What is Prenatal Care?
Prenatal care, or antenatal care, is the care a woman receives from the moment she becomes pregnant until birth. It is aimed at improving pregnancy outcomes.
While women usually receive prenatal care through their selected obstetrician-gynecologists' (OBGYN) private offices, some might obtain it through local hospitals, community clinics, and other government facilities.
It is worth mentioning that good prenatal care should begin even before conceiving with proper pre-pregnancy planning. This might include a preconception check-up with one's doctor to review one's current health status, manage chronic conditions before getting pregnant, and learn to estimate ovulation.
Benefits of Prenatal Care

Studies have shown that the benefits of prenatal care are observed not only during pregnancy, but also in postpartum, seeing as it decreases maternal and child morbidity and mortality.
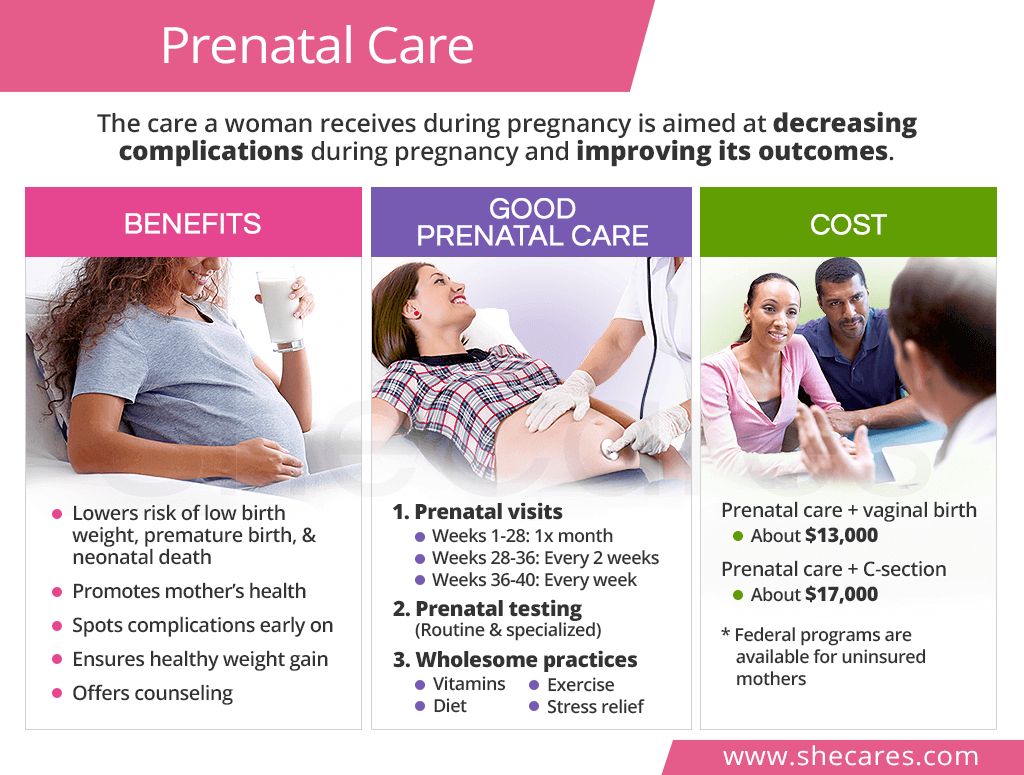
The benefits of prenatal care throughout all pregnancy stages include, but are not limited to, the following3, 4, 5, 6:
- Ensuring normal fetal development, especially proper birth weight
- Reducing the rates of premature birth
- Decreasing the risk of neonatal death after birth
- Monitoring and promoting mother's health
- Decreasing the risk of certain birth defects
- Diagnosing and treating pregnancy complications early on
- Helping women gain pregnancy weight in a healthy way
- Providing counseling and reassurance
What does Good Prenatal Care Consist of?

Good prenatal care combines regular doctor's visits with timely prenatal testing as well as maternal wholesome practices. Early and regular is key.
Prenatal Doctor's Visits
The first prenatal visit is usually scheduled around the 8th week of pregnancy. Afterwards, most appointments will take place on a monthly basis until the end of the second trimester (28 weeks). In the weeks 28 to 36 of the third trimester, they will be scheduled every two-three weeks and then weekly thereafter (weeks 36-40)7.
Prenatal Tests
Prenatal tests are an inseparable part of antenatal care. While most of them take place in the doctor's office, including pregnancy ultrasounds and prenatal blood and urine tests, more advanced types of prenatal genetic testing, such as amniocentesis, might be arranged at a specialized facility.
Wholesome Prenatal Practices
Keeping up with various antenatal testing is as important as taking care of oneself outside the doctor's clinic. During pregnancy, an OBGYN typically provides guidance on how to have a healthy pregnancy and ensure that the baby has a proper environment for his or her development. Topics advised by the OBGYN may include:
Prenatal Care Cost

Pregnancy is known to be costly. The average cost of having a baby, including prenatal care and vaginal delivery, is almost $13,000. The cost can go up to almost $17,000 if a C-section is performed.
Cost of Prenatal Care with Insurance
All private insurers are obligated to provide maternity care or childbirth insurance. However, depending on one's specific coverage, this prenatal insurance can still include co-payments, co-insurances, and deductibles that are covered out-of-pocket by the insured.
Cost of Prenatal Care without Insurance
The cost of prenatal care without insurance depends on a number of factors, including one's location, progression of pregnancy itself, and type of birth, among others. Those expectant mothers who are not insured and cannot afford prenatal insurance can receive antenatal care throughout numerous state and federal programs.
Key Takeaways
Although for most expectant women reaching for adequate prenatal care is a natural impulse and an integral part of being pregnant, for others, access to prenatal care is a challenge. The type and quality of medical care as well as a mother's own practices have crucial effects on the progression and outcomes of her pregnancy. Good prenatal care implemented early in the first trimester has been found to dramatically decrease the rates of premature birth, low birth weights, and neonatal death, among other complications. It consists of adequate prenatal vitamins, regularly scheduled doctor's visits, timely prenatal tests, and wholesome habits, including diet, exercise, and stress relief. Although the cost of prenatal care is universally known to be high, specific expenses will depend on individual coverage or pregnancy progression. For uninsured mothers-to-be, there are many government programs available so that the lack of prenatal care insurance will not be an obstacle in receiving the care they need and deserve.
Sources
- American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. (2015). 658: The impact of prenatal care of pregnancy outcomes in women with depression. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(15)02009-8/fulltext
- Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics. (2012). Lack of prenatal care in a traditional community: trends and perinatal outcomes. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00404-011-2153-x
- Child Trends. (2019). Late or No Prenatal Care. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.childtrends.org/indicators/late-or-no-prenatal-care
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2017). What is prenatal care and why is it important? Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancy/conditioninfo/prenatal-care
- March of Dimes. (n.d.). Prenatal Care. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.marchofdimes.org/pregnancy/prenatal-care.aspx
- Medline Plus. (2019). Prenatal Care. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://medlineplus.gov/prenatalcare.html
- National Vital Statistics Reports. (2013). Timing and Adequacy of Prenatal Care in the United States, 2016. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr67/nvsr67_03.pdf
- PLOS. (2013). Adequate Prenatal Care Reduces the Risk of Pregnancy Outcomes in Women with History of Infertility: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0084237
Footnotes:
- March of Dimes. (n.d.). Quick Facts: Prenatal Care. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.marchofdimes.org/peristats/ViewTopic.aspx?reg=99&top=5&lev=0&slev=1
- Healthy People.gov. (2019). Maternal, Infant, and Child Health. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topics-objectives/topic/maternal-infant-and-child-health/objectives
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Prenatal Care. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/prenatal-care
- American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. (2002). The impact of prenatal care on neonatal death in the presence and absence of high-risk conditions. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12015529
- Revista de Saude Publica. (2014). Factors associated with lack of prenatal care in a large municipality. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4285828/
- BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth. (2008). Inadequate prenatal care and its association with adverse pregnancy outcome: A comparison of indices. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://bmcpregnancychildbirth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2393-8-15
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Prenatal care and tests. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/prenatal-care-and-tests
- Truven Health Analytics. (2013). The cost of having a baby in the United States. Retrieved September 9, 2019 from http://transform.childbirthconnection.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/Cost-of-Having-a-Baby-Executive-Summary.pdf