About
What is Weight Gain?
Quick facts about Weight Gain
- A 2012 US nation-wide survey estimated that two thirds of the country's population was overweight, and that at least 30% of the was obese
- Obesity is considered as the main public health problem for the next 10 years, because it increases the risk of a large range of other conditions, from type-II diabetes to Alzheimer's
- Being overweight and obese seems strongly tied to socio-economic status: poorer, uneducated families are more likely to be overweight and to suffer from the strain of related conditions
Weight gain is an increase in a person's total body mass, either consisting of additional fat deposits, an increase in the amount of muscle tissue or even excess water being retained by the body. Out of all symptoms caused by the hormonal changes during a woman's reproductive life, weight gain is probably one of the first ones to be noticed and recognized.
While up to a certain point all types of weight gain can affect a woman's health in one way or another, when weight gain is caused by excess fat then it is overwhelmingly more likely to be detrimental to a woman's overall well-being, and this article will deal primarily with that type of weight gain.
Identifying Weight gain
Weight gain produced by excess fat deposits around the body can be classified depending on the type of adipose tissue that is being gained. There are two types of fat storages in the body, subcutaneous fat and visceral fat.
In order to gain a better understanding on the processed behind weight gain, continue on to the next section to read about their hormonal and non-hormonal causes.

Causes
In general, weight gain is caused by excessive caloric intake, which causes the body to store the excess energy as fat. However, for many women the problem is not so simple, because there are several types of hormonal fluctuations and imbalances that may cause their bodies to slow down on their energy consumption, change their appetites or cause bloating.
While the exact relationship between different hormones and weight gain is complex and not completely understood, most doctors and researchers believe hormonal changes play a significant role in weight gain. In addition to these completely normal hormonal causes, other factors and medical conditions can, in more rare instances, cause weight fluctuations.
Continue reading to learn more about both the hormonal, and other, causes of weight gain.
Hormonal Causes of Weight Gain
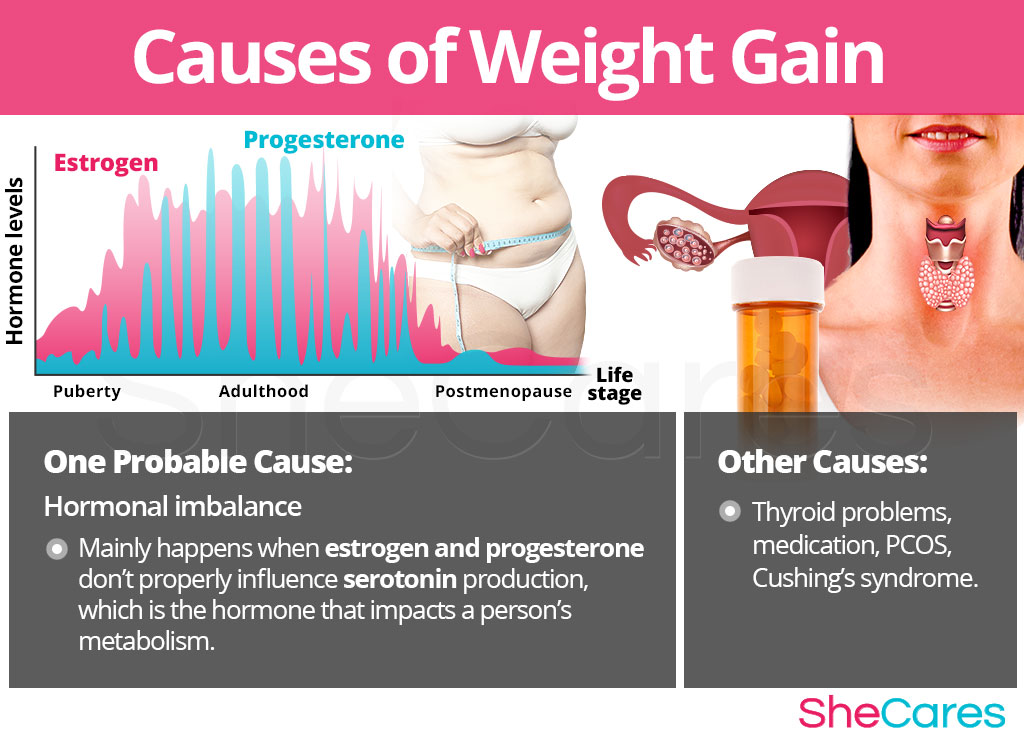
Hormones are chemical messengers that control every organ in the body. In order to make menstruation, reproduction and breastfeeding possible, a woman's body produces a series of special hormones that cause changes all over the body, known as sex-defining hormones. The most abundant hormones in this category are estrogen, progesterone, prolactin and testosterone.
The hormones estrogen and progesterone influence the production of serotonin, which is a neurotransmitter known as one of the “feel-good” chemicals. In addition to regulating mood, serotonin can also influence a person's metabolism, causing their body to slow down and spend less energy. This can set off an abrupt weight gain, even if caloric intake remains the same.
On the other hand, progesterone has a calming effect on the body, and lack of it can cause anxiety or low moods, which can increase a woman's appetite.
As part of its reproductive function, estrogen favors subcutaneous fat, especially in the hips; while testosterone enables larger muscles and visceral fat. If these hormones lose the delicate balance between them, they can cause additional fat storages in the belly area (of the dangerous intra-visceral fat) and they have been linked to thyroid problems.
Furthermore, there are also specific hormonal causes and typical environmental which can affect the way weight gain is being experienced, depending on the stage of a woman's reproductive life in which this disorder appears, such as around PMS, and during puberty, pregnancy, post-partum, and menopause.
Hormonal Causes during Different Phases in a Woman's Life
PMS is a consequence of hormonal fluctuations linked to the menstrual cycle. It is a collection of disorders, which may include minor weight gain, among others.
Puberty is the stage in which a girl's body begins to produce reproductive hormones; these and other factors, such as eating habits and social pressures, affect the experience of weight gain during puberty.
Pregnancy leads to extreme changes in the production of reproductive hormones, which bring with them a varied range of uncomfortable symptoms, in addition to a degree of expected weight gain.
Postpartum and breastfeeding is another stage where reproductive hormones are imbalanced, and where weight is expected to change. Some factors, like lifestyle influences, will affect this.
Menopause is the stage in a woman's life when production of reproductive hormones naturally declines, signaling the end of a woman's fertility. As well as hormonal causes, other factors add to the reasons for weight gain during menopause, including the metabolic changes and sedentary habits.
Other Less Common Causes of Weight Gain
While hormonal imbalance is a major underlying cause of weight gain during a woman's life, experts also point out that weight problems may be caused by other, less common, underlying conditions. These include thyroid problems, certain medication, and some chronic illnesses like Cushing's syndrome.
Keep reading to learn about these risk factors that have such a profound effect on a woman's weight gain.
Risk Factors and Triggers
Risk Factors for Weight Gain
Some women are more likely than others to suffer from weight gain for inherent psychological, behavioral and health reasons. These predisposing factors can affect a woman's hormone levels and increase the chances that a woman will develop constant weight fluctuations during her reproductive life.
Continue reading to learn more about the signs and symptoms of hormonal weight gain, as well as the process to diagnose it.

Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms of Weight Gain
While most women would recognize feeling heavier or that their clothes feel tighter immediately, for many others a combination of stress and lack of time may make them unaware of the ongoing problem.
Usually, the most noticeable signs of weight gain are a tighter feel to their clothes or even their shoes. However, on a visit to the doctor he or she may notice some more specific signs. These may include:
- An increase in the body fat percentage
- Increase in breast or waist size
- Change in body shape (pear to apple)
Diagnosis
Some women may feel that their weight gain can be so overwhelming and disruptive that they need medical attention. To diagnose and identify this symptom, the doctor will most likely perform three procedures. First, he or she should review the patient's medical history; then, conduct a physical examination, followed by some additional tests, if necessary.
Complications of Weight Gain
It is never advisable to carry around excessive amounts of fatty deposits in the body. Being chronically overweight or obese can lead to certain long-term complications, and some of them can significantly shorten a person's life expectancy, such as cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, stroke, or diabetes.
Women with a family history of weight issues or any other risk factor may be concerned about developing problematic or hard-to-control weight gain later. Continue reading to learn more about ways to prevent weight gain.

Prevention and Management
Preventing Weight Gain
While there is no single way to completely prevent weight gain, just as there is no way to stave off hormonal process relating to women's reproductive life, there are a few steps that a woman can take to lessen her chances of developing an excessive weight gain that may endanger her health, or to minimize any weight fluctuations that must occur (such as during a pregnancy).
In this sense, lifestyle changes for prevention are extremely important, especially in regard to diet, an exercise regimen and healthy habits. Moreover, a woman may seek ways to complement these lifestyle approaches with the use of supplements that help to enhance the endocrine system and help prevent or ease her chances of experiencing symptoms of hormonal imbalance such as weight gain. Continue reading to learn more about lifestyle prevention for weight gain.
For women who have already gained weight, prevention may no longer be possible, but there are many ways to help manage the unsettling symptoms and to keep the weight gain from progressing further. Keep reading to learn about the different ways to manage weight gain.
Managing Weight Gain
With practice and self-control, some women can successfully manage their weight gain and slow it down, or even stop it altogether. Below are some helpful survival tips on how to avoid and manage weight gain.
General Management Tips
- Keeping a Journal. Keeping track of any foods eaten, daily exercise practiced, and particular stressful situations that may affect eating or energy levels; as well as taking note of the specific triggers for emotional eating will help establish a pattern that will show what type of regime works for each specific person, and to prevent binges.
- Positive thinking. While struggling against weight gain, it can be beneficial to think positively. Although a woman thinks she may never be able to beat the excess weight, it is important that she keeps optimistic and rewards herself (but not with food) for any achievement she makes in her struggle.
- Long-term mentality. Many women who are trying to prevent weight gain tend to be overly severe on themselves and throw the towel once they slip up, even if only by a little bit. This may cause them to feel more depressed and look for sugary treats as a self esteem boost.
While these measures often help to reduce the frequency and intensity of weight gain, they are unable to treat the root of the problem, which is hormonal imbalance. However, there are several natural treatments that can treat the hormonal causes of weight gain. Please continue to the next section to learn more about treating and reversing weight gain. Keep reading to discover approaches to treatments for weight gain.

Treatments
At some point during her reproductive life, it will be inevitable for a woman to incur in at least some weight gain. Fortunately, because weight gain is also a consequence of fluctuations in hormones such as estrogen, testosterone and progesterone, it is possible to treat this imbalance. While there is no magical fix, the most effective approach to treating weight gain is to combine a few changes in lifestyle with alternative treatment options.
Three Approaches for Treating Weight Gain
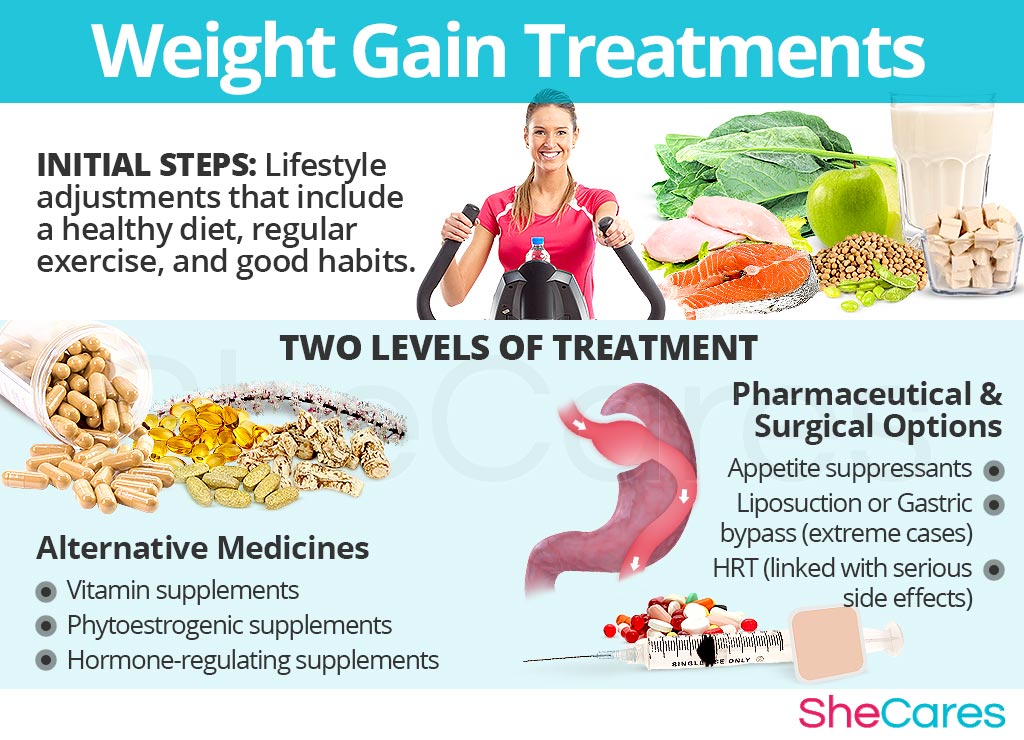
Three levels of approaches can be considered for treating weight gain. These are categorized as: (1) Lifestyle Changes, (2) Alternative Medicine and (3) Pharmaceutical and Surgical Options.
Women are encouraged to begin with the least risky approach to weight gain treatment, lifestyle changes. While they are often effective at curbing the disorder, these alone do little to address the most common cause of unexplained or hard to control weight gain - hormonal imbalance. Fortunately, alternative medicine can be combined with lifestyle changes to provide a safe and effective treatment for weight gain.
While medical intervention such as drugs and surgery are not usually necessary to treat excess weight or obesity, some women may wish to consider them if they are unable to see improvement from natural treatments. For women considering this option, it is important to understand, and carefully weigh up, the risks associated with such approaches.
Lifestyle Changes for Weight Gain
This primary level of treatment for weight gain involves the least amount of risk, though conversely it requires the highest amount of self discipline. Simple changes in lifestyle can reap huge benefits in fighting weight gain and achieving a higher overall level of health. Fundamentally, an improved diet, regular exercise, and healthy habits can do a woman great service.
While these changes will help treat and reverse weight gain, they do not directly address hormonal imbalance - which is commonly an underlying cause of unexpected weight gain - so further treatment may be necessary. Alternative medicine has proven to be an excellent way of treating and reversing weight gain related to hormonal imbalance in a safe and natural way.
Alternative Medicine for Weight Gain
Alternative medicines and supplements involve little to no risk and can be an extremely effective way to reduce weight gain. In the case of herbal supplements, there are two main types that can be used: phytoestrogenic and hormone-regulating herbal supplements.
Phytoestrogenic herbal supplements
These supplements, such as black cohosh, contain estrogenic components produced by plants that complement the low estrogen hormones in a woman's body, helping reverse weight gain. By introducing plant-based estrogens into the body, these herbs treat the underlying estrogen deficiency behind weight gain.
They are mainly effective for menopausal women who are more likely to have low estrogen levels but are not necessarily effective for women in other stages of life such as puberty.
Hormone-regulating herbal supplements
These supplements, including Macafem stimulate the body's natural hormone production by nourishing the pituitary and endocrine glands, helping the whole hormonal system produce hormones more efficiently. This ultimately results in balancing not only estrogen but other important hormones such as progesterone.
These supplements can be considered the safest and most natural way to treat the underlying hormonal imbalance behind weight gain, and can be taken throughout a woman's life, as they support the body's natural hormone production.
A combination of approaches is usually the most effective route to take. Lifestyle changes combined with alternative medicine will most likely be the best way to control and reverse weight gain. However, for some women the symptoms will be so severe that a more drastic treatment is necessary.
Drugs and Surgery for Weight Gain
Interventions for weight gain at the third level involve the highest risk and often the highest costs and side effects. Not all treatments are suitable for women at every life stage, so it is strongly recommended to speak to a licensed healthcare practitioner before starting any pharmaceutical or surgical treatments for weight gain.
There are two main types of pharmaceutical options that can be prescribed to treat weight gain: hormone-regulating medication and weight-loss medication. In addition, extreme cases may become candidates for more invasive surgical options.
If a woman is still considering this final option to treat weight gain, it is wise to speak to a healthcare professional for guidance.
These three levels of approaches are not mutually exclusive. A woman may use different approaches at different times or any combination of them to treat weight gain, depending on the duration and severity of symptoms. Today more and more women find that dealing with weight gain is best accomplished via a combination of healthy lifestyle and alternative treatments.
Sources
- American Pregnancy Association. (2011). Eating for two when under/overweight. Retrieved August 22, 2017, from http://www.americanpregnancy.org/pregnancyhealth/eatingfortwo.html
- Cleveland Clinic (2013). Overweight ad Heart Disease. Retrieved August 22, 2017, from http://my.clevelandclinic.org/heart/prevention/weight/bmi.aspx
- Leddy, M., Power M., Shulkin J. (2008). The impact of Maternal Obesity on maternal and fetal health. Reviews in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Fall Issue 1 (4): 170-178
- Marshall, S., Jones, K. (2011). Exercise and Weight Loss during Breastfeeding. Retrieved August 22, 2017, from http://www.everydayhealth.com/health-center/exercise-and-weight-loss-while-breast-feeding-info.aspx
- Mayo Clinic. (2010). Menopause Weight Gain. Retrieved August 22, 2017, from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/menopause-weight-gain/HQ01076
- Mayo Clinic. (2010). Weight loss after pregnancy. Retrieved August 22, 2017, from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/weight-loss-after-pregnancy/PR00147
- Poston L., Harthoorn L., Van Der Beek E,.(2011). Obesity in pregnancy: implications for the mother and lifelong health of the child. A consensus statement. Pediatric Research. Feb;69(2):175-80.