About
What are Anxiety Disorders?
Quick Facts about Anxiety
- Around 16% of Americans will experience some type of anxiety disorder at some point, and two thirds will be women.
- Around 10% of Americans will suffer from it this year.
- Out of all these people, only 10% will receive treatment.
- People who experience anxiety are more likely to develop a substance abuse problem or even an addiction.
Anxiety disorders are a category of mental health conditions that are characterized by excessive worry and nervous thoughts, and can affect the quality of a person's life and interfere with their daily obligations.
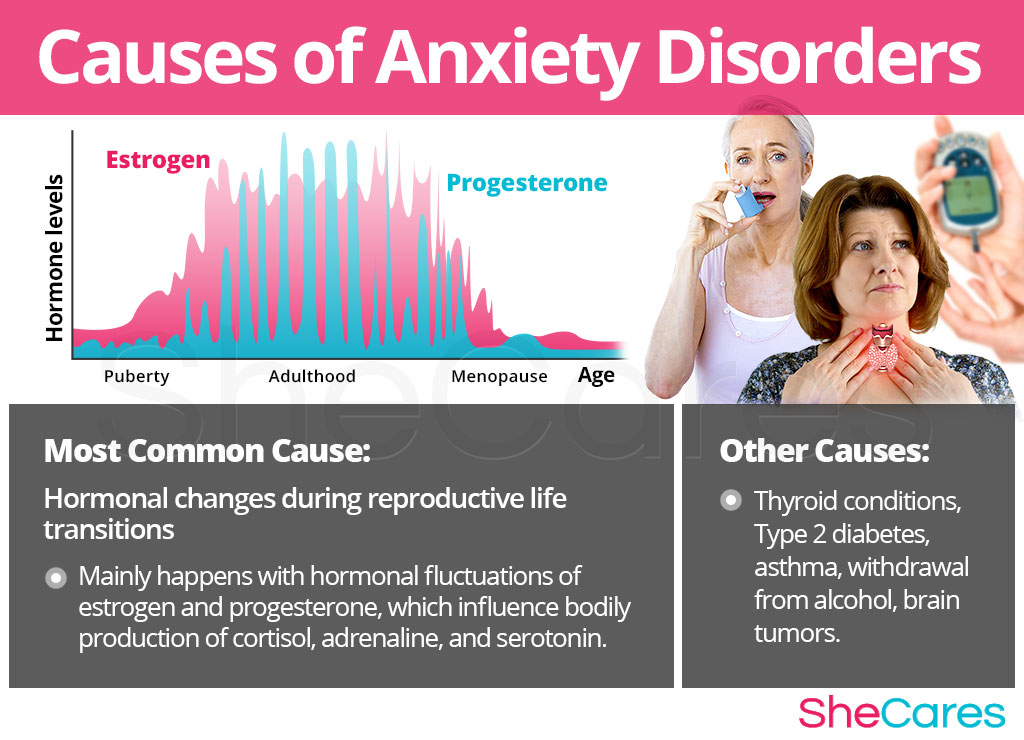
While the causes for this are not completely understood yet, there is a strong correlation between times of hormonal upheaval for women and the appearance of anxiety disorders and its symptoms. Several reproductive hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, are linked to malfunctions in thyroid functions and the body's levels of cortisol, which in turn affect a woman's mental health.
The specific types of anxiety disorders that are more prevalent among women of reproductive age are generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder. To learn more about these and other types of anxiety disorder, please continue reading.
Identifying Anxiety Disorders
There are different types of anxiety disorders, and each one of them can be experienced with varying degrees of frequency and intensity. The most common types of anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder and panic disorder.
In order to understand the process behind anxiety disorders, continue on to the next section to read about their hormonal and non-hormonal causes.

Causes
Learning about the causes of anxiety disorders provides the key to understanding how to prevent and treat these troublesome attacks. Anxiety disorders usually have multiple causes or risk factors, ranging from physical to environmental ones. However, most doctors and researchers agree that hormonal changes are the primary cause of anxiety disorders in women of reproductive age. In addition to these completely normal hormonal causes, other factors and medical conditions can, in more rare instances, cause anxiety disorders.
Continue reading to learn more about both the hormonal, and other, causes of anxiety disorders.
Hormonal Causes of Anxiety Disorders
Hormones are chemical messengers that control every organ in the body, so when changes in these hormone levels occur, certain health disorders can arise. In this sense, we can say that anxiety disorders are caused largely by the hormonal fluctuations during the transitions women go through during their reproductive life.
The hormones estrogen and progesterone influence the brain's production of cortisol and adrenaline, which are brain chemicals that regulate the body's “flight or fight” response when under stress. Imbalances between these hormones can trigger many of the physiological symptoms that are associated with anxiety, such as tachycardia, dizziness, or excessive sweating.
Estrogen also affects directly the way the body processes serotonin, a brain hormone that is responsible for happy moods; while progesterone is associated with a calming effect on the body. When the levels of both hormones fluctuate, the body becomes more sensitive to excess cortisol.
Furthermore, there are also specific hormonal and typical environmental factors which can explain the occurrence of anxiety disorders according to the stage of a woman's reproductive life in which this disorder appears, such as around PMS and during puberty, pregnancy, post-partum, and menopause.
Other Less Common Causes of Anxiety Disorders
While hormonal imbalance is one of the major underlying causes of anxiety disorders during a woman's life, experts also point out that mood disturbances may be caused by other, less common, underlying conditions including thyroid conditions, diabetes, and as part of withdrawal syndrome.
Keep reading to learn what these risk factors and triggers are that have such a profound effect on a woman's experience of anxiety disorders.
Risk Factors and Triggers
Risk Factors for Anxiety Disorders
Some women are at a higher risk of developing anxiety disorders than others for inherent psychological, behavioral and health reasons - such as obesity, stress, or past emotional trauma. These predisposing factors can affect a woman's hormone levels and increase the chances that she will develop anxiety disorders during her reproductive life.
Triggers of Anxiety Disorders
In addition to long-term risk factors, anxiety disorders can also be triggered by more specific environmental factors and behavioral habits. Avoiding these environments or habits as much as possible may help to avoid the onset of anxiety-related symptoms. These include habits like smoking and sugar binges, as well as other external triggers.
Continue reading to discover the symptoms and signs of anxiety disorders to be able to choose a treatment specific to its cause.

Signs and Symptoms
Because each woman has her own individual way of managing her emotions, stress, and of coping with the things that concern her, all women experience the symptoms of anxiety disorders differently. However, many women going through a phase of hormonal imbalance tend to experience some common symptoms, and they tend to fall under the Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) or Panic Disorder (PD) categories.
Common Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
- Feelings of apprehension or dread
- Certainty that something bad is going to happen
- Restlessness and the inability to remain still or calm
- Muscle tension and aches
- Difficulty concentrating and sleeping
- Increased heart rate
- Stomach discomfort (gasses, sudden diarrhea)
- Fatigue
- Dizziness, nausea and shortness of breath, which may make a woman feel like she's about to faint.
Each type of anxiety disorder will present these symptoms in slightly different ways or situations:
- Generalized anxiety disorder involves feeling all these symptoms in a permanent or steady manner (for example, once a day) for at least 6 consecutive months.
- Panic attacks usually present all the symptoms at once and seemingly out of the blue
- Specific phobias are characterized because several symptoms lump together and appear under a very specific trigger or situation.
Signs of Anxiety Disorders
As opposed to more noticeable symptoms, medical signs are measurable criteria that are usually assessed by a physician. The following medical signs will most likely be taken into account by a physician when diagnosing the disorder:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Fluctuating blood pressure
- Slightly elevated or reduced body temperature
- Abnormal blood levels of reproductive hormones
- Abnormal bone density reading
Diagnosis of Anxiety Disorders
To diagnose and identify the symptoms of hormonal-related anxiety, a doctor usually must perform four procedures. First, he or she should review the patient's medical history, then conduct a physical exam, and finally do a psychological questionnaire. In some cases, if necessary, the doctor may also order additional tests.
Complications of Anxiety Disorders
In rare cases, when anxiety disorders are left untreated, they can lead to certain complications, which are more risky for a woman's emotional and mental health. These possible, but uncommon, complications of anxiety disorders can include chronic headaches, depression, and other mental health problems, and they have some specific warning signs.
It is important to keep a watchful eye for any warning signs and monitor them properly in order to distinguish them when they could signal a more serious condition.
Women who experience severe and frequent symptoms of anxiety disorders may wish to treat or even prevent them. Keep reading below to learn about how to prevent and manage anxiety disorders.

Prevention and Management
Preventing Anxiety Disorders
While there is no single way to completely prevent anxiety disorders just as there's no way to stave off hormonal process relating to women's reproductive life, there are a few steps that a woman can take to lessen her chances of developing them, or to minimize the impact that anxiety disorders have on her life.
Lifestyle changes for prevention are extremely important, especially with regard to diet, exercise and healthy habits. Moreover, a woman may seek ways to complement these lifestyle approaches with the use of supplements that help to enhance the endocrine system and, therefore, help to prevent or ease symptoms of hormonal imbalance such as anxiety disorders.
For women who are already experiencing anxiety disorders, prevention may no longer be possible if symptoms have already appeared. Fortunately, there are many ways to manage them in order to prevent the “flare-ups” or lessen the intensity of the symptoms. Keep reading to learn about the different ways to manage anxiety.
Managing Anxiety
Women who suffer from anxiety disorders - especially panic attacks- have several ways to manage the symptoms in order to reduce their frequency and severity. Making minor daily changes and avoiding triggers can make a huge difference for women who are trying to manage anxiety disorders.
There are certain tips and tricks available that can help improve the experience of anxiety disorders, giving women the tools they need to cope with panic attacks and uncontrollable anxiety. There are general tips that women of all ages can use, such as breathing techniques, playing the right music, or keeping the right diet.
Alternative Management Tips
Alternative treatments are also a great way to manage anxiety disorders. These treatments will not tackle the hormonal cause behind most women's symptoms of anxiety, but they are effective in reducing stress in the short and medium term. Alternative treatments include acupuncture, biofeedback and emotional freedom techniques.
While these measures often help to reduce the frequency and intensity of the symptoms of anxiety disorders, they are unable to treat the root of the problem, which in most cases is hormonal imbalance. However, there are several natural treatments that can treat the hormonal causes of anxiety disorders.
Please continue to the next section to learn more about treating anxiety disorders.

Treatments
Anxiety disorders can be frustrating and debilitating for any woman who experiences them. Many times the fear of experiencing further symptoms may cause women to avoid social situations and isolate themselves. Fortunately, it is more than possible to find an effective treatment for anxiety disorders.
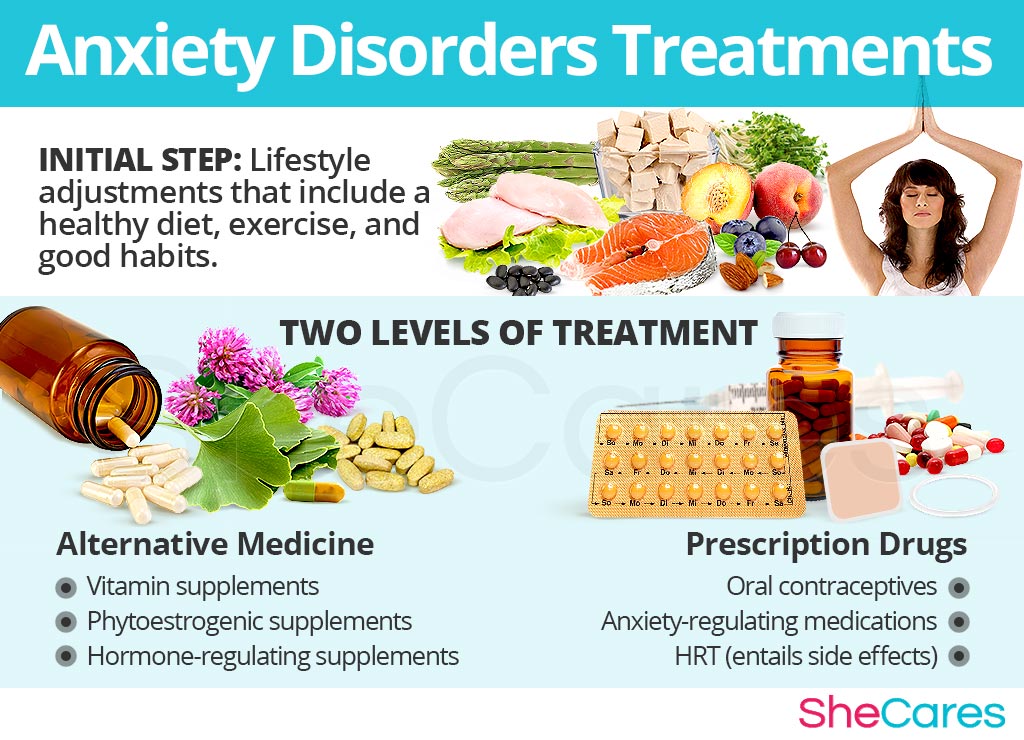
Three Approaches to Treat Anxiety Disorders
Three levels of approaches can be considered for treating anxiety disorders. These are categorized as (1) Lifestyle Changes, (2) Alternative Medicine, and (3) Pharmaceutical Options.
Women are encouraged to begin with the least risky approach to anxiety disorders treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and then proceed to the next level of care. While medical intervention is not usually necessary to treat anxiety disorders, some women who are unable to find relief from lifestyle changes and alternative medicine may wish to consider pharmaceutical options, after properly assessing the risks associated with such a treatment.
Lifestyle Changes for Anxiety Disorders
The primary level of treatment for anxiety involves the least amount of risk, though conversely it requires the highest amount of self discipline. Many times some simple changes in lifestyle can reap huge benefits in fighting symptoms of hormonal imbalance and achieving a higher overall level of health. Fundamentally, an improved diet, regular exercise, and healthy habits, can do a woman great service.
While these changes will help alleviate anxiety disorders, they do not directly address hormonal imbalance - the most common cause of anxiety disorders - so further treatment may be necessary. Alternative medicine has proven to be an excellent way of treating anxiety disorders related to hormonal imbalance in a safe and natural way.
Alternative Medicine for Anxiety Disorders
Alternative medicines and supplements involve little to no risk and can be an extremely effective way to treat anxiety disorders. In the case of herbal supplements, there are two main types that can be used: phytoestrogenic and hormone-regulating herbal supplements.
Phytoestrogenic herbal supplements
These supplements, such as black cohosh, contain estrogenic components produced by plants that complement the low estrogen hormones in a woman's body, helping alleviate symptoms of anxiety. By introducing plant-based estrogens into the body, these herbs treat the underlying estrogen deficiency behind anxiety disorders.
They are mainly effective for menopausal women who are more likely to have low estrogen levels but are not necessarily effective for women in other stages of life such as puberty.
Hormone-regulating herbal supplements
These supplements, including Macafem stimulate the body's natural hormone production by nourishing the pituitary and endocrine glands, helping the whole hormonal system produce hormones more efficiently. This ultimately results in balancing not only estrogen but other important hormones such as progesterone.
These supplements can be considered the safest and most natural way to treat the underlying hormonal imbalance behind anxiety disorders, and can be taken throughout a woman's life, as they support the body's natural hormone production.
Additionally, there are some other types of supplements that can also alleviate symptoms of anxiety, or at least make them more manageable, including vitamins and other herbal supplements.
A combination of approaches is usually the most effective route to take. Lifestyle changes combined with alternative medicine will most likely be the best way to alleviate the symptoms of anxiety disorders. However, for some women the symptoms will be so severe that a more drastic treatment will be necessary.
Pharmaceutical Options for Anxiety Disorders.
Interventions at the third level involve the highest risk and often the highest costs. Not all treatments are suitable for women at every life stage, so it is strongly recommended to speak to a licensed healthcare practitioner before starting any pharmaceutical treatments for anxiety disorders.
There are two main types of pharmaceutical options that can be prescribed to treat anxiety disorders: hormone-regulating medication and anxiety-regulating medication.
These three approaches are not mutually exclusive. A woman may use different approaches at different times or any combination of them, depending on the duration and severity of symptoms. Today more and more women find that dealing with symptoms of hormonal imbalance is best accomplished via a combination of healthy lifestyle and alternative treatments.
Sources
- Anxiety Center. (n.d.). Anxiety Statistics. Retrieved January 29, 2013 from http://www.anxietycentre.com/anxiety-statistics-information.shtml
- American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and Statistic Manual IV Edition. Text Revision. American Psychiatric Publishing.
- Cleveland Clinic (2013). Overweight ad Heart Disease. Retrieved January 29, 2013 from http://my.clevelandclinic.org/heart/prevention/weight/bmi.aspx
- Mayo Clinic (2010) Comprehensive overview. Retrieved January 29, 2013 from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/anxiety/DS01187
- NHS Choices. (2011). 10 stress busters. Retrieved January 29, 2013 from http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/stress-anxiety-depression/Pages/reduce-stress.aspx
- Pigott, T (1999). Gender differences in the epidemiology and treatment of anxiety disorders. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 18:4-15.
- Rapkin , A. Morgan, M. Goldman, L. Brann. D. Simone, D. Mahesh, V. (1997). Progesterone metabolite allopregnanolone in women with premenstrual syndrome. Obstetrics and Gynecology Review. Nov;90(5):709-14.
- Tartakovsky, M. (2012). 4 facts about anxiety during pregnancy you should know. Retrieved January 29, 2013 from: http://psychcentral.com/blog/archives/2012/04/19/4-facts-about-anxiety-during-pregnancy-how-to-find-help/
- Umea University. (2011). Effects of allopreganolone in women with Pre Menstrual Syndrome. Retrieved January 29, 2013 from: http://www.news-medical.net/news/20111222/Effects-of-allopregnanolone-in-women-with-severe-pre-menstrual-syndrome.aspx






