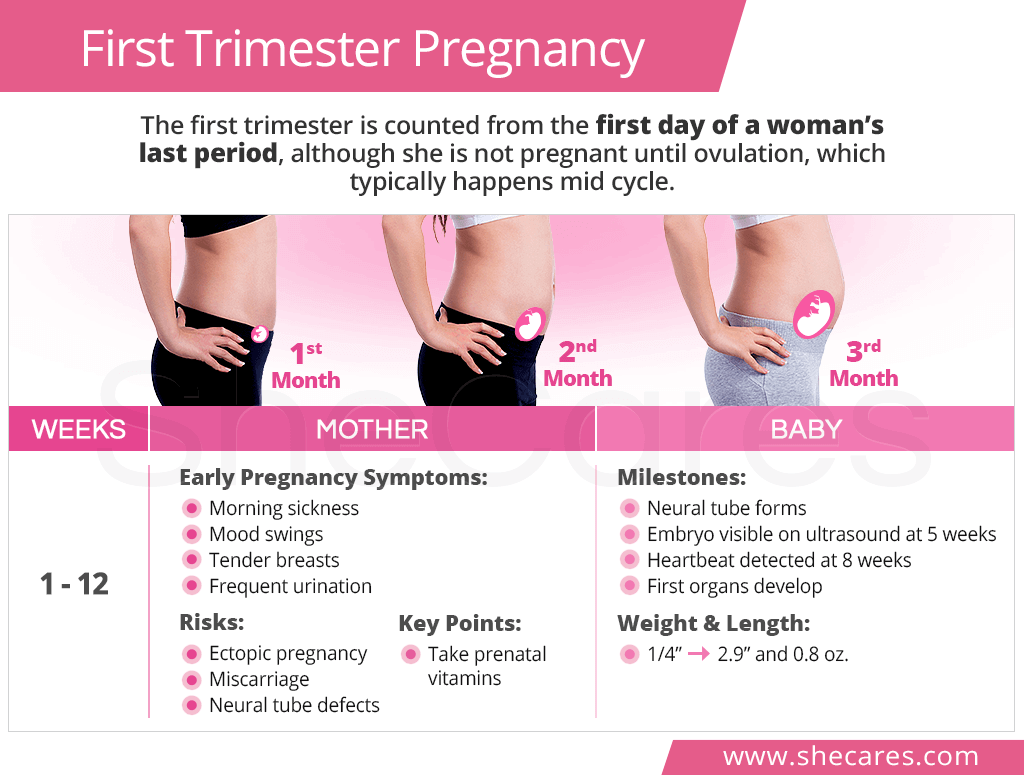
First Trimester Weeks

The first trimester of pregnancy is counted from the first day of a woman's last period before becoming pregnant. As such, it covers the time from week 1 until the end of week 12.1
It is important to notice that since pregnancy is counted in such way, a woman is not yet pregnant from the start of her period until the day of her ovulation. Depending on the length of her menstrual cycle, she might be three to five weeks pregnant by the time she missed her period, takes a pregnancy test, and realizes she is expecting.
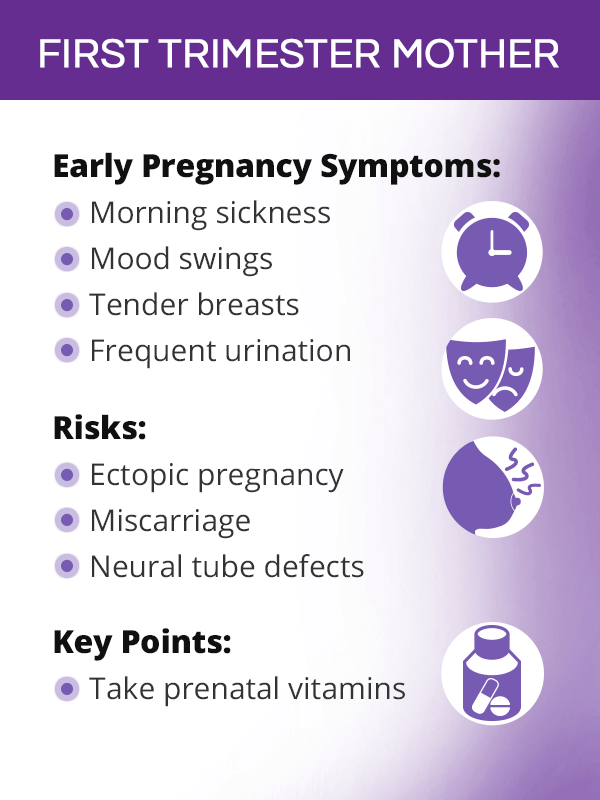
First Trimester Mother
The changes in a woman's body occur rapidly during the first trimester, but the majority of them happen inside and are not yet visible on the outside.
In order for the fertilized egg to successfully implant itself in the uterine wall and continue developing, massive hormonal changes have to take place to facilitate that. This rapid influx of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), estrogen, and progesterone can bring about various early pregnancy signs and symptoms in a first trimester mother, including:
- Blood hCG 25 mIU/mL and above
- Gestational sac on ultrasound after week 5
- Yolk sac visible at 5.5 weeks
- Fetal pole visible at 6-6.5 weeks
- Fetal heartbeat detected at 6-8 weeks
- Missed period
- Morning sickness
- Breast tenderness
- Fatigue
- Implantation bleeding
Many of the aforementioned pregnancy symptoms will disappear or lessen soon as a woman begins her second trimester.
First Trimester Baby

Fetal development is expressed in terms of gestational age, which is also counted from the first day of a woman's last period.
During the first trimester, the fertilized egg passes through three stages of fetal development. Starting right after conception and until week 4, the germinal stage consists of the fertilized egg moving down the fallopian tube to the uterus for implantation. By week 5, the embryonic stage begins with the egg (now called embryo) embedded and growing in the uterine wall. The third and the longest stage, called fetal, starts at week 10 and lasts until birth.
In the first month of pregnancy, the neural tube is formed. A few weeks later around week eight, baby's heartbeat can already be first detected. By the end of the first trimester, the main organs and limbs are developed, and the baby grows from being ¼ of an inch long to measuring 2.9 inches and weighing 0.8 ounces.
First Trimester Tests
The very first test a woman takes in pregnancy is the pregnancy test itself, either with a urine or blood sample. Once confirmed pregnant, she will be advised to schedule her first prenatal visit around week 8.
Besides assessing a woman's health, a doctor will offer her various prenatal tests aimed at ruling out ectopic pregnancy, estimating baby due date, and detecting early embryonic structures. These first trimester tests might include the following:
Physical exam with vital signs, breast exam, and pelvic exam, including pap smear
Prenatal blood tests: for blood type, Rh factor, and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) as well as maternal blood serum to evaluate the risk of Down syndrome and birth defects
Prenatal ultrasounds: dating ultrasound (week 8) and nuchal translucency screening (weeks 11-14)
Chorionic villus sampling: a type of prenatal genetic testing to diagnose abnormalities (weeks 10-13)
Women will also be recommended prenatal vitamins with 400 mcg of folic acid if they have not started taking them prior to conceiving.2 The purpose of these supplements is to decrease the risk of neural tube defects.
First Trimester Tips
During the first prenatal doctor's visit, a woman is typically encouraged to instill healthy practices to lower the risk of pregnancy complications, including miscarriage, which is the highest in the first three months. Some of the most important first trimester tips include the following:
- Taking prenatal vitamins
- Quitting addictions to cigarettes and alcohol
- Maintaining a wholesome pregnancy diet, while avoiding raw fish or meats
- Staying active with non-strenuous, moderate-level exercise during pregnancy
- Practicing yoga, meditation, and breathing techniques to lower stress during pregnancy
- Reaching out for help in the case of unresolved emotional difficulties
Key Takeaways
Although a woman is filled with the joy of carrying a child, her first trimester, spanning from the first to the twelfth week of pregnancy, is usually burdened with notorious discomforts, like morning sickness, tender breasts, or fatigue. They are a by-product of intense hormonal shifts that occur inside a woman as her body sustains pregnancy. Though not quite visible on the outside, these hormonal changes in the first trimester help the baby develop major organs, including the heart, whose first beats can be detected as early as the eighth week of gestation. During the initial three months, a woman will also undergo various tests and will be encouraged to maintain a healthy lifestyle, all aimed at reducing pregnancy complications and giving the baby a healthy start.
Sources
- Better Health Channel. (2018). Pregnancy - prenatal tests. Retrieved May 8, 2019 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/pregnancy-prenatal-tests
- Better Health Channel. (n.d.). Pregnancy - week by week. Retrieved May 8, 2019 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/HealthyLiving/pregnancy-week-by-week
- Cleveland Clinic. (2014). Fetal Development: Stages of Growth. Retrieved May 8, 2019 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7247-fetal-development-stages-of-growth
- Mayo Clinic. (2017). What's the significance of a fundal height measurement? Retrieved May 8, 2019 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-answers/fundal-height/faq-20057962
- Medline Plus. (2019). Fetal Health and Development. Retrieved May 8, 2019 from https://medlineplus.gov/fetalhealthanddevelopment.html
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Stages of pregnancy. Retrieved May 8, 2019 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/stages-pregnancy
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Prenatal care and tests. Retrieved May 8, 2019 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/prenatal-care-and-tests
- Planned Parenthood. (n.d.). Pregnancy Month by Month. Retrieved May 8, 2019 2019 from https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/pregnancy/pregnancy-month-by-month
Footnotes:
- KidsHealth. (n.d.). A Week-by-Week Pregnancy Calculator. Retrieved September 9, 2021 from https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/pregnancy-calendar-intro.html
- CDC. (2021). Folic Acid. Retrieved September 9, 2021 from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/folicacid/about.html