About
Irregular periods are defined as any irregularity in the menstrual cycle that relates to its length, period flow, ovulation patterns, or symptoms that accompany monthly bleeding.
An irregular period is one that differs from the following characteristics of a healthy period:
- The cycle lasts between 21 to 35 days, with 28 days being the average.
- The bleeding lasts for 3 to 7 days
- Total blood loss per period is about 2.7 oz. (60mL).
- Ovulation occurs about 14 days before the next period.
- Only mild period symptoms are present a day before and a day or two into bleeding.
Identifying Irregular Periods
Identifying irregular periods might be tricky because what is considered “normal” for one woman may be abnormal for another. Also, it is common that women with intense symptoms or heavy bleeding accept their menstrual patterns as a normal part of menstruation, without seeking help.
Yet, irregular periods can be easily distinguished from what is accepted as a healthy menstruation. They come in several types, all of which fall under a broad category of menstrual disorders. They include the following:
Amenorrhea: Absent periods
Oligomenorrhea: Infrequent periods (cycles longer than 35 days)
Polymenorrhea: Frequent periods (cycles shorter than 21 days)
Menorrhagia: Heavy periods
Hypomenorrhea: Light periods
Metrorrhagia: Spotting between periods
Dysmenorrhea: Painful periods
Anovulation: Absence of ovulation
Oligoovulation: Irregular or infrequent ovulation
In order to understand why each one of these variants of irregular periods occur, please read the next section to learn about the hormonal and non-hormonal causes of irregular periods
Causes
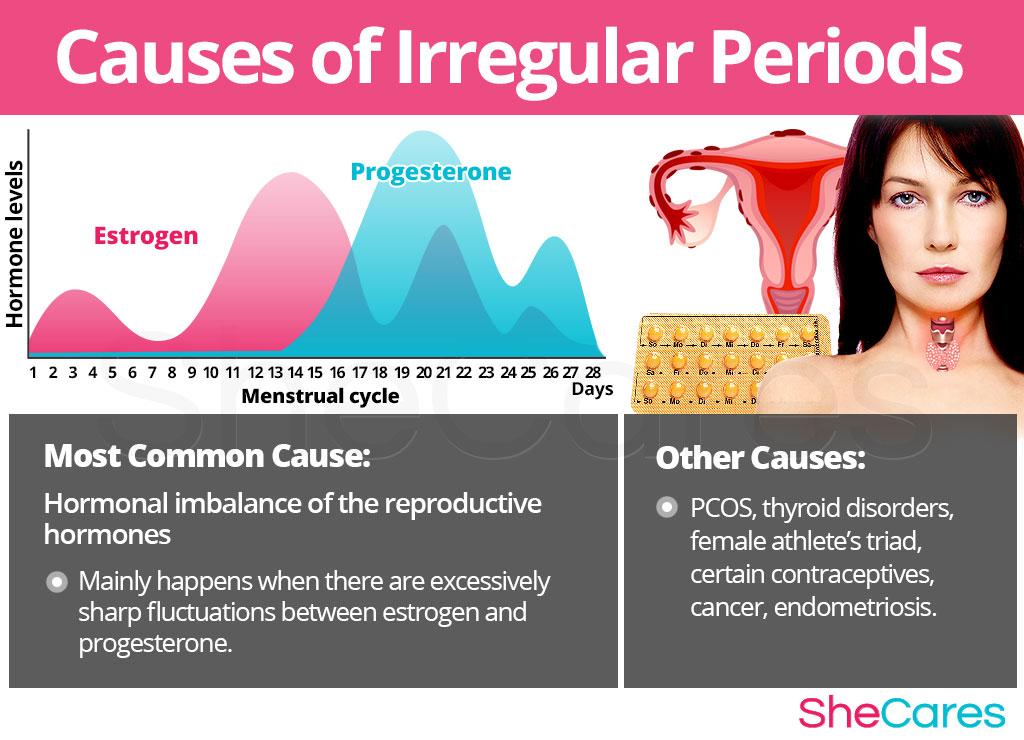
In order to be able to properly prevent and treat irregular periods, it is important to understand its underlying causes. While the disorder could be influenced by a variety of factors, such as stress levels, weight fluctuations, or changes in the amount of physical activity that is being performed, most doctors and researchers agree that hormonal fluctuations are the primary reason behind irregular periods. Furthermore, it is very common for any other related factor to be directly related to, or having an impact on the body's amount of reproductive hormones.
Continue reading to learn more about both the hormonal, and other, causes of irregular periods.
Hormonal Causes of Irregular Periods
It is well-known that the ultimate organ responsible for regulating and coordinating the different functions around the body is the brain. However, the brain relies on hormones in order to carry the appropriate messages to each organ around the body. There are several types of hormones and they are secreted in different organs; such as the pituitary, the thyroid gland, the adrenal glands or the reproductive system, all of which conform the endocrine system. The hormones that regulate menstrual cycles are produced in the reproductive system (mainly in the ovaries), and are estrogen and progesterone.
The fluctuations in the body's levels of each of these hormones are responsible for the maturation and release of an egg from the ovaries, and from producing the uterine lining that will “feed” the fertilized egg and make the full pregnancy possible, should conception happen. If conception doesn't happen, then these are responsible for shedding of the unused egg and the uterine lining, triggering menstrual bleeding. While estrogen is typically in charge during the first half of the cycle, after ovulation its levels drop and progesterone becomes dominant.
In addition to regulating the menstrual cycle, estrogen and progesterone also affect the amounts of other hormones like serotonin and cortisol, which in turn influence appetite, sleep, sexual desire, memory, weight fluctuations, and the body's response to stress. In this sense, we can say that any excessively sharp fluctuation between these two hormones will be responsible for irregular periods, and most likely cause an exacerbation of any symptoms that constitute PMS.
During certain delicate periods of a woman's reproductive life, it is quite common for these hormones to lose the delicate balance between them, causing heavy bleeding, spotting, severe pelvic pain, or even for a period to disappear altogether. Furthermore, many lifestyle or environmental factors typical of certain life stages can further explain the prevalence of irregular periods, and should be taken into account when managing or attempting to treat the disorder.
Hormonal Causes during Different Phases in a Woman's Life
Puberty is the stage in which a girl's body begins to produce reproductive hormones, triggering the beginning of menstruation. The initial hormonal adjustment, combined with other factors, makes periods commonly irregular.
Pregnancy is known for the extreme changes it causes in the body, but also because during it periods normally stop. However, spotting may be present during pregnancy.
Postpartum and breastfeeding is another stage women are expected not to ovulate, nor to menstruate. However, some factors may influence the length of this phase.
Menopause is the stage in a woman's life when her fertility ends. In preparation for this, her production of reproductive hormones will decline and fluctuate naturally, until her periods stop altogether. During the years leading up to menopause, irregular periods are common.
Other Less Common Causes of Irregular Periods
While hormonal imbalance is always involved in the onset of irregular periods during a woman's life, experts also point out that irregular periods can be influenced by other, less common, secondary causes which in turn may be causing an abrupt shift in reproductive hormones. These include thyroid disorders, abrupt weight fluctuations and polycystic ovarian syndrome.
In addition to these uncommon causes, there are other risk factors that can make some women more likely to experiencing irregular periods throughout her reproductive life span. In addition, there are also certain specific triggers that can set off the disorder.
Keep reading to learn more about what these risk factors and triggers are.
Risk Factors and Triggers
Risk Factors for Irregular Periods
Some women are more likely than others to suffer from irregular periods for inherent psychological, behavioral and health reasons. These predisposing factors can affect a woman's hormone levels and increase the chances that a woman will develop irregular periods during her reproductive life.
Triggers of Irregular Periods
In addition to long-term risk factors, irregular periods can also be triggered by certain environmental phenomena and behavioral habits. Avoiding these habits as much as possible may help to avoid the onset of symptoms of irregular periods. These include habits like unhealthy sleep schedules or taking antibiotics.
Continue reading to discover the symptoms and signs of irregular periods, in order to be able to choose the most appropriate treatment.

Signs and Symptoms
Because each woman has her own way of monitoring and experiencing her menstrual cycle, having an irregular period can mean different thing for each one of them. As a general rule, for adult women (but not for adolescent girls) a normal period should come every 24 to 35 days and can last anywhere from 4 to 8 days. However, many ways in which this cycle can become irregular are common for women going through a phase of hormonal imbalance:
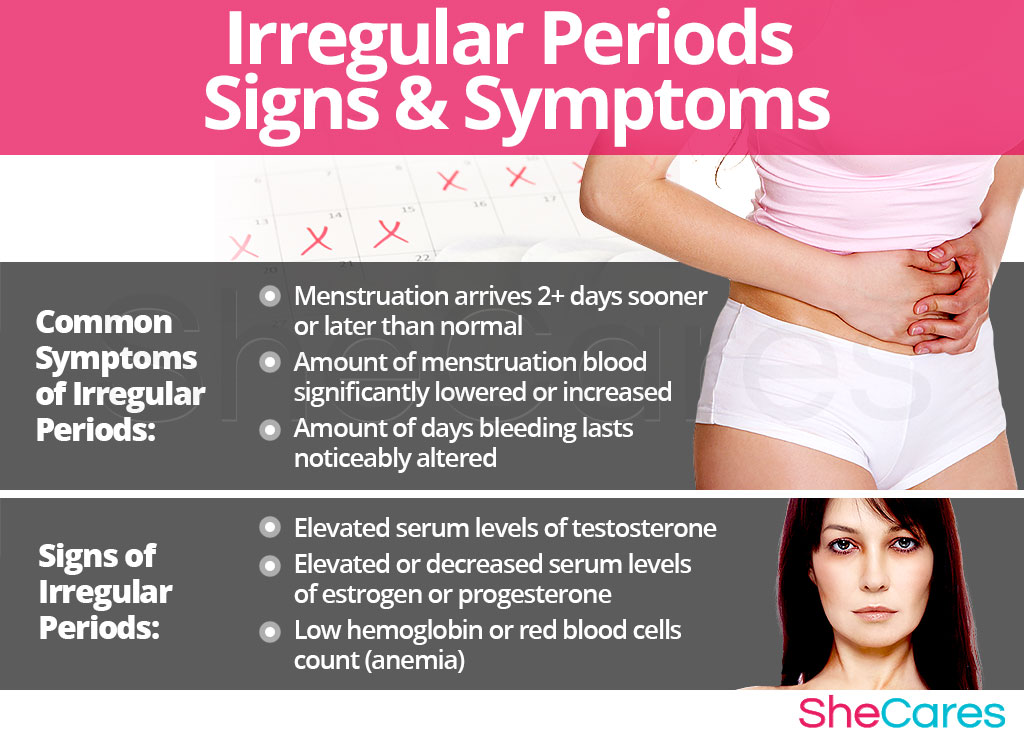
Common Symptoms of Irregular Periods
- Menstruation takes 2 or more days longer to arrive than it usually does.
- Menstruation arrives 2 or more days sooner than it usually does.
- The amount of blood that comes with menstruation seems to have significantly lowered.
- The amount of blood that comes with menstruation seems to have significantly increased.
- The amount of days that bleeding lasts seems to have altered noticeably.
Some women feel that their irregular periods are so severe or disruptive that they interfere with their daily life. Women may often seek treatment to help prevent and manage their irregular periods. Before attempting to treat irregular periods, it is advisable that women see medical attention so they can receive a proper diagnosis.
Signs of Irregular Periods
Because irregular periods are usually a symptom of something else, there are other, more specific, measurable criteria that will most likely be assessed by a doctor when diagnosing menstrual irregularities. In addition, there are other factors that may become of relevance to discard complications to health.
- Elevated serum levels of testosterone
- Elevated or decreased serum levels of estrogen
- Elevates or decreased serum levels of progesterone
- Low hemoglobin or red blood cells count (anemia).
Diagnosis of Irregular Periods
To diagnose and identify the symptoms of irregular periods, a doctor must typically perform three procedures. First, they should review the patient's medical history; then, they should conduct a physical exam, and finally order some additional tests, if necessary.
Complications of Irregular Periods
Although rare, the possibility for irregular periods to lead to more dangerous complications exists if they are left untreated for too long. However, it is important to keep in mind that most cases of irregular periods will not require any serious medical intervention. These possible, but uncommon complications are mostly related to frequent cases of spotting or menorrhagia, and include iron-deficiency anemia and hypoglycemia, among others.
Women who experience severe and frequent irregular periods may wish to treat or even prevent them. Keep reading below to learn about how to prevent and manage irregular periods.
Prevention and Management
Preventing Irregular Periods
While there is no single way to completely prevent irregular periods, just as there is no way to stave off hormonal process, there are a few steps that a woman can take to lessen her chances of developing them in the first place, or to minimize the impact or length of time that symptoms occur.
In this sense, a proper lifestyle is one of the best preventive measures available, especially with regard to diet, exercise and healthy habits. Women can also choose to combine these lifestyle changes with the right supplements that help to enhance the endocrine system and, therefore, get an extra level of protection against irregular periods and other problems related to hormonal imbalance.
For women who are already experiencing irregular periods, prevention may not be possible if symptoms already appeared. Fortunately, there are many ways to manage them in order to prevent their recurrence or to lessen their intensity. Keep reading to learn about the different ways to manage irregular periods.
Managing Irregular Periods
Suffering from irregular periods can put a great strain on intimate relationships or social activities. However, there are some steps that can be taken in order to make the impact of an unexpected bleed a minor nuisance, keeping it from ruining any special plans or moments.
While these measures often help reduce the impact that irregular periods may have on women's lives, they are unable to treat the root of the problem, which is hormonal imbalance. However, there are several natural treatments that can treat the hormonal causes of irregular periods. Keep reading to discover treatments approaches for irregular periods.

Treatments
Irregular periods are frustrating for many women precisely because of their unexpected nature, and they have ruined many women's beach trip or romantic getaways. Luckily, it is possible to find an effective treatment for irregular periods.
Three Approaches to Treat Irregular Periods
Three levels of approaches can be considered for treating irregular periods. These are categorized as: (1) Lifestyle Changes, (2) Alternative Medicine, and (3) Drugs and Surgery.
Women are encouraged to begin with the least risky approach to treat irregular periods, lifestyle adjustment. While these are often effective at curbing the disorder, they alone do nothing to address the most common underlying cause of irregular periods -hormonal imbalance. Fortunately, alternative medicine can be combined with lifestyle changes to provide a safe and effective irregular periods treatment.
While medical intervention is not usually necessary to treat irregular periods, some women may wish to consider drug options if they are unable to find relief from natural treatments. For women considering this option, it is important to understand, and carefully weigh, the risks associated with such treatments for irregular periods.
Lifestyle Changes for Irregular Periods
This primary level of treatment involves the least amount of risk, though conversely it requires the highest amount of self discipline. Many times some simple changes in lifestyle can reap huge benefits in fighting irregular periods and achieving a higher overall level of health. Fundamentally, an improved diet, regular exercise and healthy habits can do a woman a great service.
Alternative Medicine for Irregular Periods
Alternative approaches involve little to no risk and can be an extremely effective way to treat irregular periods. This level of approach can involve several different therapies, and in the case of herbal supplements they can be classified in two main groups: phytoestrogenic and hormone-regulating supplements.
Phytoestrogenic herbal supplements
These supplements, such as black cohosh or vitex chasteberry, are sometimes used to help women regulate their periods or lessen other symptoms of low estrogen levels, because they contain plant-made chemical compounds very similar to human estrogen, which can act as a replacement and diminish the underlying estrogen deficiency.
They are mainly effective for menopausal women who are more likely to have low estrogen levels but are not necessarily effective for women in other stages of life such as puberty.
Hormone-regulating herbal supplements
These supplements, including Macafem stimulate the body's natural hormone production by nourishing the pituitary and endocrine glands, helping the whole hormonal system produce hormones more efficiently. This ultimately results in balancing not only estrogen but other important hormones such as progesterone.
These supplements can be considered the safest and most natural way to treat the underlying hormonal imbalances behind irregular periods, especially when there is more than one disorder being experienced. Furthermore, they can be taken throughout a woman's life, since they support the body's natural hormone production.
Additionally, there are other types of supplements that can alleviate the discomfort caused by frequent, heavy, or painful periods, including vitamins and other herbal supplements.
A combination of approaches is usually the most effective route to take. Lifestyle changes combined with alternative medicine will most likely be the best way to alleviate the symptoms of irregular periods. However, for some women the symptoms will be so severe that a more drastic treatment is necessary.
Pharmaceutical Options for Irregular Periods
Interventions at the third levels involve the highest risk and often the highest costs. Not all treatments are suitable for women at every life stage, so a licensed healthcare practitioner should be consulted before considering any pharmaceutical treatments for irregular periods.
Pharmaceutical options used to treat irregular periods are usually designed towards hormonal regulation, and include both hormonal replacement and different types of contraception.
These three levels of approaches are not mutually exclusive. A woman may use different approaches at different times or any combination of them, depending on the duration and the severity of symptoms. Today more and more women find that dealing with the symptoms of hormonal imbalance, like irregular periods, is best accomplished via a combination of healthy lifestyles and alternative treatments.
Sources
- MenopauseNow.(n.d.). Irregular Periods. Retrieved August 16, 2017, from https://www.menopausenow.com/irregular-periods
- Cleveland Clinic.(n.d.).Abnormal Menstruation. Retrieved August 16, 2017, from http://my.clevelandclinic.org/anatomy/female_reproductive_system/menstruation/hic-abnormal-menstruation.aspx
- Paula J. Adams Hillard. (2008). Menstruation in Adolescents: What's Normal? Retrieved August 16, 2017, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2644006/
- Mayo Clinic.(2014).Amenorrhea. Retrieved August 16, 2017, from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/amenorrhea/DS00581/DSECTION=preparing-for-your-appointment
- Mayo Clinic.(2014).Menorrhagia. Retrieved August 16, 2017, from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/menorrhagia/DS00394/DSECTION=tests-and-diagnosis
- Sagodi L,Barkai L. (n.d). Diagnosis difficulties of polycystic ovarian syndrome in adolescent girls. Retrieved August 16, 2017, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23335723 Diagnostic difficulties of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in Adolescent Girls
- Sharpley, M., Jordan, K., Croft, P. (2004). An epidemiological survey of symptoms of menstrual loss in the community. Retrieved August 16, 2017, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1266170/
- The New Yorker. (2008). Menstrual Periods -Heavy, Prolonged or Irregular. Retrieved August 16, 2017, from http://health.nytimes.com/health/guides/symptoms/menstrual-periods-heavy-prolonged-or-irregular/risk-factors.html






