Surrogacy consists of a couple making legal arrangements for another woman, a surrogate, to get pregnant and carry a child with the intention of giving that child to said couple after birth without reserving any parental rights.
Hiring a surrogate might be an option when a woman does not have a uterus due to a hysterectomy or genetic factors, when pregnancy could be endangering a woman's life, or when same-sex couples or single men want to have children.
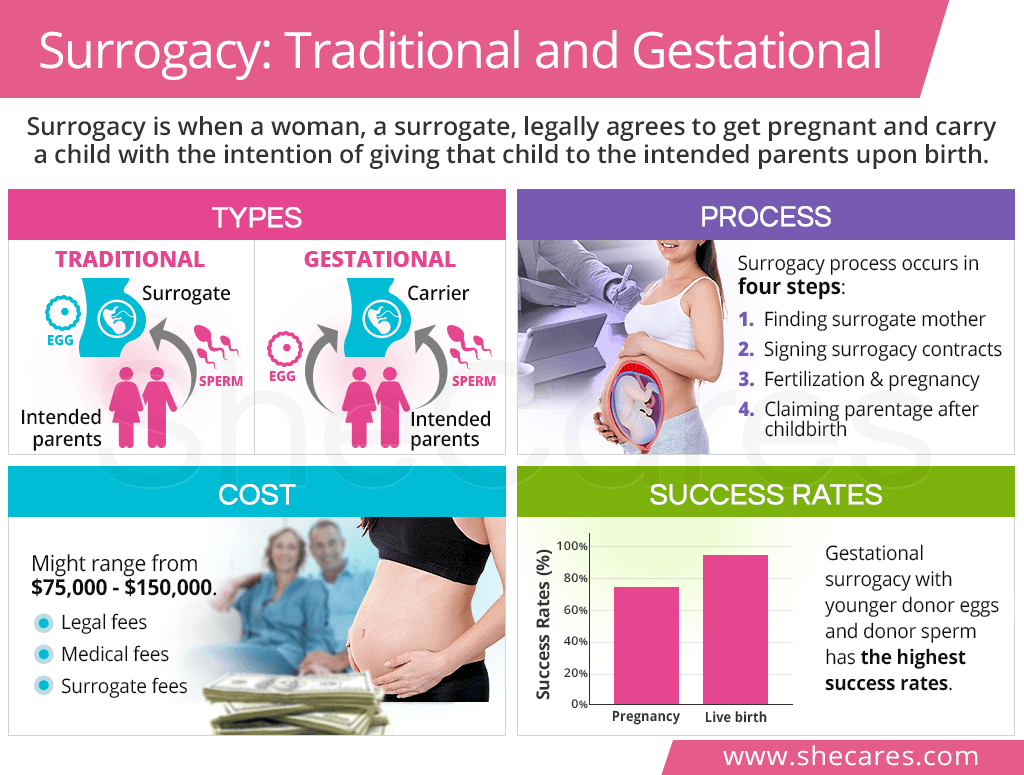
Types of Surrogacy
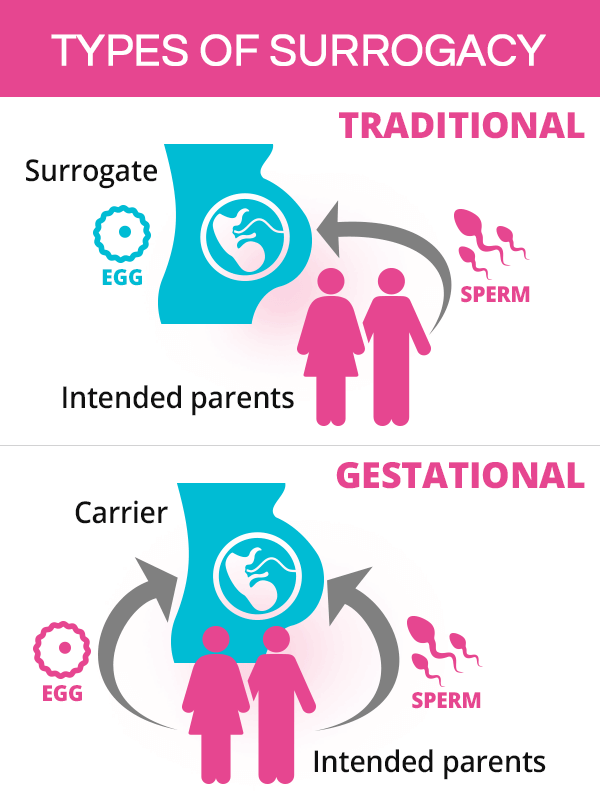
There are two types of surrogacy, depending on whose eggs are used for fertilization:
Traditional surrogacy, also referred to as partial or genetic surrogacy, is when a surrogate gets pregnant through artificial insemination (AI) using her own eggs and the sperm obtained from the intended father or a donor. As such, a traditional surrogate is genetically related to the child.
Gestational surrogacy, also called host or full surrogacy, is when a woman gets pregnant through in vitro fertilization (IVF) using eggs and sperm obtained from the intended parents. It is also possible to use either donor eggs, donor sperm, or both. As such, a gestational surrogate, also called a gestational carrier, is not genetically related to the child.
Surrogacy Process

Because of a number of legal issues with surrogacy, the process is known to be complex and thorough. It consists of the following four steps:
Finding a Surrogate Mother
Selecting the right surrogate is the most important part of the surrogacy process. Couples can choose a family member or a stranger and pursue independent surrogacy, or they can hire a surrogacy agency, which handles the entire matching and screening process.
The selection process includes medical and psychological evaluations and is guided by a set of strict requirements, such as having a clean criminal record; being between 21 to 45 years of age; having had at least one, uncomplicated pregnancy, but not more than five with only two through a Cesarean section; among other requirements.
Signing Surrogacy Contracts
Both the chosen surrogate and the intended parents undergo legal counseling in order to settle on arrangements that suit both parties.
It is highly important to go through this legal surrogacy process with an experienced attorney in order to prepare a contract that clearly outlines each party's goals and roles and secures everyone's rights. This will include many aspects, like finances, the surrogate's pregnancy diet, or the decisions in the case of pregnancy complications.
Surrogate Fertilization & Pregnancy
With traditional surrogacy, the sperm from the partner will be obtained, and the surrogate will be artificially inseminated. In the case of a gestational surrogate, the eggs and sperm will be obtained from the intended parents to be fertilized in a dish or through intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Once embryos (fertilized eggs) are ready, they will be transferred to the surrogate's uterus for implantation.
Throughout the course of pregnancy, the intended parents typically participate in medical exams and support their surrogate mothers.
Claiming Parentage after Childbirth
In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate mother and her husband, if applicable, sign documents after childbirth stating that they are not the legal parents, and the intended parents are granted parentage. Traditional surrogates, on the other hand, have to renounce their parental rights so that the intended parents can claim their rights through a stepparent adoption. As such, it is a more complex process.
Surrogacy Cost

Hiring a surrogate mother is known to be expensive as it can range from $75,000 - $150,000. The exact surrogate cost is influenced by many variables, such as whether intended parents will hire a surrogate agency or pursue independent surrogacy, whether fertilization will occur through AI or IVF, or whether the surrogate will carry one or multiple babies.
The intended parents cover all associated costs that might be broken up as follows:
Legal fees: agency fees, attorney fees, counseling and support
Medical fees: medical and psychological evaluations; IVF or AI; prenatal care, prenatal testing, delivery, etc.
Surrogate fees: compensation, travel expenses, and monthly allowance
However, commercial surrogacy, in which the surrogate mother is paid for her services, in only legal in a few countries around the world and some US states. In many cases, local laws only permit altruistic surrogacy, in which the surrogate mother is not paid for her services.
Surrogacy Laws
Though the laws surrounding surrogacy vary greatly depending on where it is pursued, the process tends to be complex and heavily regulated as it concerns the rights of three parties: the intended parents, the surrogate mother, and the child.
Traditional surrogacy is banned in many US states and countries because of the complexity of legal aspects concerning the surrogate mother's parental rights. Other countries do not have proper regulations in place yet. As such, gestational surrogacy is easier and more commonly pursued.
Moreover, most countries only allow altruistic surrogacy, which is why many aspiring parents search opportunities abroad and pursue international surrogacy in countries like India or Russia, where commercial surrogacy is legal and cheaper than in the US states that permit it.
Surrogacy Success Rates
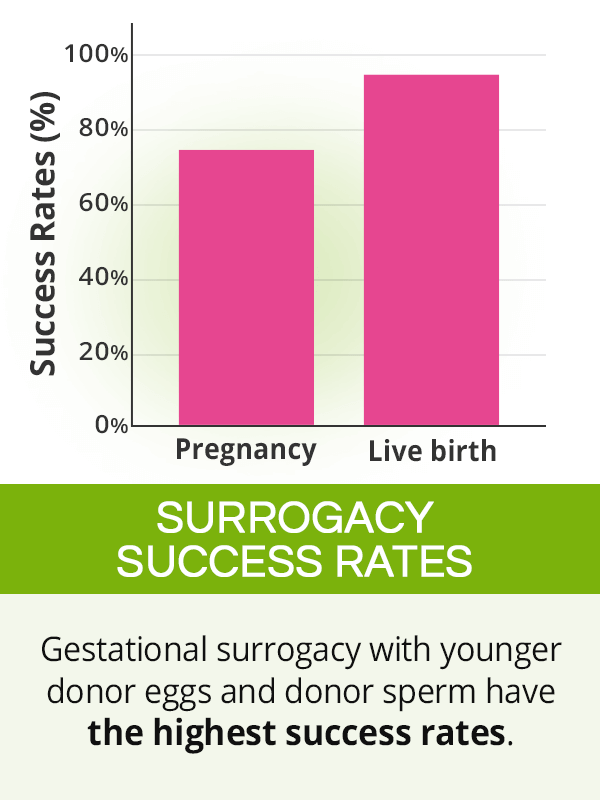
Because of a lack of proper legal regulations around the world, reliable surrogacy success rates are difficult to be obtained.
Many clinics claim an up to a 75% pregnancy rate and a 95% rate of live births for gestational surrogacy. However, it is important to take into account that this data most often only concerns IVF pregnancies using a young gestational carrier impregnated with younger donor eggs and highly-screened donated sperm.
Although gestational surrogacy has, in fact, shown higher rates of implantation and live births than traditional surrogacy, the specific success rates vary greatly depending on a woman's age, sperm quality, among other variables. As such, reported statistics should be approached with caution as many clinics might emphasize successful surrogacy stories, while omitting those with poor outcomes.
Key Takeaways
Surrogacy is an innovative method of enabling infertile couples to become pregnant. Aspiring parents can choose to use a traditional surrogate that will be artificially inseminated with the intended father's sperm, or they can use their own eggs and sperm by hiring a gestational carrier that will undergo IVF with the couple's embryos. Although growing in popularity, surrogacy is a complex process that many countries and US states might heavily restrict or even prohibit, especially if it involves compensating the surrogate mother for her services. Because of its legal complexities, hopeful couples are encouraged to use experienced surrogate agencies and attorneys to guide them through the process of becoming legal parents of the surrogate baby.
Sources
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (n.d.). Gestational Carrier (Surrogate). Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://www.reproductivefacts.org/news-and-publications/patient-fact-sheets-and-booklets/documents/fact-sheets-and-info-booklets/gestational-carrier-surrogate/
- Better Health Channel. (n.d.). Surrogacy. Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/HealthyLiving/surrogacy
- Human Reproduction. (2015). Surrogacy: outcomes for surrogate mothers, children and the resulting families – a systematic review. Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://academic.oup.com/humupd/article/22/2/260/2457841
- Human Reproduction. (2003). Surrogacy: the experiences of surrogate mothers. Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://academic.oup.com/humrep/article/18/10/2196/622680
- Indian Journal of Community Medicine. (2012). Surrogacy: Ethical and Legal Issues. Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3531011/
- University of Utah. (n.d.). Gestational Surrogacy. Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://healthcare.utah.edu/fertility/treatments/gestational-surrogacy.php
- CDC. (2018). ART and Gestational Carriers. Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://www.cdc.gov/art/key-findings/gestational-carriers.html
- Fertility and Sterility. (2016). Trends and outcomes of gestational surrogacy in the United States. Retrieved April 2, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27087401