retrieved November 2, 2018 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/17000-fertility-preservation
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2017). What is fertility preservation? Retrieved November 2, 2018 from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/infertility/conditioninfo/fertilitypreservation
- Mayo Clinic Proceedings. (2011). Fertility Preservation. Retrieved November 2, 2018 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3012633/
- Mayo Clinic. (2016). Fertility preservation: Understand your options before cancer treatment. Retrieved November 2, 2018 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/fertility-preservation/art-20047512
- The New England Journal of Medicine. (2017). Fertility Preservation in Women. Retrieved November 2, 2018 from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1614676