About
Quick Facts about Endometriosis
- It is estimated that somewhere between 7 and 8.5 million women in North America suffer from endometriosis, with varying degrees of intensity.
- Many women mistakenly take the severe pre-menstrual pain typical of endometriosis as normal, and they delay seeking medical attention for years.
- While many women start experiencing symptoms as early as puberty (right after their menarche or first period), the average age of diagnosis is 27 years old.
- The pain and heavy bleeding it causes is sometimes misdiagnosed as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), pelvic congestion, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Endometriosis is a commonly painful condition characterized by the misplaced overgrowth of endometrial tissue, which is supposed to grow on the inside of the uterus but starts growing on the outside instead. In some rare, extreme cases, this tissue will spread outside the pelvic region.
However, the misplaced tissue will continue to act as a “normal” endometrial tissue should, so it will thicken, break, and bleed at the appropriate times of each menstrual cycle. Depending on where it is located, this can cause a particularly copious bleeding or an acute pain, because it may not be able to exit the body and will become trapped, causing clots or tender spots around the pelvic area.
The tissue overgrowth typical of endometriosis can interfere with a woman's ability to conceive and get pregnant (subfertility and infertility). In the U.S., it is one of the top three causes for fertility problems, but it is also one of the top three most easily treated ones. Other complications that can arise from it are anemia, because of the chronic heavy bleeding, and more rarely, depression among women who deal with extreme versions of the pain it causes. It had also been linked to a slightly higher chance of giving birth prematurely. However, it is important to note that most women attempting to get pregnant with endometriosis succeed in doing so without major complications or long-term consequences for the child.
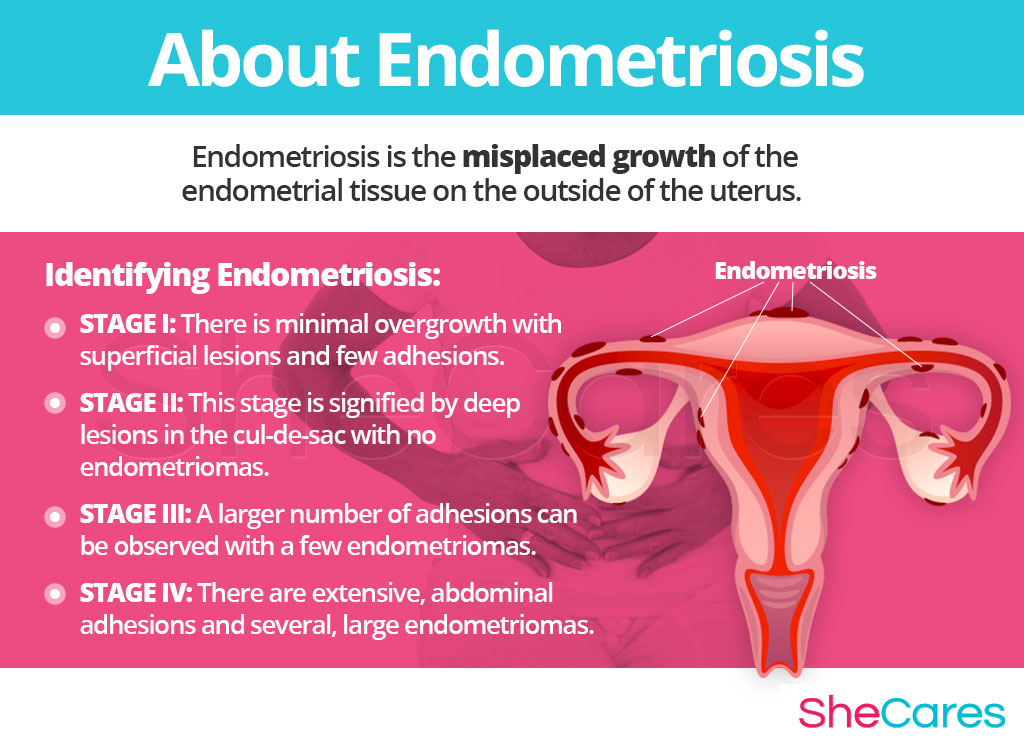
Identifying Endometriosis
The American Society of Reproductive Medicine has classified endometriosis into 4 stages, based on their degree of severity, with stage I being the least amount of growth and IV being the most.
Continue reading to learn about the causes and mechanisms of endometriosis.
Causes
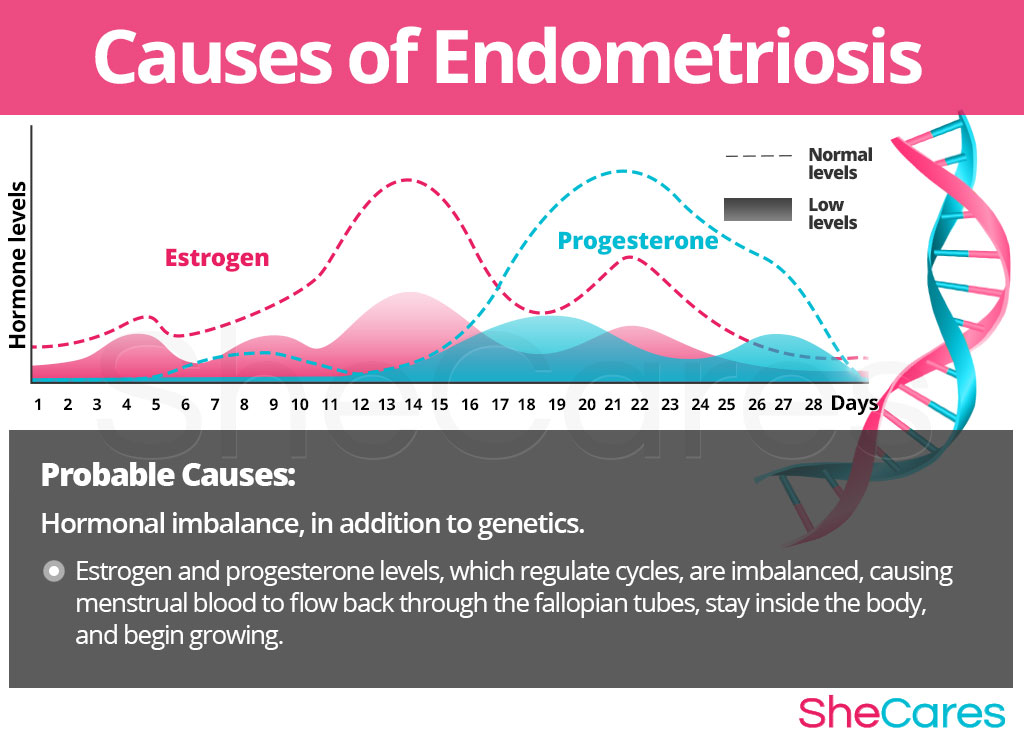
Learning about the causes of endometriosis provides the key to understanding how to prevent and treat this troublesome condition. While the exact cause that sets off endometriosis is not yet completely understood, most doctors and researchers believe hormonal changes, in addition to genetics, are the primary cause of endometriosis. In addition to these causes, other factors and conditions seem to be related to its appearance.
Continue reading to learn more about both the hormonal, and other, causes of endometriosis.
Hormonal Causes of Endometriosis
Hormones are chemical messengers that control every organ in the body. When fluctuations occur, organs don't receive the correct signals to function adequately, so hormonal disorders occur. In particular, the hormones estrogen and progesterone are in charge of regulating a woman's reproductive functions, such as her menstrual cycle and fertility.
When a woman's hormones become imbalanced, her menstrual cycles may be thrown off and she may experience several different symptoms. Some women with a previous genetic predisposition seem to develop retrograde menstruation, which causes menstrual blood (that contains endometrial cells) to flow back through the fallopian tubes and stay inside the body. These cells then end up “lost” around the pelvic walls or near other pelvic organs, where they begin growing.
In this sense, it can be said that endometriosis is caused largely by a hormonal imbalance among women who are genetically predisposed, especially during the transitional periods women go through their reproductive life. Hence the reason why many women experience sharper or milder pain at certain delicate periods of their lives, like puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. The estrogen and progesterone fluctuations during these periods cause endometrial tissue to grow faster or slower.
Furthermore, there are also specific hormonal changes according to each stage of a woman's reproductive life that can exacerbate the disorder. These specific hormonal factors can influence a woman's individual experience of endometriosis, as shown below:
Hormonal Causes during Different Phases in a Woman's Life
PMS is a consequence of hormonal fluctuations linked to the menstrual cycle. These fluctuations can greatly exacerbate the symptoms of endometriosis.
In addition to the cyclical symptoms experienced during PMS, women experience specific transitional periods that are strongly linked to an exacerbation or recurrence of the pain felt from endometriosis.
Puberty is the stage in which a girl's body begins to produce reproductive hormones; these and other factors, such as school and family pressures, contribute to pelvic pain during puberty.
Pregnancy leads to extreme changes in the production of reproductive hormones, which along with other factors, like uterus growth, can affect the experience of endometriosis.
Post-partum and breastfeeding is another stage where reproductive hormones are imbalanced, influencing endometrial pain.
Menopause is the stage in a woman's life when production of reproductive hormones naturally declines, signaling the end of a woman's fertility. This decrease in hormone levels affects the experience of pelvic pain, usually positively.
Continue reading to learn more about the risk factors that can worsen the pain or symptoms of endometriosis.
Risk Factors and Triggers
Risk Factors for Endometriosis
Some women are more likely than others to suffer from endometriosis for inherent health and behavioral reasons. These predisposing factors can affect a woman's hormone levels and increase the chances that a woman will develop endometriosis or that she will see her symptoms worsen during her reproductive life.
There are also some substances and lifestyle choices that have been linked to both increased prevalence and severity of endometriosis. Click here to know more about the risk factors and triggers for endometriosis.

Signs and Symptoms
Because the precise intensity and frequency of symptoms of endometriosis will depend on the exact location where the misplaced tissue is located, all women experience the symptoms differently. However, many symptoms of endometriosis are common among the majority of women who have the condition, especially they are undergoing a phase of hormonal imbalance.
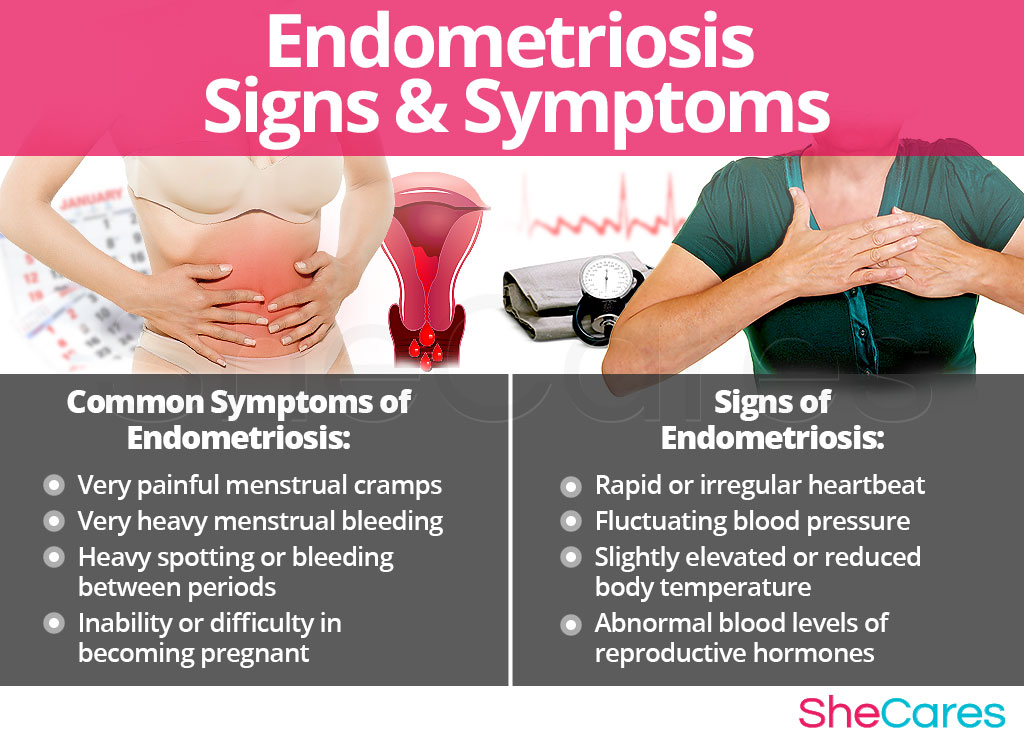
Common Symptoms of Endometriosis
- Very painful menstrual cramps
- Very heavy menstrual bleeding
- Unusually long menstrual bleeding (more than seven days)
- Heavy spotting or bleeding between periods
- Inability or difficulty in becoming pregnant
What other symptoms might occur with endometriosis?
In addition to these general symptoms, endometriosis may be accompanied by other more specific symptoms depending on the exact location of the endometrial tissue. Many of these symptoms may be experienced throughout the entire month or just during the PMS days.
Signs of Endometriosis
As opposed to more noticeable symptoms, medical signs are measurable criteria that are usually assessed by a physician. The following medical signs will most likely be taken into account by a physician when diagnosing the disorder:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Fluctuating blood pressure
- Slightly elevated or reduced body temperature
- Abnormal blood levels of reproductive hormones
- Abnormal bone density reading
- Low blood iron level
Some women feel that their symptoms of pain or heavy menstrual bleeding are severe enough that they interfere with daily life, or they find them to be concerning enough to warrant medical attention. There are ways to treat and manage endometriosis, but before attempting to do this, it is advisable for women to seek medical attention so they can receive the proper diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition that is quite simple to treat when caught early. Unfortunately, many women don't recognize their symptoms as abnormal, or don't feel they are worth mentioning when they visit the OB/GYN, and it can take them many years to finally be able to receive a proper diagnosis.
To diagnose and identify the symptoms of endometriosis, a doctor must typically perform four procedures. First, they should review the patient's medical history; then, they should conduct a physical exam, followed by a pelvic exam. The doctor may also order an ultrasound, if necessary.
Keep reading below to learn about how to prevent and manage endometriosis.
Prevention and Management
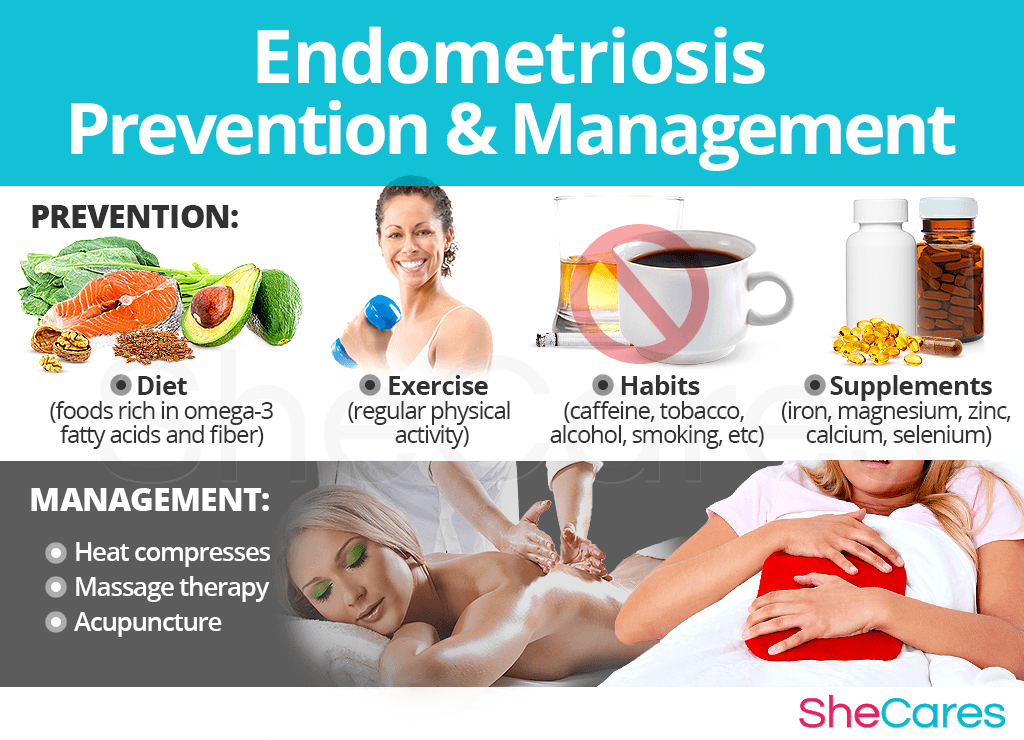
While there is no way to completely prevent endometriosis, just as there is no way to stave off hormonal process, there are a few steps that a woman can take to lessen her chances of developing severe pain cause by endometriosis, or to minimize the impact or length of time during which this pain occurs.
In this sense, lifestyle changes for prevention are extremely important, especially with regard to diet, exercise, and healthy habits. Moreover, a woman may seek ways to complement these lifestyle approaches with the use of supplements that help to enhance the endocrine system and, therefore, help to prevent or ease symptoms of hormonal imbalance and the development of endometriosis. Continue reading to learn more about lifestyle changes for prevention of endometriosis.
For women who are already going through the disorder, prevention may not be possible if endometriosis has already appeared. Fortunately, there are many ways to manage the disorder in order to prevent the “flare-ups” or lessen the intensity of the pain it produces. Keep reading to learn about the different ways to manage endometriosis.
Managing Endometriosis
The chronic pain that can be brought on by endometriosis can be very damaging to a woman's psychological health and it may interfere with her daily activities. Fortunately, making minor daily changes can make a huge difference for women who are trying to manage their discomforts, especially those who are thinking about getting pregnant with endometriosis.
While these measures often help to reduce the intensity of the pain and disruption that comes with endometriosis, they are unable to treat the root of the problem, which is hormonal imbalance. However, there are several natural treatments can address the underlying hormonal causes directly. Please continue to the next section to learn more about treating endometriosis and discover treatment approaches.
Treatments
Because of the chronic pain it produces and its effects on fertility, endometriosis can leave a woman feeling constantly fatigued or even like there is something “broken” about her body. Luckily, it is more than possible to find an effective treatment for endometriosis.
Three Approaches to Treat Endometriosis
Three levels of approaches can be considered for treating endometriosis. These are categorized as: (1) Lifestyle Changes, (2) Alternative Medicine, and (3) Pharmaceutical and Surgical Options.
Women are encouraged to begin with the least risky approach to endometriosis treatment, lifestyle adjustments. While these are often effective at curbing the pain and heavy bleeding associated with the disorder, they alone do nothing to address the underlying hormonal imbalance or to slow down the endometrial tissue overgrowth. Fortunately, alternative medicine can be combined with lifestyle changes to provide a safe and effective endometriosis treatment.
At a certain point, some women may wish to consider pharmaceutical options or other types of medical intervention if they are unable to find relief from natural treatments. For women considering this option, it is important to understand and carefully weigh the risks associated with such courses of treatment.
Lifestyle Changes for Endometriosis
This primary level of treatment involves the least amount of risk, though conversely it requires the highest amount of self-discipline. Many times, simple changes in lifestyle can reap huge benefits in fighting the pain related to endometriosis and achieving a higher overall level of health. Fundamentally, an improved diet, regular exercise, and healthy habits can do a woman great service.
While these changes will help alleviate the pain associated to endometriosis, they do not address the problem directly at the hormonal source, so further treatment may be necessary. Alternative medicine has proven to be excellent for treating endometriosis in a safe and natural way.
Alternative Medicine for Endometriosis
Alternative approaches involve little to no risk and can be an extremely effective way to treat endometriosis. This level of approach can involve several different therapies. Supplements are the most prominent, though in addition women may turn to other stress relieving techniques such as massage or acupuncture which may help stabilize hormones or delay the misplaced endometrial tissue growth. In the case of supplements, there are two main types: phytoestrogenic and hormone-regulating herbal supplements.
Phytoestrogenic herbal supplements
These supplements, such as black cohosh, contain estrogenic components produced by plants that complement the low estrogen hormones in a woman's body, helping alleviate endometrosis. By introducing plant-based estrogens into the body, these herbs treat the underlying estrogen deficiency behind endometrosis.
They are mainly effective for menopausal women who are more likely to have low estrogen levels but are not necessarily effective for women in other stages of life such as puberty.
Hormone-regulating herbal supplements
These supplements, including Macafem, stimulate the body's natural hormone production by nourishing the endocrine glands, helping the whole hormonal system produce hormones more efficiently. This ultimately results in balancing not only estrogen but other important hormones such as progesterone.
These supplements can be considered the safest and most natural way to treat the underlying hormonal imbalance behind endometrosis, and can be taken throughout a woman's life, as they support the body's natural hormone production.
Additionally, there are some other types of supplements that can also alleviate endometrosis, or at least make them more manageable, including vitamins and other herbal supplements.
A combination of approaches is usually the most effective route to take. Lifestyle changes combined with alternative medicine will most likely be the best way to alleviate the symptoms of endometriosis. However, for some women the symptoms will be so severe that a more drastic treatment is necessary.
Pharmaceutical and Surgical Options for Endometriosis
Interventions at the third level involve the highest risk and often the highest costs. Because not all options are viable for every life stage, it highly recommended to speak with a doctor before starting a treatment. Prescription medications and surgical options to treat endometriosis include oral contraceptives and hysterectomy, among others.
If a woman's endometriosis is at the level of severity that she is still considering pharmaceutical and surgical options, it is wise to speak to a healthcare professional for guidance.
These three levels of approaches are not mutually exclusive. A woman may use different approaches at different times or any combination of them, depending on the duration and severity of symptoms. Today more and more women find that dealing with symptoms of hormonal imbalance is best accomplished via a combination of healthy lifestyle and alternative treatments.

Sources
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Endometriosis. Retrieved July 11, 2013, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/endometriosis
- Endometriosis Foundation of America. (n.d.). Endometriosis. Retrieved July 11, 2013, from http://www.endofound.org/endometriosis
- Endometriosis- Resolved. (n.d.). Endometriosis - Diet and Nutrition. Retrieved July 11, 2013, from http://www.endo-resolved.com/diet.html
- Harvard Medical School. (n.d). Symptoms of Endometriosis: Endometriosis symptoms after menopause. Retrieved July 11, 2013, from http://www.health.harvard.edu/press_releases/symptoms_of_endometriosis
- Iran Journal of Reproductive Medicine. (2013). Curcumin inhibits endometriosis endometrial cells by reducing estradiol production. Retrieved February 4, 2021 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3941414/
- Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research. (2010). The effects of massage therapy on dysmenorrhea caused by endometriosis. Retrieved February 4, 2021 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3093183/
- Journal of Pain Research. (2016). Is acupuncture effective in the treatment of pain in endometriosis? Retrieved February 4, 2021 from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27069371
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d). Endometriosis. Retrieved July 11, 2013, from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/endometriosis/DS00289


