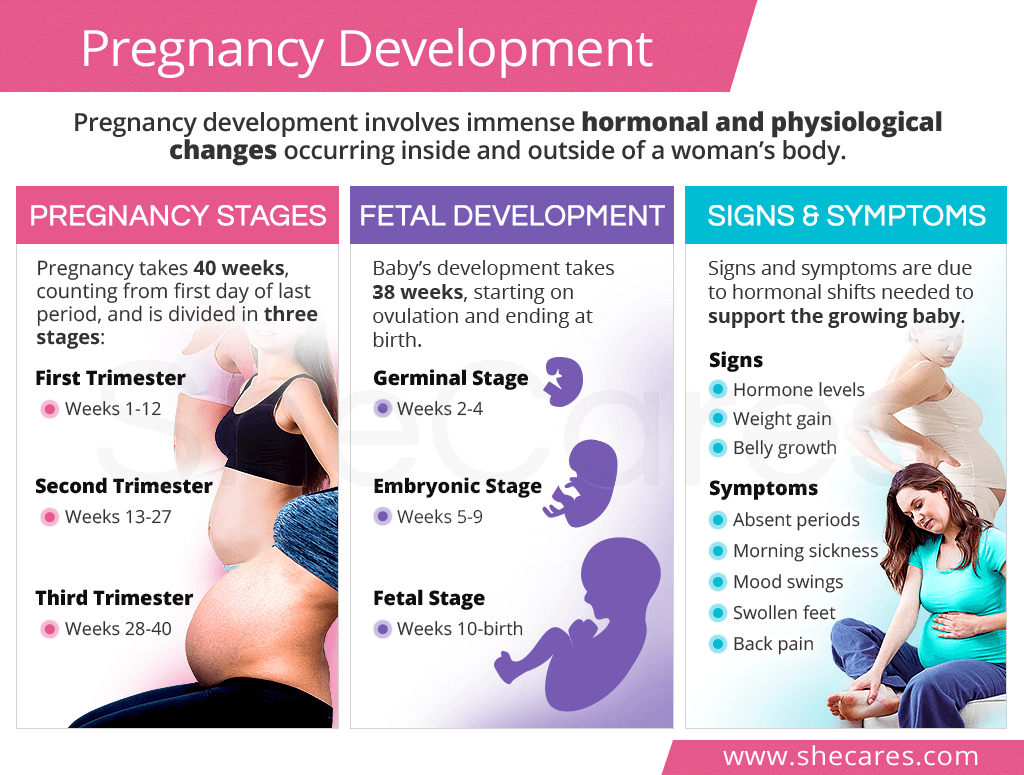
Pregnancy Stages

Pregnancy, also called gestation period, is a 40-week journey divided into three trimesters. Massive hormonal and subsequent physiological changes during pregnancy take place to support the growing fetus.
First Trimester (Weeks 1-12)
First trimester is counted from the first day of a woman's last menstrual period, although she is not pregnant until ovulation, which typically happens mid cycle.
The first three months are usually burdened with a variety of early pregnancy signs and symptoms, like morning sickness, fatigue, or breast tenderness. Because the risk of miscarriage is the highest during the first trimester, prenatal vitamins are of the essence.
Second Trimester (Weeks 13-27)
Second trimester is usually the least burdensome of the three as most of the early discomforts lessen or disappear, and many women start looking pregnant and experiencing the pregnancy glow.
During the next three months, many important tests will be done, including gender reveal ultrasound or prenatal genetic testing. The risk of miscarriage is significantly lower, and women are encouraged to stay active and exercise during pregnancy to relieve back pain and strengthen the body before labor.
Third Trimester (Weeks 28-40)
Third trimester is all about the baby growing and both the mother and baby preparing for the delivery.
As they near their pregnancy due date, women might become uncomfortable carrying more weight with limited mobility. Some might experience practice contractions, called Braxton hicks contractions, which is how the uterine muscles rehearse before real labor. Women are also monitored for pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia.
Keep on reading to discover more information about pregnancy stages or move to the section to learn about the baby's development.
Fetal Development

Although a woman is not actually pregnant in the first week or two, the baby's gestational age is calculated similarly to the gestation period: from the first day of the last period.
However, fetal development itself takes about 38 weeks from the moment the egg meets the sperm on ovulation until the baby is born. It occurs in three stages: germinal, embryonic, and fetal.
Germinal Stage (Weeks 2 - 4)
This primary stage of fetal development begins at the moment of conception, which is when the sperm fertilizes the egg. It starts to rapidly multiple as it moves down the fallopian tube to the uterus for implantation. Once embedded in the uterine wall, the gestational sac and yolk sac form, which protect it and provide nutrients for its growth.
Embryonic Stage (Weeks 5 - 9)
The second stage of pregnancy development is the embryonic stage, during which major organs begin to form. As such, it is a time of major fetal milestones, such as the detection of the first embryonic structures on an ultrasound around week 5 and the first heartbeat by week 8.
Fetal Stage (Weeks 10 - birth)
The last and the longest stage of prenatal development is the fetal stage. All major organs finish forming and begin to work, and the baby gradually grows in size and moves in the womb. Childbirth typically occurs around 37 - 42 weeks of the gestation period, but the fetus has a chance of surviving outside the womb at weeks 22 - 26, if born prematurely.
Keep on reading to familiarize yourself with more details about fetal development or continue reading about the most common pregnancy signs and symptoms.
Pregnancy Signs & Symptoms

Pregnancy discomforts are known all too well to aspiring mothers even before conceiving; however, while carrying one's own child, it is easy to give in to anxious thoughts when new and sometimes scary symptoms appear.
As such, understanding the consequences of natural hormonal changes during pregnancy can help women handle pregnancy discomforts more peacefully.
Pregnancy Signs
Pregnancy signs are what can be obtained and measured through pregnancy tests, prenatal testing, and regular OBGYN exams. They are expected and universal across all women and include the following:
Influx of hormones during pregnancy, like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), estrogen, and progesterone, measured by blood tests
Signs of fetal development, like heartbeat, size, and movement, detectable on ultrasound
Weight gain that healthily ranges between 25 - 35 lb. (11.5 - 16 kg) for women with a normal BMI (18.5 - 24.9)
Belly growth that is carefully measured in terms of fundal height as it is a reflection of fetal growth
Pregnancy Symptoms
In contrast to pregnancy signs, symptoms of being pregnant are reported by a woman. They are believed to be brought about by rapid hormonal changes during pregnancy and include the following:
Absent periods from fertilization well into postpartum
Morning sickness is most prominent in the first trimester
Headaches are common, but if present with high blood pressure, they might indicate preeclampsia
Spotting affects a third of all pregnant women and usually does not indicate complications
Mood swings can not only be caused by hormones, but also fatigue and anxiety before becoming a mother
Swollen feet, as well as face and hands, are caused by fluid retention and worsen in the last trimester
Back pain is caused by extra weight and hormones relaxing pelvic ligaments before labor
Continue reading to discover the most important pregnancy signs and symptoms for a full picture of what to expect while expecting.
Key Takeaways
The human gestation period consists of 40 weeks filled with numerous changes within a woman's body, all specifically aimed at supporting the baby's growth. The physiological changes during pregnancy span over three trimesters, each with its own characteristics and milestones.
Although the gestation period is counted from the first day of a woman's last period, she is not actually pregnant in the first one or two weeks until she ovulates and conceives. As such, fetal development takes 38 weeks from the moment the sperm fertilizes the egg until birth, and it has its own three distinct stages: germinal, embryonic, and fetal. As the baby develops, the influx of hormones during pregnancy causes notorious signs and symptoms, like weight gain, belly growth, morning sickness, and back pain. Fortunately, they are soon a thing of the past once the long awaited baby is born and in the arms of his or her parents.
Sources
- American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. (2002). Comparison of pregnancy dating by last menstrual period, ultrasound scanning, and their combination. Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12501080
- American Pregnancy Association. (n.d.). Pregnancy Calculator. Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-calculator/
- Better Health Channel. (n.d.). Pregnancy – week by week. Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/HealthyLiving/pregnancy-week-by-week
- Cleveland Clinic. (2014). Fetal Development: Stages of Growth. Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7247-fetal-development-stages-of-growth
- Mayo Clinic. (2017). What's the significance of a fundal height measurement? Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-answers/fundal-height/faq-20057962
- Medline Plus. (2019). Fetal Health and Development. Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://medlineplus.gov/fetalhealthanddevelopment.html
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Stages of pregnancy. Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/stages-pregnancy
- Planned Parenthood. (n.d.). Pregnancy Month by Month. Retrieved June 24, 2019 from https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/pregnancy/pregnancy-month-by-month