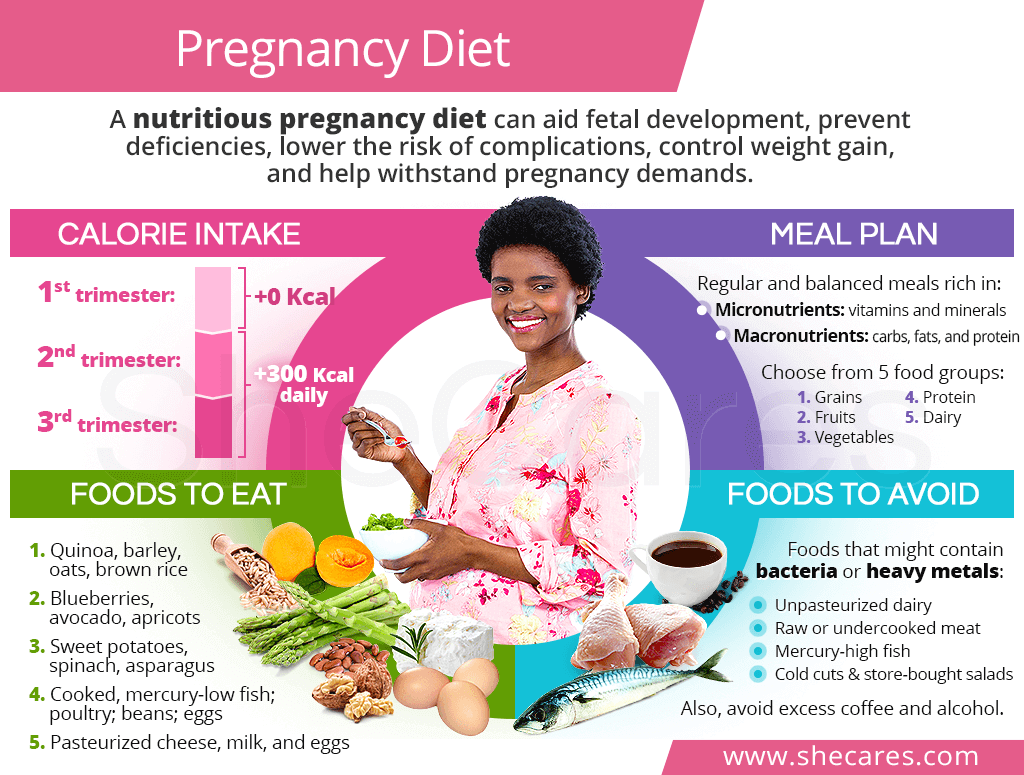
Calorie Intake During Pregnancy
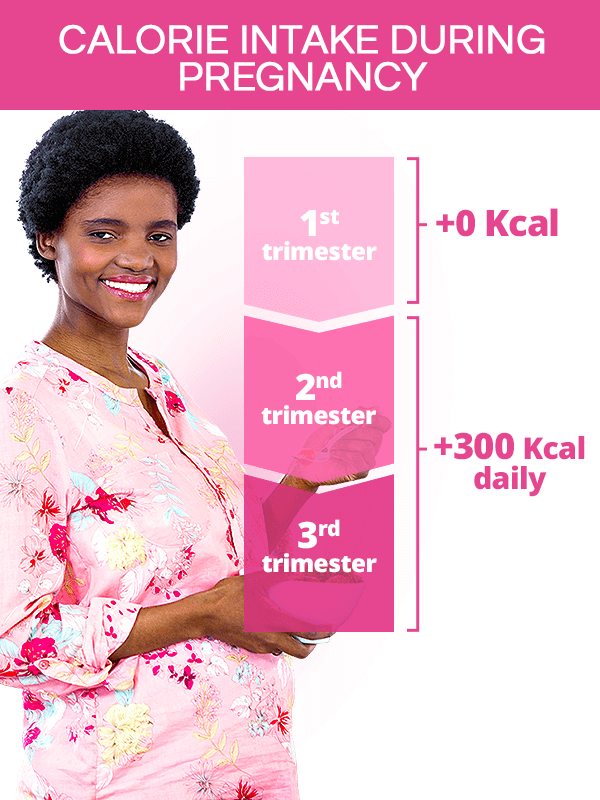
It is a common misconception that pregnant women have to eat for two as they are growing a human being in their wombs. Experts agree that key to a healthy pregnancy diet is focusing on the quality of food, not its quality.
Although gaining weight during pregnancy is necessary for the baby to grow and properly develop, doing so gradually and within the recommended range is of the utmost essence and the best way to prevent complications.
For women with normal pre-pregnancy weight, the body mass index-dependent caloric intake throughout the trimesters should be as follows:1,2
Weight gain and calorie intake recommendations for underweight, overweight, or obese women as well as those carrying twins or other multiples vary from the aforementioned and should be consulted with one's doctor.
Pregnancy Meal Plan

Because the food a woman eats when pregnant fuels her baby's development, it has to be rich in both micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) and all three macronutrients (carbohydrates, fats, and protein).
A special focus should be placed on foods rich in iron, folic acid, calcium, vitamin D, and iodine, as pregnancy imposes higher requirements for those nutrients.3
While the exact portions will vary depending on weight and individual dietary needs, when composing a pregnancy meal plan, a woman should choose foods from all five food groups:4
- Grains: 6-11 servings a day
- Fruits: 2-4 servings a day
- Vegetables: 4 or more servings a day
- Protein: 3 servings a day
- Dairy: 4 servings a day
For expectant mothers who need help composing their pregnancy meal plans, The United States Department of Agriculture's portal, ChooseMyPlate, can be a valuable resource.
Foods to Eat While Pregnant

There is no one food a woman can eat in pregnancy that would ensure she gets all the necessary nutrients. Rather, a pregnancy diet is about choosing from a wide range of foods in order to consume balanced and nutritious meals.
Nevertheless, some of the best foods to eat while pregnant include the following:
Whole Grains
When choosing grains for the next meal, a woman should opt for those that are whole grain. These not only provide the body with vitamins and minerals as well as energy, but also are rich in dietary fiber and complex carbohydrates that help control blood sugar levels, regulate digestion, and contribute to a healthy weight.5
- Oatmeal
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
- Whole wheat pasta
- Brown rice
- Millet
Fruits & Vegetables
A colorful variety of fruits and vegetables throughout the day will help ensure proper vitamin and mineral levels as well as adequate amounts of dietary fiber to prevent pregnancy-related constipation. Some fruits and vegetables are also naturally rich in healthy fats and iron, which are beneficial for the baby's growth and maternal health.6 They include:
- Vegetables: sweet potatoes, broccoli, tomatoes, and spinach
- Fruits: apricots, olives, avocados, bananas, and blueberries
Lean Protein
A woman has a rich variety of options to ensure adequate protein intake necessary for the baby's growth. Fish and many plant-based proteins are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that fuel fetal brain development; eggs are abundant in choline, which can help prevent neural tube defects; and beans and legumes contain folate for birth defects prevention.7,8,9
- Beans and legumes: chickpeas, lentils, soy, and split peas
- Nuts and seeds: sunflower, pumpkin, walnuts, and almonds
- Lean meats: chicken, turkey, and - moderately consumed - beef, lamb, or veal
- Low-mercury fish: herring, trout, salmon, halibut, cod, shrimp, pollock, tilapia, and snapper
Pasteurized Dairy
The best foods to eat while pregnant in terms of dairy are rich in probiotics, protein, and calcium, all of which can fulfill a woman's nutritional needs and prevent complications, including vaginal infections.10 Consuming only pasteurized and properly refrigerated dairy products is key to preventing foodborne sicknesses.
- Yogurt (plain or Greek)
- Cheese
- Milk
- Kefir
Foods to Avoid While Pregnant

Generally, a woman should avoid foods that might carry bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses, like those causing salmonella or listeriosis, as well as contain heavy metals, such as mercury, as they have been linked to birth defects, miscarriage, stillbirth, or other pregnancy complications.11
As such, foods to avoid during pregnancy include the following:
- Unpasteurized dairy
- Raw or undercooked meat
- High-mercury fish (Big eye tuna, king mackerel, marlin, tilefish, swordfish)
- Raw or undercooked fish (e.g. sushi)
- Cold cuts, hot dogs, luncheon, or store-bought salads
- Excess coffee (no more than 200 mg of caffeine a day, or one 12-oz. cup of coffee)1
- Alcohol
Additional Advices
Besides following a nutritious pregnancy diet, is it also important to remember the following recommendations:
Prenatal Vitamins
Taking prenatal vitamins with 400 mcg of folic acid is one of the best and easiest ways of preventing pregnancy complications and giving the baby the nutrients he or she needs to grow.12
It is very important to consult any supplements with one's doctor. While prenatal vitamins are key to a healthy pregnancy, other nutritional supplements can cause elevated levels of certain nutrients, like vitamin A, which has been shown to cause birth defects.13
Exercise during Pregnancy
Staying physically active throughout pregnancy is a proven way to decrease the pregnancy burden on a woman' and lower the risk of serious complications by helping her control weight gain.
The recommendations for exercise during pregnancy consist of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic workout per week, which might include brisk walking, light jogging, or swimming, among others.14
Key Takeaways
Figuring out what foods to eat during pregnancy and what to avoid is not as difficult as it might seem at first. Taking the time to plan ahead and establish a healthy pregnancy meal plan can consist of choosing the most natural and least processed foods from five groups: grains, fruits, vegetables, protein, and dairy. While during the first trimester, there is no need for additional calories, in the second and third trimesters, a woman is advised to increase her daily intake by 300 calories. The best foods to eat while pregnant include whole grains, lean protein, pasteurized dairy, and a colorful variety of fruits and vegetables. At the same time, an expecting woman should be mindful of the foods to avoid during pregnancy, such as those that might contain bacteria or heavy metals, like high-mercury fish, raw meat, unpasteurized dairy, excess coffee, or alcohol. Combined with prenatal vitamins and exercise, a nutritious pregnancy diet is the best tool an aspiring mother has to use in order to ensure her and her baby's well-being.
Sources
- Better Health Channel. (n.d.). Pregnancy and diet. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/pregnancy-and-diet
- FDA. (2019). Advice about Eating Fish for Women Who Are or Might Become Pregnant, Breastfeeding Mothers, and Your Children. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.fda.gov/food/consumers/advice-about-eating-fish
- United States Department of Agriculture - Choose My Plate. (2018). Nutritional needs During Pregnancy. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.choosemyplate.gov/nutritional-needs-during-pregnancy
Footnotes:
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2018). Nutrition During Pregnancy. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://medlineplus.gov/pregnancyandnutrition.html
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2013). Health Tips for Pregnant Women. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/health-tips-pregnant-women
- Medline Plus. (2019). Pregnancy and Nutrition. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://medlineplus.gov/pregnancyandnutrition.html
- American Pregnancy Association. (n.d.). Diet during pregnancy. Retrieved August 21, 209 from https://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/diet-during-pregnancy/
- Nutrients. (2019). Types of Carbohydrates Intake during Pregnancy and Frequency of a Small for gestational Age newborn: A Case-Control Study. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6471256/
- Cleveland Clinic. (2018). Pregnancy Nutrition. Retrieved August 21, 209 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/12593-pregnancy-nutrition
- American Pregnancy Association. (n.d.). Omega-3 Fish Oil and Pregnancy. Retrieved August 21, 209 from https://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/omega-3-fish-oil/
- Nutrition Today. (2007). Choline: Dietary Requirements and Role in Brain Development. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18716669/
- Food and nutrition bulletin. (2008). Effects of folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies during pregnancy on fetal, infant, and child development. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18709885
- Current diabetes reports. (2015). Probiotics and pregnancy. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25398206
- Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. (2019). Eat Healthy During Pregnancy: Quick Tips. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://healthfinder.gov/healthtopics/category/pregnancy/nutrition-and-physical-activity/eat-healthy-during-pregnancy-quick-tips
- CDC. (2018). Folic Acid. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/folicacid/about.html
- Food and Nutrition Bulletin. (20019). Safety and toxicity of vitamin A supplements in pregnancy. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/156482650102200304
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2019). Exercise During Pregnancy. Retrieved August 21, 2019 from https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Exercise-During-Pregnancy?