About Infertility in Women
Infertility occurs when a woman is not able to get pregnant after a year of trying, or six months if she is at the age of 35 or older. It also includes when a woman cannot carry a pregnancy to full term
Although female fertility naturally ends with menopause due to a normal decline of reproductive hormones, conception problems might occur earlier on in a woman's ripe reproductive years. As such, infertility touches the lives of at least 10% of women of childbearing age.
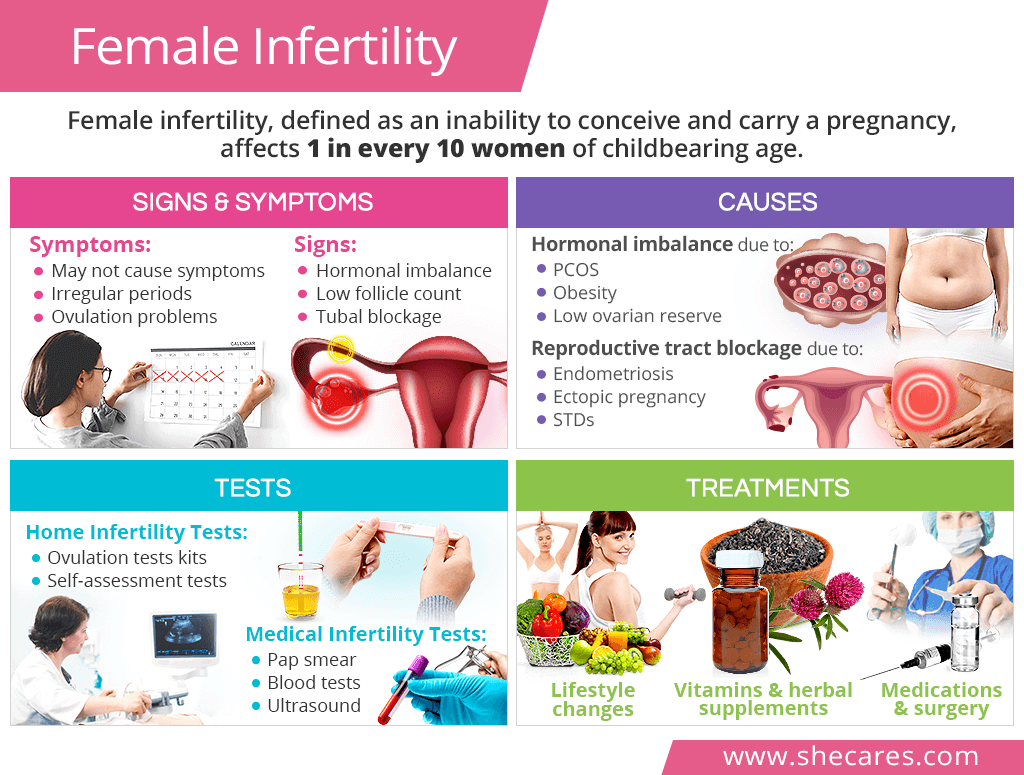
Signs & Symptoms of Female Infertility
Symptoms of Female Infertility
In most cases of female infertility, women do not experience clear symptoms.
However, there might be symptoms characteristic to other medical conditions known to cause infertility in women, including:
- Irregular periods, including absent menses, long or short cycles, heavy bleeding
- Ovulation problems, including irregular or absent ovulation
- Changes in libido
Signs of Female Infertility
In contrary to symptoms reported by women themselves, infertility signs are measurable criteria that are usually assessed by a physician through a variety of diagnostic tools.
- Imbalance of reproductive hormones
- Abnormal thyroid hormones
- Positive STD test
- Low antral follicle count
- Blocked fallopian tubes
- Uterine scarring
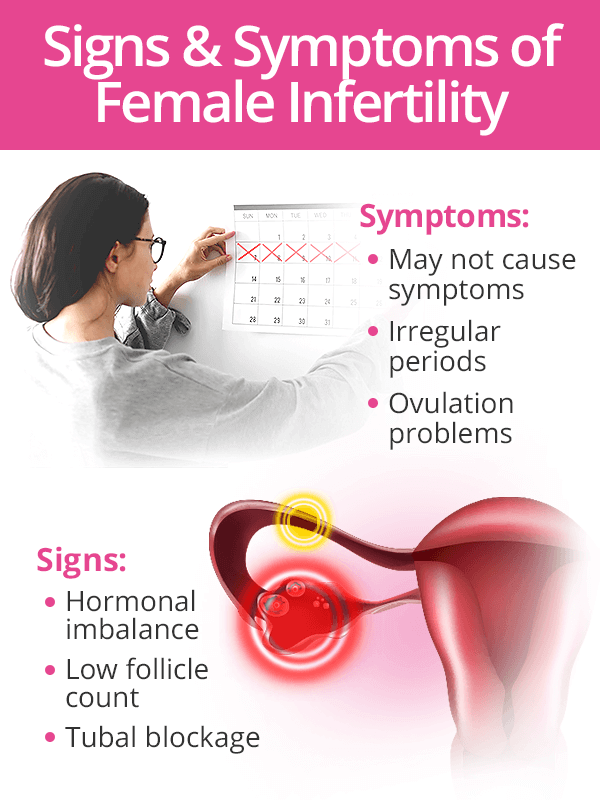
Causes of Female Infertility
Hormonal Imbalance
The main cause of infertility in women is hormonal imbalance, particularly estrogen and progesterone. Because the functioning of a healthy reproductive system is governed by hormones, their imbalance have a direct effect on a woman's ovulation. With ovulation problems, the chance of pregnancy is reduced.
Hormonal imbalance leading to abnormal ovulation can have the following causes:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Hypothalamic or pituitary dysfunction
- Premature ovarian insufficiency
- Prolactinemia
- Low ovarian reserve
Damage or Blockage in the Reproductive Tract
Besides hormonal imbalance, infertility in women might also occur due to damaged or blocked reproductive organs, namely the cervix, fallopian tubes, or uterus. When the tubes are not permeable to sperm, conception cannot occur, a condition called tubal infertility. Similarly, if the uterus is scarred, the fertilized egg cannot implant itself in its wall.
Blockage or scarring in the fallopian tubes or uterus can have the following causes:
- Endometriosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic tuberculosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Abnormal uterine anatomy
- Cervical stenosis
Unexplained Female Infertility
Although in the majority of female infertility cases, the underlying cause can be determined, about 10% remain without a clearly identified cause. It is believed that unexplained infertility can be due to a combination of some undiagnosed health conditions, certain lifestyle practices, and male partner factors.
Risk Factors of Female Infertility
Various factors have been associated with increasing the risk of infertility directly or indirectly by elevating the likelihood of developing conditions known to diminish a woman's fertility. They include the following:
- Age (above 35)
- Prolonged high stress
- Strenuous exercise
- Obesity (BMI of 30 kg/m2 or above)
- Underweight (BMI 18.5 kg/m2 or below)
- Eating disorders (anorexia, bulimia, binge eating)
- Smoking and excessive alcohol use
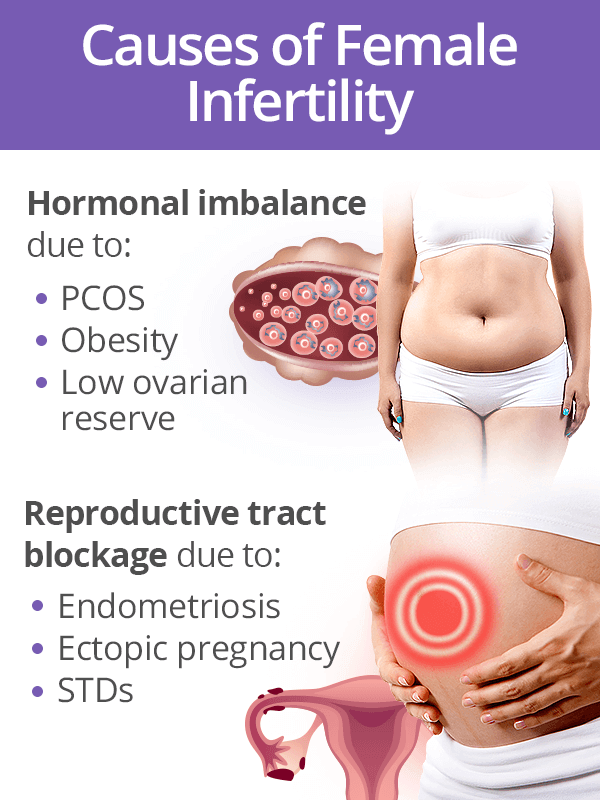
Female Infertility Tests
After not being able to get pregnant after 12 months, a woman is typically advised to undergo various fertility tests to pinpoint the underlying cause of infertility. Because fertility at 35 diminishes at more rapid rates, women in their mid-30s should get tested after six months.
Although the suspected infertility in women will most commonly be evaluated with medical tests, a woman also has various at-home tools to assess her fertility.
Home Female Infertility Tests
Since abnormal ovulation is the leading infertility, all female infertility tests taken at home are designed to determine whether a woman's ovulation is occurring timely.
Ovulation test kits detect urine levels of reproductive hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) or follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to verify if a woman is ovulating.
Ovulation microscopes help identify ferning patterns that appear in the saliva due to rising estrogen before ovulation.
Measuring basal body temperature helps observe slight temperature changes triggered by hormone changes around ovulation.
Checking cervical mucus is an easy self-test to confirm that ovulation is approaching.
Checking cervical position can also give clues as to when ovulation is most likely to take place.
These aforementioned at-home fertility tests are important as they can give the doctors view of a woman's menstrual and ovulatory patterns and help them determine the cause of infertility more efficiently.
Medical Female Infertility Tests
Proper medical workup for infertility in women starts from the least invasive tests and progresses only if the underlying causes has not been relieved yet.
Physical exam, which always precedes any infertility tests, is when a woman's overall health is assessed as well as medical and sexual history is discussed, her medications are reviewed, and menstrual patterns are taken note of.
Pap smear is the most standard gynecological test initiating infertility evaluations. It can give view of potential cervical problems and ongoing STDs.
Blood tests are used to check for hormonal imbalance, possible endocrine disorders, undiagnosed infections, and the state of ovarian reserve, all potential causes of female infertility.
Diagnostic examinations usually start with a transvaginal ultrasound to count ovarian eggs and rule our anatomical problems within the reproductive tract. More advanced diagnostic tests, such as hysteroscopy or biopsy, are performed as necessary.
Genetic testing for possible chromosomal defects is performed when all female infertility tests thus far have failed to provide clues.
Female Infertility Treatments
Female infertility treatment depends on the exact cause and other individual characteristics, such as a woman's age and overall health status. Because fertility issues are mainly caused by hormonal balance, treatment options are oriented towards restoring proper hormone levels, thus improving or inducing ovulation.
Women struggling with infertility can approach its treatment in three ways: (1) lifestyle adjustments, (2) alternative medicine, or (3) conventional medicine.
Lifestyle Adjustments
For women planning to conceive, maintaining healthy lifestyle habits is of essence not only for the sake of their fertility, but the safety of their pregnancies and the health of their future babies. They might include following a well-balanced fertility diet, such as one that is rich in phytoestrogens and full-fat dairy; keeping up with fertility exercise to enhance hormonal balance and maintain a healthy weight; and considering alternative therapies for fertility, such as stress-reduction techniques.
Alternative Medicine
Fertility can also be restored naturally with the help of various fertility supplements and vitamins, including herbal phytoestrogenic supplements, such as red clover, black cohosh, or ginseng; hormone-regulating supplements, such Macafem; or other supplements, like folic acid, lipoic acid, omega-3 fatty acids, or coenzyme Q10.
Conventional Medicine
Medications to treat infertility in women most commonly include fertility drugs and injections, which stimulate or regulate ovulation. Other medications might be used to manage ongoing health conditions contributing to infertility, like thyroid disorders or STDs. Fertility surgery is the usually the last resort in treating female infertility and can consist of removing tubal blockages or uterine scarring as well as procedures to induce ovulation, like ovarian drilling, among others.
Reproductive Assistance for Female Infertility
Women whose infertility could not be treated with the aforementioned treatments can achieve pregnancy with the help of assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs). Women most commonly choose between an artificial insemination (AI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF). The exact success rate of ARTs vary from woman to woman.
Key Takeaways
Women know that their chances of becoming a mother are limited by their age; however, when their fertility is suddenly reduced sooner while they are still in their reproductive years, it understandably creates anxiety and despair. Female infertility affects one in every six women between the ages of 15 and 44, heavily compromising their chances of having children unless prompt treatment is sought after. The main underlying cause is hormonal balance, which disrupts ovulation and the whole functioning of the reproductive system. Fortunately, infertility in women can be successfully resolved through lifestyle changes, including fertility-boosting diet and exercise; vitamins and herbal supplements; and conventional medications and surgery.
Sources
- Better Health Channel. (n.d.). Infertility in women. Retrieved November 29, 2018 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/ConditionsAndTreatments/infertility-in-women
- CDC. (2018). Infertility FAQs. Retrieved November 29, 2018 from https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/index.htm
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2017). Fertility Treatments for Females. Retrieved November 29, 2018 from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/infertility/conditioninfo/treatments/treatments-women
- Mayo Clinic. (2018). Female Infertility. Retrieved November 29, 2018 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/female-infertility/symptoms-causes/syc-20354308
- Medline Plus. (2018). Female Infertility. Retrieved November 29, 2018 from https://medlineplus.gov/femaleinfertility.html
- Office on Women's Health. (2018). Infertility. Retrieved November 29, 2018 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/infertility