What is a Miscarriage?
A miscarriage is a spontaneous fetal loss that occurs within the first 20 weeks of gestation, as opposed to a stillbirth that happens when a baby dies in utero after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Most miscarriages occur during the first trimester, or 13 weeks with 50 - 75% of pregnancy losses occurring shortly after implantation. As a result, many women may not even realize they were pregnant and experienced a miscarriage.
Some types of pregnancy complications, such as molar or ectopic pregnancies, also end in a miscarriage.
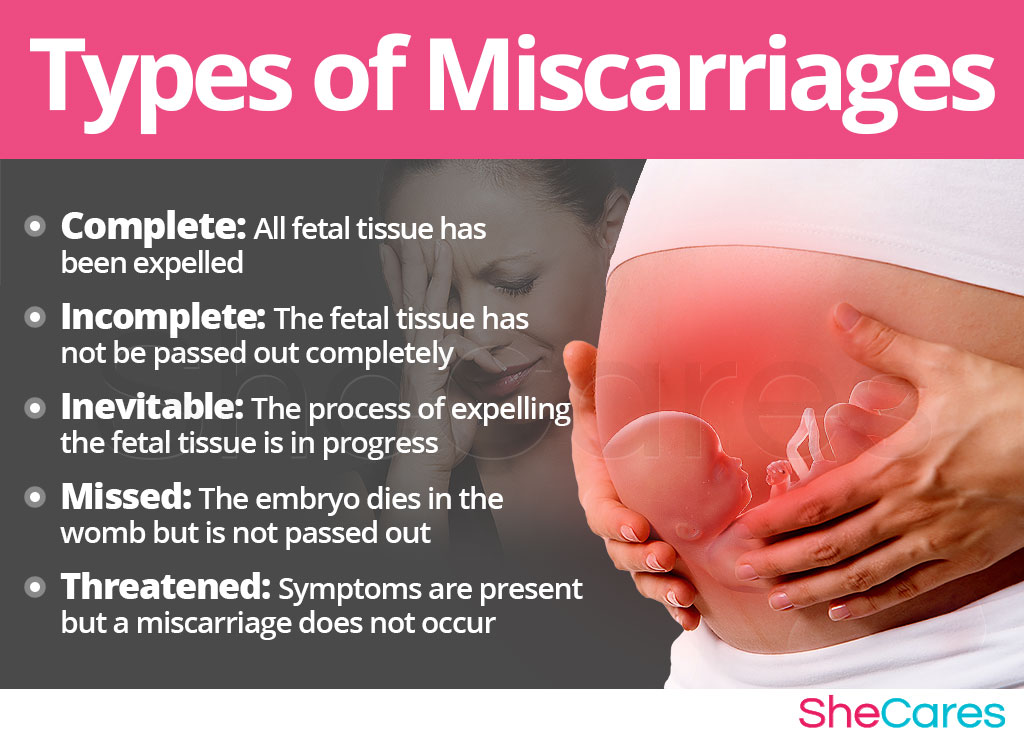
Types of Miscarriages
Although all types of pregnancy loss are simply referred to as a miscarriage, there are five distinguished types of a miscarriage, such as:
- Complete miscarriage occurs when all of the fetal tissue has been passed out of the body.
- Incomplete miscarriage occurs when most of the fetal tissue has been passed, but some remains in the uterus and must be removed surgically.
- Inevitable miscarriage occurs when the cervix is open and the process of expelling the fetal tissue has begun and cannot be stopped.
- Missed miscarriage (also called "silent" or "delayed") occurs when embryonic death has happened, but the embryo is not entirely expelled from the uterus. Sometimes, it can be passed naturally, while others it has to be removed surgically.
- Threatened miscarriage occurs when there is early uterine bleeding with abdominal pain, cramping, or lower backache, but the pregnancy continues since the cervix remains closed.
Causes and Risk Factors for Miscarriage
In the majority of cases, a miscarriage has no relationship to what a woman did or didn't do. Most pregnancy losses occur due to chromosomal abnormalities, preventing the fetus from developing normally.
Other possible causes and factors that might contribute to putting women at a greater risk for a miscarriage include:
Risk Factors for Miscarriage
- Hormonal imbalances and nutritional deficiencies
- Uncontrolled disorders, such as lupus, PCOS, thyroid disease, or diabetes as well as uterine or cervical problems
- Infections, including sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- Multiple pregnancies
- Pregnancy at age 35+
- Alcohol, smoking, or illicit drug use
- Abnormal maternal weight (underweight, eating disorders, or obesity)
- Invasive prenatal tests, such as amniocentesis
Contrary to common belief, having sexual intercourse during pregnancy does not cause a miscarriage.

Signs and Symptoms of Miscarriage
Women experience miscarriage symptoms of varying degrees, with some not displaying symptoms at all and discovering that their pregnancy ended during a routine ultrasound scan.
Symptoms of Miscarriage
Vaginal bleeding or spotting, including clots
Unusual vaginal discharge
Intense cramping that feels like a period
Pain in lower abdomen (dull ache to severe pain)
Signs of Miscarriage
Womb abnormalities
No heartbeat in a transvaginal ultrasound after 6 weeks
Presence of extra or missing chromosomes
High blood levels of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibody and lupus anticoagulant
It is important to note that bleeding or spotting in the pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, does not always signify a miscarriage.

Effects and Complications of Miscarriage
Effects on Fertility
Having a miscarriage generally does not diminish fertility. Within a few weeks, after at least one menstrual cycle, most women are cleared by their doctor to conceive again, if they wish to do so.
Effects on the Mom
The majority of women physically recover from a miscarriage in couple of weeks. In some cases, however, a miscarriage might lead to developing a hemorrhage or an infection, especially if the fetal tissue has not been completely expelled by the body.
Also, some women struggle with mental health issues, such as depression, stress, or anxiety disorders, after suffering from a miscarriage.
Complications of Miscarriage
If bleeding extends past 14 days or becomes very heavy, or if you are experiencing dizziness or one-sided pain in the abdomen, pelvis, or shoulder, seek immediate medical care as you might be suffering from potentially serious complications or an ectopic pregnancy.
Prevention of Miscarriage
Although miscarriages cannot be entirely prevented, replacing unhealthy and harmful practices with more wholesome habits can effectively reduce the likelihood of a miscarriage. They include:
Prenatal vitamins, such as folic acid or iron, taken before conceiving and during pregnancy have been found to decrease the risk of a miscarriage.
Balanced diet can resolve potential nutritional deficiencies that might be the underlying cause of miscarrying.
Hormone-regulating supplements, such as Macafem, might help you balance hormones and prepare for healthy conception.
Exercise can help you reach a healthy weight and prevent under- or overweight, both of which have been linked to causing pregnancy loss.
Addiction control before conceiving might decrease the risk of a miscarriage and protect your baby from developing certain birth defects.
Stress reduction through meditation or breathing exercises can successfully alleviate the negative symptoms of emotional turmoil and its effects on sustaining a pregnancy.

Treatment for Miscarriage
Treating a Miscarriage as it is Happening
Things to Remember
The bleeding lasts for seven to 10 days.Makesure you have your partner, relative, or a friend around you for support. You will also need high-absorbency sanitary pads and pain relievers to ease the pain.
If you notice any unusual symptoms, such as bleeding or cramps, contact your OBGYN right away or call for an ambulance. It does not always mean a miscarriage, but it should be evaluated.
When your doctor confirms that you are experiencing a miscarriage, his recommended treatment approach will depend on the stage of your pregnancy. They might include:
Resting at home. In most cases, a woman experiencing a miscarriage in early pregnancy is advised to rest at home and allow the body to expel the fetal tissue naturally.
Medications might be prescribed to cause the uterus to contract and expel the fetal tissue more quickly.
Dilation and curettage procedure (D&C) might be necessary in more advanced pregnancies to remove the remaining fetal tissue from the uterus and prevent complications.
Managing the After Care
Most women recuperate physically within a few days to a few weeks, and their menstruation restarts in a month or two following a miscarriage.
However, some women need more time to recover psychologically. Every woman goes through pregnancy loss differently and having various - often conflicting- emotions is a part of the natural coping process. Remember that help is readily available through your doctor, local therapists, or numerous support groups that assist women with similar experiences to get through this tough time.

Key Takeaways
Although often heart-breaking and difficult to accept, miscarriages are a natural part of our reproductive life. In a great majority of cases, pregnancy loss is a one-time event in a woman's life, and it does not inhibit her fertility. With time, you and your partner might feel ready to welcome the thought of getting pregnant after a miscarriage. With wholesome lifestyle practices to maintain nutritional and hormonal balance, you can prepare yourself for conceiving and giving birth to healthy children.
Sources
- American Journal of Epidemiology. (2014). Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Miscarriage and Maternal Exposure to Tobacco Smoke During Pregnancy. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3969532/
- American Pregnancy Association. (n.d.). Miscarriage. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from http://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-complications/miscarriage/
- American Psychological Association. (2012). Miscarriage and loss. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from http://www.apa.org/monitor/2012/06/miscarriage.aspx
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. (2016). Vitamin supplementation for preventing miscarriage. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0012521/
- Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism. (2013). Luteal insufficiency in first trimester. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3659905/
- Miscarriage Association. (n.d.). Pain, bleeding or spotting. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from http://www.miscarriageassociation.org.uk/information/signs-and-symptoms/pain-bleeding-or-spotting/
- NHS. (2018). Miscarriage. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Miscarriage/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- Pregnancy, Birth & Baby. (n.d.). Miscarriage. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from http://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/miscarriage
- The Royal Women's Hospital. (2018). Treating miscarriage. Retrieved February 5, 2018 from https://www.thewomens.org.au/health-information/pregnancy-and-birth/pregnancy-problems/early-pregnancy-problems/treating-miscarriage/
