Ovulation Cycle
What is Ovulation?
Ovulation consists of the release of mature egg from the ovary and its journey through the fallopian tubes down to the uterus for potential fertilization.
Even though ovulation is commonly referred to as an ovulation cycle or a phase, ovulation lasts only for 12 to 24 hours. It is an integral part of healthy menstruation.
When Does Ovulation Occur?
Typical ovulation occurs roughly half way through a menstrual cycle between its two main phases:
Follicular phase, which starts on the first day of menses, and
Luteal phase, which follows ovulation and lasts until the next bleeding.
Although the length of a woman's menstrual cycle can range from 21 to 35 days, ovulation usually happens two weeks before her next bleed. However, it is normal for women to ovulate on varying days each month.
How does Ovulation Occur?
When an egg is released from an ovary, it makes its way through the fallopian tubes, where it can be fertilized if sperm is present. It takes about 12 to 24 hours to reach the uterus.
If fertilization does not occur, the egg and uterine lining are shed with the next period.
When is a Woman Fertile?
A woman is only fertile when she is ovulating.
But because sperm can survive in the reproductive tract for up to 5 days, having sex and depositing sperm in the vagina three to five days before ovulation can also result in pregnancy. Those few days of increased fertility are called the fertile window.
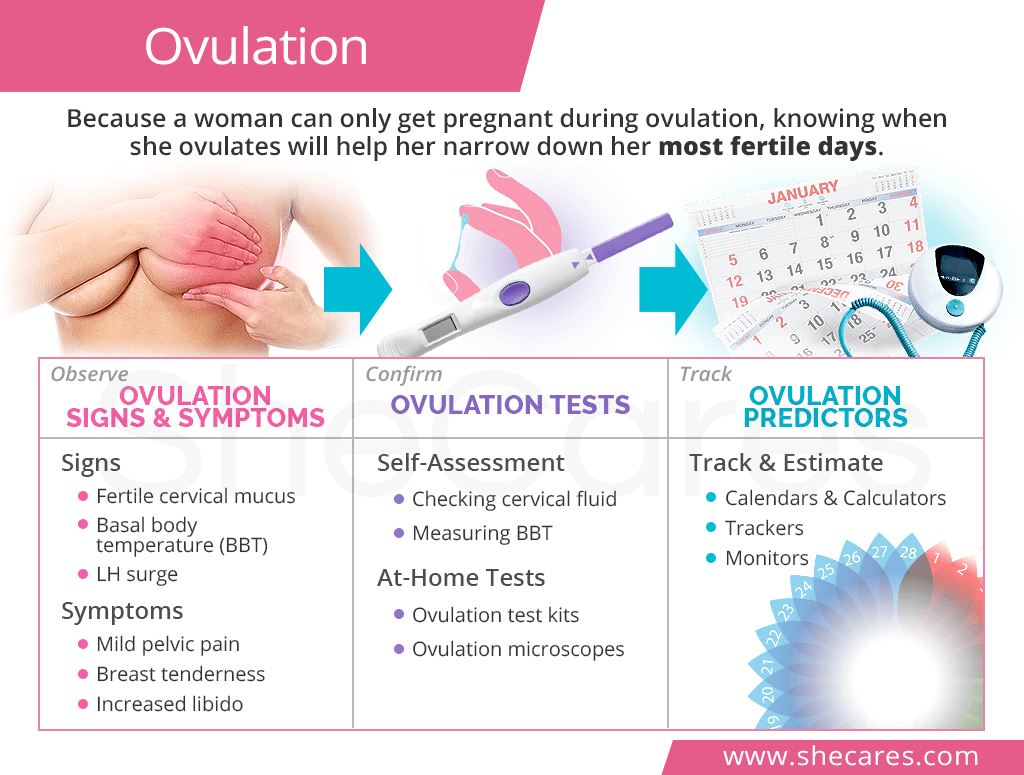
Ovulation Signs & Symptoms
Many women are not aware of the time of their ovulation due to the fact that ovulation signs and symptoms are usually mild and short-lived, if there are any.
Ovulation Symptoms
The severity of the symptoms experienced around ovulation can vary from woman to woman or even from month to month. It is important to note that the absence of these normal ovulation symptoms does not mean a woman is not ovulating.
- Mild pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- Light vaginal spotting
- Changes in libido
- Breast tenderness
- Increased libido
- Bloating
- Moodiness
- Increased sense of smell
If they persist or become severe, it might be a signal of other underlying conditions, such as endometriosis, ovarian cysts, or an ectopic pregnancy.
Ovulation Signs
Ovulation signs consist of diagnostic measurements that can be used to confirm ovulation. They include:
Cervical mucus. In the days leading up to ovulation, the body increases the production of estrogen, which causes the cervical mucus to become more abundant, clear, and stretchy, resembling egg whites.
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the temperature of the body at rest. As ovulation is approaching, BBT slightly decreases and then sharply increases by 0.5°F to 1°F once ovulation ends.
LH levels in the urine increase 24-36 hours before ovulation, which is called a LH surge. The hormone's levels peak at 25 - 40 mlU/mL on ovulation day.
Cervical changes. As the body approaches ovulation, the cervix moves higher up and becomes soft, moist, and open.
- Ferns are crystal-like patterns visible in dried saliva, which are caused by gradually increasing estrogen levels days before ovulation.
Ovulation Tests
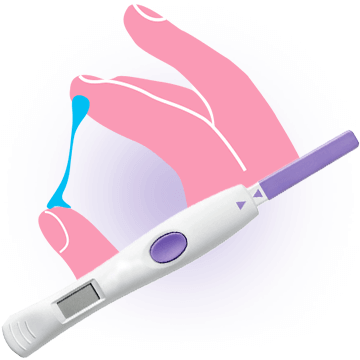
All tests for ovulation can be self-administered at home. Since the exact ovulation date can change slightly on a monthly basis, ovulation tests should be performed for several months for more accurate predictions.
Self-Assessment
A thorough observation of one's body can give the most accurate hints on ovulatory patterns. When diligently done for a few months, these self-assessment measurements can also improve the accuracy of at-home ovulation tests.
Measuring basal body temperature with a special thermometer sensitive to slight temperature changes should be done as soon as a woman wakes up and before getting out of bed.
Checking cervical mucus by inserting a clean finger into the vagina and analyzing its structure can help determine when she is the most fertile.
Checking cervical position by inserting a clean finger into the vagina can help determine when the cervix is in its most fertile state.
At-Home Ovulation Tests
Ovulation tests measure the changes in hormonal levels that happen before and during ovulation. For best results, ovulation tests kits should be done in combination with self-assessment.
- Ovulation test kits detect the LH surge in urine. A positive result means the ovulation is likely to occur in the next 24-36 hours. However, ovulation test kits do not confirm whether ovulation has actually occurred, which can be misleading to women with ovulation problems.
- Ovulation microscopes are used to test a sample of dried saliva for the presence of ferns. The test should be done daily throughout the cycle for accurate readings, preferably in the mornings before eating or brushing one's teeth.
Other Ovulation Tests
Other less common methods of confirming ovulation is through transvaginal ultrasound or a blood test.
Transvaginal ultrasound allows for the view of maturing follicles nearing the rupture.
Blood test can measure the levels of progesterone, which rises with the onset of ovulation.
Click on the following for more information on ovulation tests or continue to the next section to discover more about ovulation predictors.
Ovulation Predictors

The ultimate purpose of ovulation predictors is to help women estimate their fertile window. Because the time of ovulation can vary slightly month to month, these tools are not bulletproof and are only used as an estimation.
Ovulation Calendar
Ovulation calendars are used to record a woman's menses on a monthly basis to be able to manually estimate the ovulation day. It can be done by simply marking the period dates on a house calendar, personal agenda, or a computer print-out.
Ovulation Calculator
Once a woman has recorded her period dates for at least two months, she can take advantage of ovulation calculators. These tools are widely available on the internet as a quick reference. They consist of an interactive table that requires only two pieces of information to offer possible dates for the upcoming ovulation:
The first day of last menstrual period (LMP)
The average length of her menstrual cycle
Ovulation Trackers
There are also a number of ovulation trackers available to women for free, which mainly consist of online programs or mobile applications.
These trackers analyze input data to estimate the ovulation day and fertile window as well as the chances of pregnancy on a given day so that a couple can plan to have sex accordingly. Other extra features include daily logs concerning:
- Period dates
- Recent intercourses
- Ovulation signs, such as texture of the cervical mucus, cervical position, and BBT
- Ovulation symptoms, such as pelvic pain, bloating, or breast tenderness
A woman can also use a printable fertility chart, on which she can manually record essential ovulation-related information month to month.
Ovulation Monitors
Ovulation monitors combine an ovulation test and a tracker in one device. Although they can be quite expensive, they offer more benefits, such as:
- All contain the testing device, such as urine strips, saliva or cervical fluid sensors, or a BBT thermometer.
All store information from the previous cycles, often six months back, and estimate ovulation day, fertile window, and upcoming period.
All have a notification system, which alerts a woman on Testing Days and Peak Fertility Days so that a couple knows when it is best to have sex to conceive.
Ovulation Problems
Even though normal ovulation lasts for only one day, there are numerous reproductive events occurring throughout the entire menstrual cycle that, if disrupted, can result in ovulation problems.
Abnormal ovulation is one of the main causes of female infertility, especially in women with irregular periods. However, it is important to remember that having regular periods does not necessarily mean a woman is ovulating, which often delays the diagnosis.
Types of Ovulation Problems
Ovulation problems come in two types, namely irregular ovulation or lack thereof.
- Anovulation is when a woman is not ovulating
- Oligoovulation is when a woman is ovulating irregularly
Causes and Risk Factors
There are a wide variety of recognized causes and risk factors for female ovulation problems. Oftentimes, however, the underlying reason is unknown.
Common Causes
- Hormonal causes: Dysfunction of hypothalamus or pituitary glands, thyroid disorders
- Chronic conditions: PCOS, ovarian failure, diabetes, or endometriosis
- Other causes: Low ovarian reserve, fallopian tube blockage, early menopause, or side effects of medications
Risk Factors
- Obesity or underweight
- Poor eating habits
- Prolonged stress
- Strenuous exercise
- Excess alcohol or illicit drugs
- Smoking
Treatment of Ovulation Problems
Depending on the underlying cause, ovulation can be effectively stimulated with natural or pharmacological methods. They generally show effectiveness within two to four months, given that male infertility is ruled out.
Natural supplements
- Hormone-balancing supplements, such as Macafem, encourage the endocrine and pituitary glands to improve their hormone production, thus regulating menstrual cycles and ovulation.
- Phytoestrogenic herbal supplements, like dong quai or black cohosh, regulate the levels of estrogen, which, in turn, affects the levels of LH, triggering ovulation.
Lifestyle habits
- Reaching a healthy weight and quitting unhealthy addictions can bring about hormonal balance, thus improving the quality of eggs and restoring ovulation.
- Implementing a fertility diet with full-fat dairy, healthy fats, and phytoestrogens can help resolve ovulation problems rooted in nutritional deficiencies and help improve body mass index (BMI).
Medications
- Ovulation induction with prescription medications can be necessary to treat some ovulation problems. These medications are considered fertility drugs and can be a part of infertility treatment, especially for women preparing for intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Conclusions
Since typical ovulation only takes one day out of a menstrual cycle, learning to time it is of great importance to prospective mothers. Self-observation can help you gain a deeper knowledge of the reproductive processes occurring in your body. It can also enable you to catch ovulation problems and treat them with fertility diet, natural supplements, like Macafem, or medications.
Once you understand ovulation, your next step in planning to get pregnant is to focus on your fertility. This includes factors that affect it, such as egg quality or age, to fertility problems and their treatment as well as effective ways to boost it naturally.
Sources
- American Pregnancy Association. (2018). Understanding Ovulation. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from http://americanpregnancy.org/getting-pregnant/understanding-ovulation/
- Better Health Channel. (2018). Ovulation. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/ovulation
- Cleveland Clinic. (2013). Female Reproductive System. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9118-female-reproductive-system
- March of Dimes. (2018). Ovulation Calendar. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from http://americanpregnancy.org/ovulation-calendar/
- Mayo Clinic. (2016). How to get pregnant. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/getting-pregnant/in-depth/how-to-get-pregnant/art-20047611
- Medline Plus. (2018). Pregnancy – identifying fertile days. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007015.htm
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (n.d.). Women's Health Infographic: Ovulation. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/newsroom/digital-media/infographics/ovulation
- The British Medical Journal. (2000). The timing of the “fertile window” in the menstrual cycle: day specific estimates from a prospective study. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC27529/
- Your Fertility. (2018). Women's guide to getting the timing right. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://yourfertility.org.au/for-women/timing-and-conception/
- Office on Women's Health. (2018). Trying to conceive. Retrieved August 14, 2018 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/you-get-pregnant/trying-conceive