What is Early Menopause?
Early menopause is defined as menopause that occurs between the ages of 40 and 45. It is said to affect 5% of women.1 As with regular menopause, it means that a woman is no longer menstruating and cannot get pregnant naturally.
It is often confused with premature menopause, which is defined as one that takes places before the age of 40.1
For reference, the average menopause age in the United States is 51, with the majority of women entering the transition between the ages of 45 and 55.2
What Causes Early Menopause?
While up to 60% of cases of early menopause happen for unknown reasons, some can be traced back to a specific cause.3 These may directly disrupt ovarian function or interrupt hormone signaling between the ovaries and the brain.
The most common causes of early menopause include the following:
- Family history, such as having a close relative who has undergone early menopause
- Autoimmune diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis
- Chromosomal abnormalities, such as Fragile X or Turner's syndrome
- Viral infections, like mumps, cytomegalovirus,or HIV
- Radio- or chemotherapy side effects
- Oophorectomy, which is surgical removal of ovaries, the main estrogen and progesterone producers
- Unhealthy habits, such as smoking
Signs & Symptoms of Early Menopause
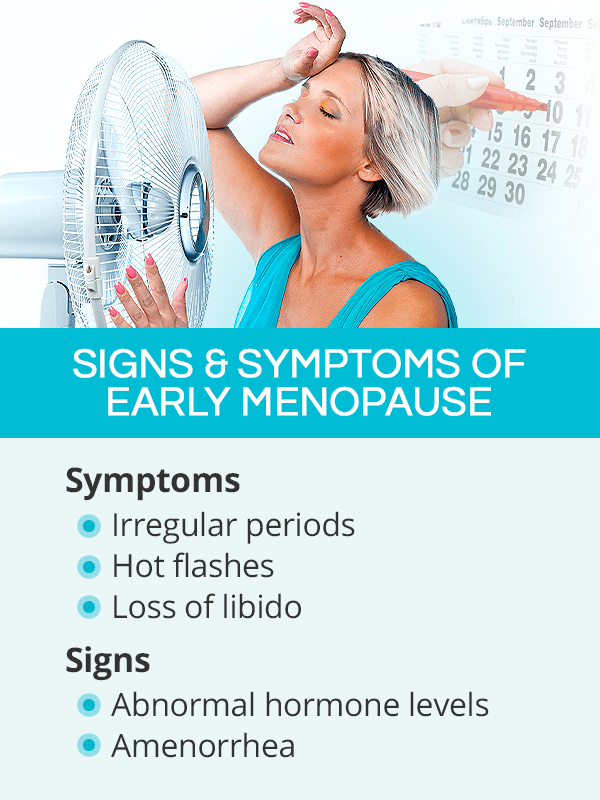
Signs and symptoms of early menopause are similar to those when a woman enters it in her late 40s and early 50s.
Early Menopause Symptoms
Before a woman has her last period and is confirmed menopausal 12 months later, she will likely experience a range of menopause symptoms. This menopause-preceding stage is called perimenopause and varies in duration from woman to woman.
During that period, one of the first symptoms women notice are irregular periods. Others may include the following:
Early Menopause Signs
Physical and psychological early menopause symptoms are generally sufficient to confirm a woman's entry into the stage. However, a doctor may run a variety of tests, results of which will produce menopause signs to complete the diagnosis.
Most commonly analyzed signs of menopause include the following:
- Abnormal hormone levels, such as estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Amenorrhea, which is the absence of menstrual periods
Because thyroid disorders may cause similar symptoms, a doctor may also look at thyroid hormones to rule them out.
Early Menopause Risks & Consequences
The risks associated with early menopause mainly concern low estrogen levels since they will persist for a longer period of time than in women entering menopause at the typical age. They include the following:
Menopausal heart disease. Studies have linked younger age at menopause with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.4
Osteoporosis. Consistently low estrogen and progesterone levels may cause the bones to become less dense, making women more prone to fractures.5
Fertility loss. When it happens as a consequence of early menopause,it may be especially difficult for women who were trying to get pregnant as they will have to rely on in vitro fertilization(IVF) with donor eggs.
Early Menopause Treatments

Early menopause cannot be treated or reversed. The main focus of menopause treatment approaches is relieving symptoms and reducing the associated health risks.
Natural treatments for early menopause
Women are encouraged to implement a variety of wholesome practices that may help balance levels of fluctuating hormones and alleviate their effects on the body. They may consist of the following:
Healthy habits. They can include following a menopause diet with foods rich in calcium and phytoestrogens, plant compounds that help with hormonal imbalance, as well as regular menopause exercise, among others.
Complementary therapies. To help relieve stress and alleviate menopause symptoms, women may take advantage of the beneficial effects of acupuncture, massage therapy, and meditation.
Menopause supplements. Made with various herbs for menopause that help naturally relieve symptoms, they can include phytoestrogenic supplements, like black cohosh, or hormone-balancing supplements, like Macafem.
Medical treatments for early menopause
Depending on the type and severity of symptoms a woman experiences, she may be offered a variety of medications, including the following:
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is recommended to counteract the risks associated with early menopause. It is generally prescribed short-term until women reach the typical menopause age. It is worth keeping in mind that HRT should be used with caution due to the increased health risks associated with its long-term use.6
Other medications may be given depending on specific symptoms, including sleeping aids for sleep disorders, antidepressants for depression, and others.
Studies have shown that cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can effectively reduce menopause symptoms, both physical and emotional.7
Key Takeaways
Menopause usually surprises women even if it happens at the typical age. However, when it occurs early, it can wreak havoc on women's physical and emotional health, triggering hot flashes, mood swings, and other discomforts. Early menopause, defined as one that occurs between the ages of 40 to 45, can have a variety of causes, including family history, autoimmune diseases, and oophorectomy. Due to consistently low hormone levels, women who enter menopause early are at a higher risk of certain health complications, like heart disease or osteoporosis. To decrease those risks, they are usually recommended HRT until they reach the typical menopause age. However, HRT should be used short-term and cautiously to prevent serious side effects. Women can also ease their symptoms with a range of natural approaches, including diet, exercise, and herbal supplements.
Sources
- Cleveland Clinic. (2019). Premature and Early Menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21138-premature-and-early-menopause
- Health Direct. (2019). Menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/menopause
- Medline Plus. (2016). Menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://medlineplus.gov/menopause.html
- National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). Early Menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/early-menopause
- National Institute on Aging. (2017). Menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-menopause
- NHS. (2018). Menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/menopause/
- Office on Women's Health. (2018). Early or premature menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/menopause/early-or-premature-menopause
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/menopause
Footnotes:
- Menopause. (2014). The North American Menopause Society Recommendations for Clinical Care of Midlife Women. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from http://www.menopause.org/docs/default-source/2014/nams-recomm-for-clinical-care.pdf
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2020). The Menopause Years. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/the-menopause-years
- Better Health Channel. (2018). Premature and early menopause. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/premature-and-early-menopause
- The Lancet. (2019). Early menopause and risk of cardiovascular disease: an issue for your women. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpub/article/PIIS2468-2667(19)30184-7/fulltext
- Menopause. (2007). Effect of early menopause on bone mineral density and fractures. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17476146/
- The Lancet. (2019). Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(19)31709-X/fulltext
- Menopause. (2019). Cognitive behavior therapy for menopausal symptoms (CBT-Meno): a randomized controlled trial. Retrieved February 1, 2021 from https://journals.lww.com/menopausejournal/Abstract/2019/09000/Cognitive_behavior_therapy_for_menopausal_symptoms.6.aspx