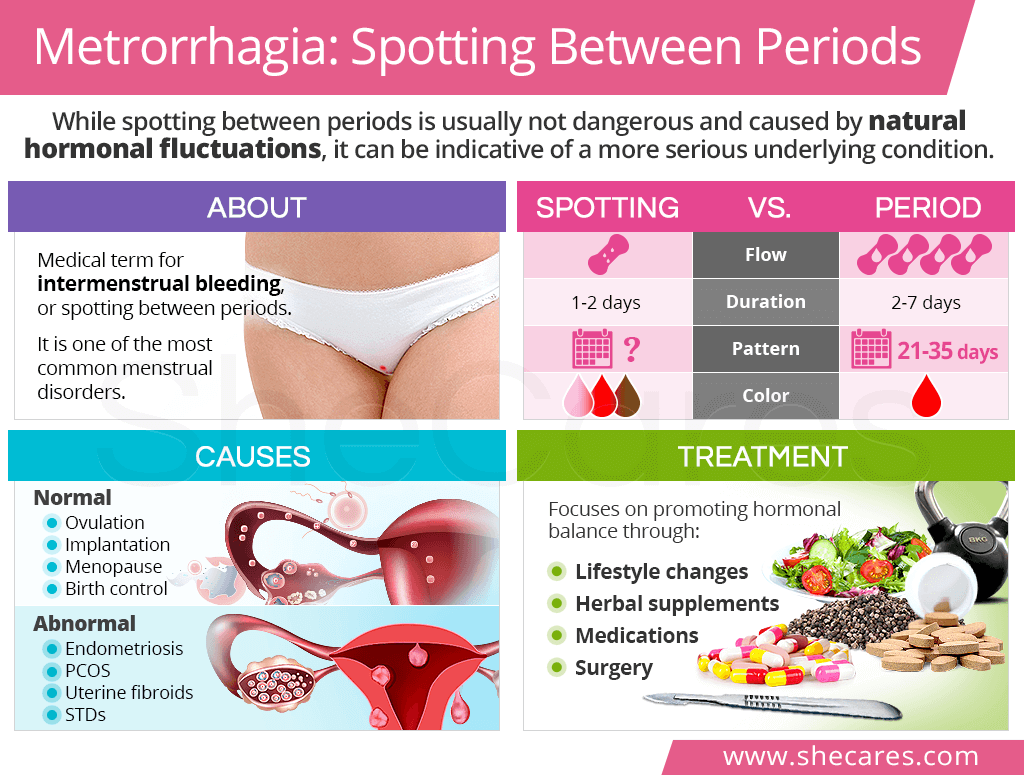
What is Metrorrhagia?

Metrorrhagia, also referred to as intermenstrual bleeding, is a medical term for bleeding or spotting between periods.
It is characterized by light spotting that occurs outside of one's period patterns and does not need sanitary protection.1
Abnormal uterine bleeding, such as metrorrhagia, is one of the most common menstrual disorders.
Metrorrhagia Symptoms
Spotting between periods is generally just that: occasional light drops of blood that are noticeable on a panty liner or toilet paper. While it generally does not produce its own symptoms, some women may report mild cramps while spotting mid-cycle.
However, because metrorrhagia can be caused by various medical conditions, it can be accompanied by symptoms specific to them, such as:
- Loss of libido
- Hot flashes
- Dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
- Pelvic pain
Difference between Spotting and a Period
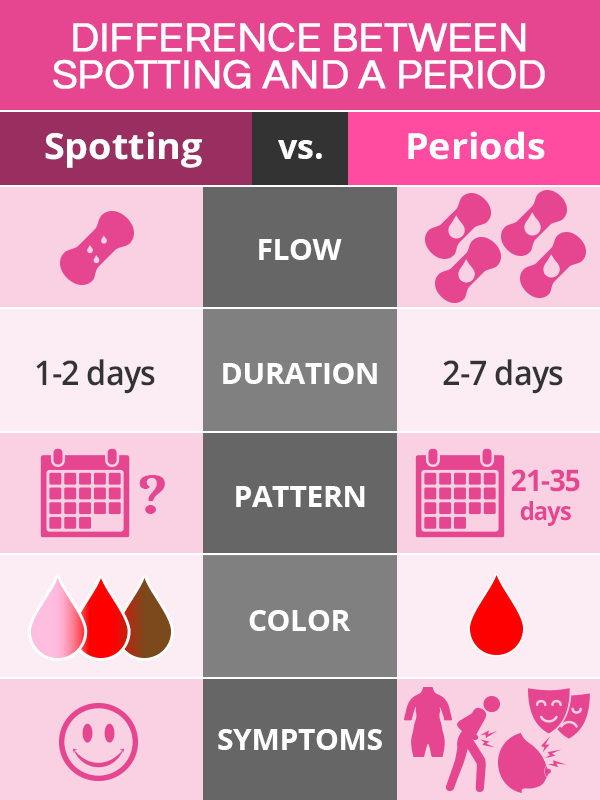
It is important not to mistake spotting between periods for an actual period.
To have a clear understanding of one's menstrual patterns, women are encouraged to use a period tracker to take note of normal periods as well as any instances of spotting between periods and bothersome symptoms.
Keeping the following characteristics in mind can help women tell mid-cycle bleeding apart from normal monthly periods:
Usually without major period-like symptoms
Causes Of Spotting Between Periods
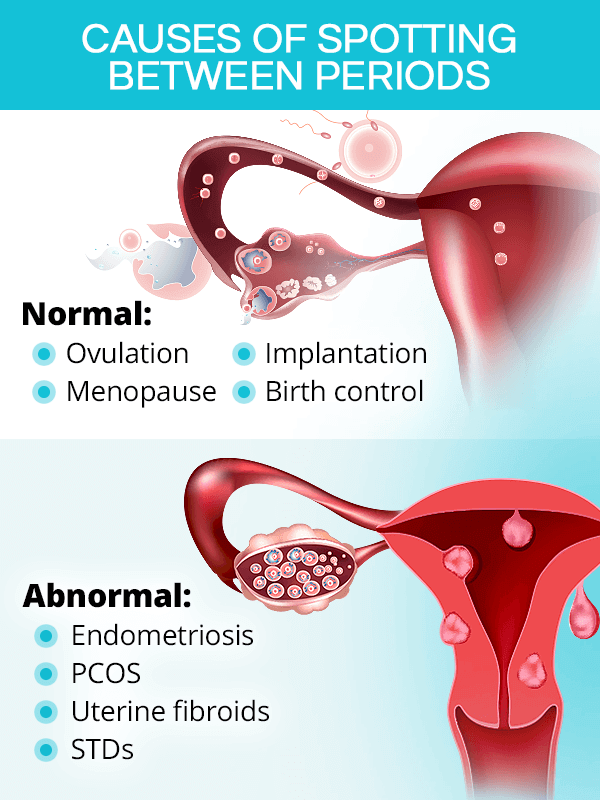
There are many possible reasons for spotting between periods, from normal causes that do not signal problems to more serious conditions that require proper attention. Most causes, however, are related to hormonal imbalance, both directly and indirectly.
Normal Causes
Light intermenstrual bleeding is common during times of hormonal fluctuations, which may occur naturally or triggered by medications. Most common ones include the following:
- Ovulation (most common)
- Pregnancy (implantation bleeding)
- Menopause
- Birth control (breakthrough bleeding)
- Breastfeeding
- Puberty
- Medication side effects
- Infertility treatments
Abnormal Causes
Bleeding or spotting between periods can also be indicative of various medical conditions or lifestyle practices, such as:
- Endometriosis
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Uterine fibroids or polyps
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STD)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Coagulation disorders
- Being underweight or malnourished
- Prolonged high stress
- Cancers
Complications of Metrorrhagia
In most cases, occasional light bleeding between periods does not carry major health risks, besides being inconvenient. However, frequent, consistently heavy spotting or bleeding between periods can have negative consequences on a woman's health.
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia may be triggered by significant blood loss on a monthly basis as well as poor nutrition, which is one of the causes of bleeding between periods. It is said to affect up to 20% of women of reproductive age and has been linked to infertility, depression, heart problems, and other complications.5
Other Complications
Another complication of metrorrhagia that is not properly treated is the progression of the condition that causes it. While most conditions can have detrimental effects on a woman's well-being and daily functioning, leaving some without treatment can be life-threatening. This includes PID, certain STDs, coagulation disorders, or cancers.
Metrorrhagia Treatment

If spotting between periods is light, infrequent, and due to normal causes, treatment is generally not necessary and efforts might be put on promoting hormonal balance in the body. However, if bleeding results from abnormal causes or is severe, a more advanced treatment approach might be required.
As such, metrorrhagia treatment can encompass a variety of approaches, from optimizing one's lifestyle practices and using alternative medicine to relying on pharmacological or surgical options.
Lifestyle Changes
A nutritious diet rich in iron and phytoestrogenic foods - like lentils or soy - can help women regulate their cycles and maintain a healthy weight, which is essential to menstrual health.
Regular exercise that focuses on losing excess weight and strengthening the body can restore period regularity and improve overall health.
Stress-relief techniques can help reduce the negative effects of accumulated cortisol on menstrual health and their role in causing intermenstrual bleeding.
Alternative Medicine
Nutritional supplements, like iron, might be necessary for those whose spotting between periods put them at risk of developing anemia.
Phytoestrogenic supplements, like chaste berry, can be used short-term to supply the body with plant-based estrogenic compounds that work to promote hormonal balance.
Hormone-regulating supplements, like Macafem, can be safely used long-term to stimulate the endocrine glands from within toward optimal hormone production.
Medications & Surgery
Medications will typically focus on treating conditions like vaginitis, PCOS, or STDs that might be behind bleeding between periods. They might include antibiotics, pain relievers, and birth control pills, among others.
- Surgery is usually reserved for instances of heavy intermenstrual bleeding as well as severe symptoms, such as abdominal pain. Depending on the root cause, it may involve removing fibroids, polyps, or endometrial lesions.
Key Takeaways
Because a woman's menstrual patterns are a good indicator of her overall health, particularly the state of her hormones, instances of intermenstrual bleeding should not be overlooked. Medically known as menorrhagia, spotting between periods is – in most cases – normal and related to periods of hormonal fluctuations in a woman's life. However, it can also signal other underlying conditions, which, if left untreated, can take a toll on her health. As such, women are encouraged to track period patterns and implement practices to restore hormonal balance through diet, exercise, and stress-relief as well as herbal supplements, like Macafem. Those with heavy bleeding between periods might need more conventional treatments to reestablish menstrual and overall health.
Sources
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2017). Abnormal Uterine Bleeding. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Abnormal-Uterine-Bleeding?IsMobileSet=false
- Better Health Channel. (2012). Vaginal bleeding – irregular. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/vaginal-bleeding-irregular
- Cleveland Clinic. (2018). Bleeding Between Periods? How to Tell If It's a Problem. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://health.clevelandclinic.org/when-should-you-worry-about-spotting-between-periods/
- Epidemiology. (2002). Influence of medical conditions and lifestyle factors on the menstrual cycle. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12410008/
- Health Direct. (2019). Bleeding between periods. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/bleeding-between-periods
- Mayo Clinic. (2019). Vaginal bleeding. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/vaginal-bleeding/basics/definition/sym-20050756
- Medline Plus. (2019). Vaginal bleeding between periods. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003156.htm
- NHS. (2019). What causes bleeding between periods? Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/womens-health/what-causes-bleeding-between-periods/
- Office on Women's Health. (2018). Menstrual Cycle. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/menstrual-cycle
- University of Michigan. (2018). Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/abvbd
Footnotes:
- American Journal of Epidemiology. (2012). Menstrual Bleeding Patterns among Regularly Menstruating Women. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3299419/
- InformedHealth.org. (2009). Heavy periods: Overview. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279294/
- Cleveland Clinic. (2019). Abnormal Menstruation (Periods). Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14633-abnormal-menstruation-periods
- The Ohio State University. (2019). Why spotting between periods happens and when to be concerned. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://wexnermedical.osu.edu/blog/spotting-between-periods
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (n.d.). Iron-Deficiency Anemia. Retrieved February 6, 2020 from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/iron-deficiency-anemia