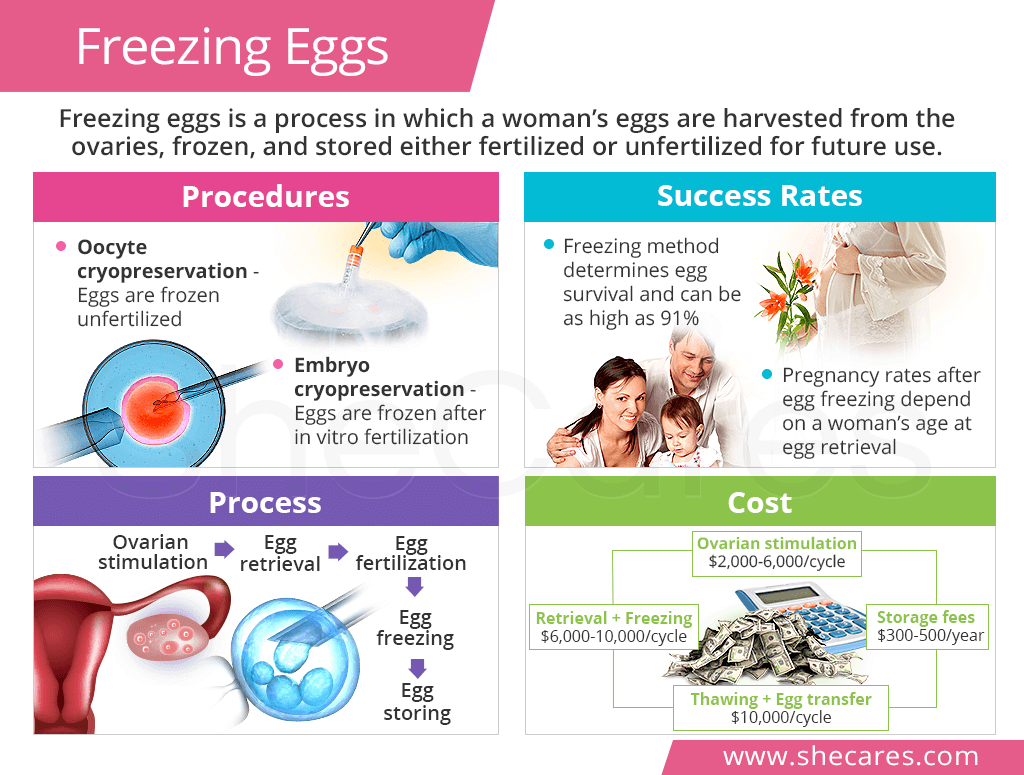
Types of Egg Freezing Procedures
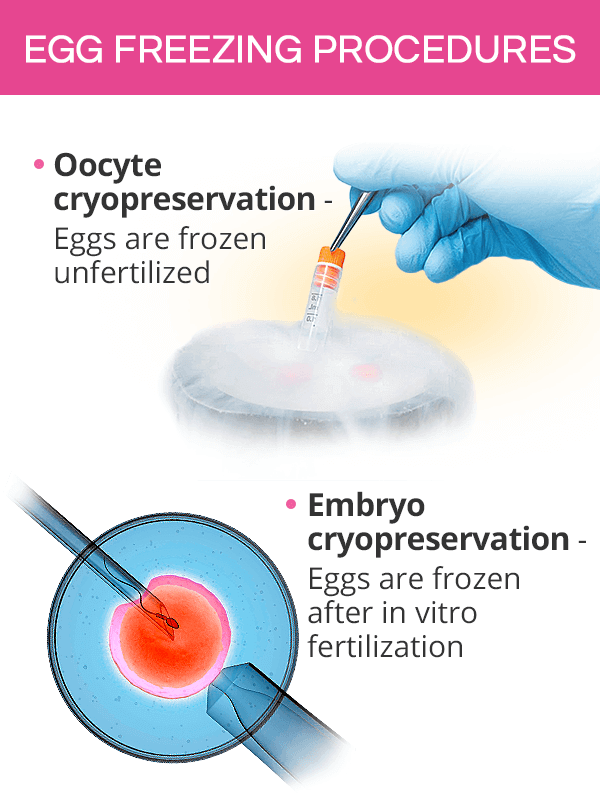
A woman's eggs can be frozen in two forms, unfertilized and fertilized:
Oocyte Cryopreservation. In this type of procedure, the eggs (oocytes) are frozen without being fertilized in vitro.
Embryo Cryopreservation. This egg freezing procedure involves freezing eggs that have been fertilized in the laboratory. Fertilized eggs are referred to as embryos.
Freezing Methods
Regardless of whether the eggs are frozen fertilized, the freezing technique itself can be of two types:
Slow freezing method consists of gradually decreasing the eggs' temperature over several hours until it reaches the storage temperature, namely -320ºF (-196ºC), at which all cell processes are stopped.
Vitrification method, also called flash freezing, involves quickly submerging the eggs in liquid nitrogen, which freezes them instantly. This method takes several minutes.
Steps in Egg Freezing Process
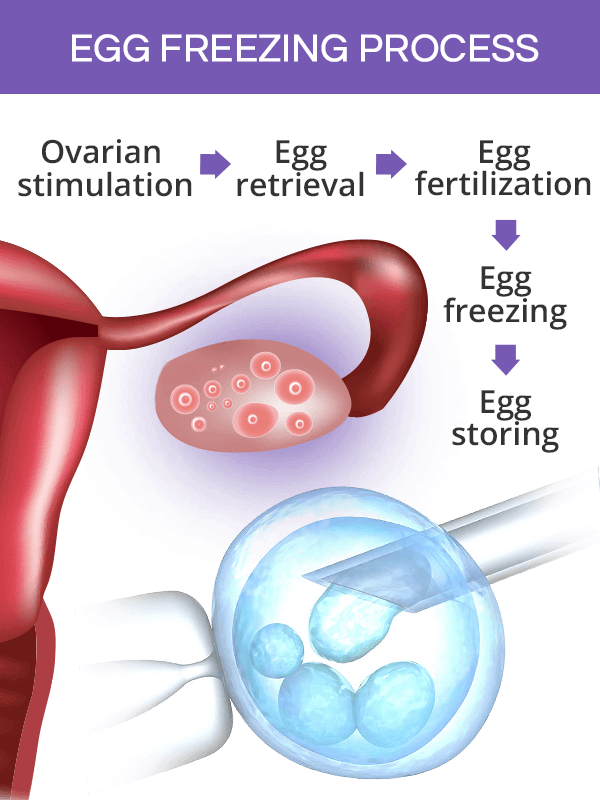
The egg freezing process resembles the standard course of in vitro fertilization (IVF), with the exception that the eggs are frozen half-way through the process, instead of being fertilized fresh and transferred back to the uterus as it normally happens with IVF.
The oocyte and embryo cryopreservation procedures follow almost the same steps. The only point where they differ is the egg fertilization, which only occurs in embryo cryopreservation. The whole process takes about 10-14 days.
Ovarian Stimulation. Normally, there are about 1,000 eggs maturing in the ovaries in every menstrual cycle, but only one matures enough to be released on ovulation. In order to obtain several mature eggs that will be harvested for freezing, a woman has to undergo hormone therapy. The hormone injections are usually self-administered for eight to 11 days, and their effects are monitored almost daily by a doctor.
Egg Retrieval. Once eggs are mature, they can be retrieved. Egg harvesting is performed by inserting a needle through the vaginal wall and gently sucking the eggs out of the ovaries into test tubes. The procedure is performed under sedation and takes about 15 minutes. Once retrieved, the eggs are prepared for either fertilization or freezing, depending on a patient's wish. About 80% of retrieved eggs are viable to continue to the next steps.
Egg Fertilization. The process of fertilizing the eggs before they are frozen follows the same steps as in vitro fertilization (IVF). Sperm can be provided by a woman's partner or an anonymous donor. In vitro fertilization is typically done through a technique called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), which has the highest success rates.
Egg Freezing. Fertilized or unfertilized eggs are then frozen with one of two methods, slow freezing or vitrification. To date, the longest recorded period of time for which a woman has frozen her eggs is 14 years.
Egg Storing. Once properly frozen, preserved eggs can remain stored for years until a woman decides she wants to get pregnant. The length of time the eggs remain frozen have shown not to affect their quality and pregnancy rates.
Once a woman has decided she wants to get pregnant, the eggs have to go through a thawing process. She once again treated with hormones to prepare the uterus so that it can support the embryo. If eggs were frozen unfertilized, they are fertilized with sperm at this point and then transferred to the uterus.
Egg Retrieval Side Effects
Generally, the retrieval step of egg freezing has not been associated with major complications. It is a minimally-invasive procedure, which has not been associated with major complications. Some women experience mild, period-like cramping for several days after the procedure.
In rare cases, however, the ovarian stimulation might lead to a complication called ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). It happens when ovaries are overstimulated, leading to swelling, enlargement, and fluid accumulation in the abdomen. Most cases of OHSS resolve without the need forintervention, while some require surgery.
Egg Freezing Success Rates

The effectiveness of egg or embryo freezing is not only determined based on whether the eggs have survived the freezing and thawing processes, but also whether they were viable to progress into pregnancies.
Egg Survival Rates after Freezing
The chance of the survival of eggs after freezing and thawing depends on the freezing method used.
Slow freezing method isthe initial technique used since the mid-80s. It has a 55-61% survival rate, which is significantly lower in comparison to the alternative technique due to an increased likelihood of ice crystal formation, which can damage the eggs.
Vitrification method is a newer method with about a 91% survival rate. This freezing technique reduced the risks of the formation of ice crystals, increasing eggs' viability.
Pregnancy Rates after Egg Freezing
Egg freezing success rates in terms of future pregnancy mainly depend on a woman's age at the time of egg retrieval. Generally, the younger the woman is at the time of egg freezing, the higher chances of success.
This association with a woman's egg is related to her ovarian reserve, which is the number and quality of eggs in the ovaries. Because ovarian reserve gradually declines as a woman ages, and DNA abnormalities accumulated over time can compromise conception efforts, women are encouraged to freeze their eggs before turning 35, which is when their ovarian supplies are abundant in good quality eggs.
Despite this recommendation, there is no egg freezing age limit. Freezing eggs at 40 or older is still possible, but it is important to remember that at that age, the majority of eggs have DNA changes, which is why the rates of miscarriage and birth defects are higher. As a result, women over 40 looking into freezing eggs or embryos might require several retrieval cycles to achieve conception.
Freezing Eggs Cost
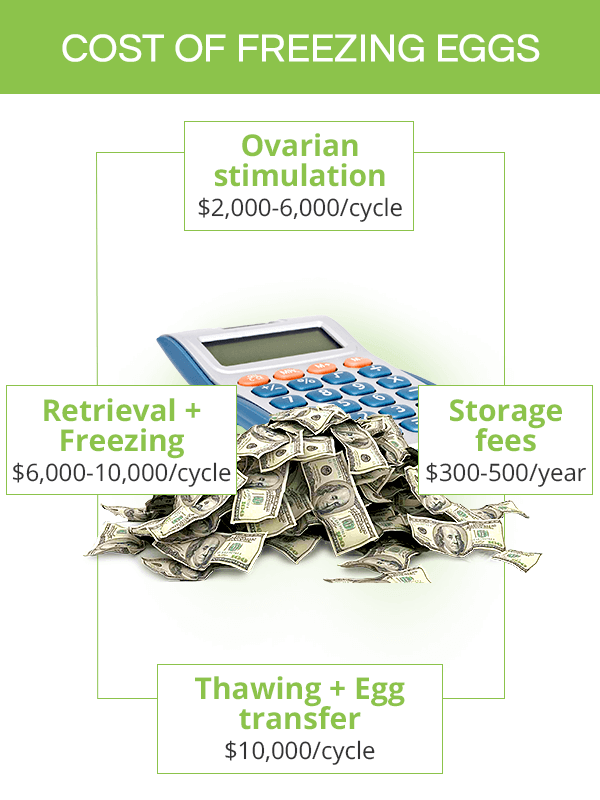
Oocyte and embryo cryopreservation are expensive, and they are generally not covered by health insurance carriers. If they are performed in women who are undergoing radiation or chemotherapy for cancer or other health conditions, they might be partially reimbursed by the insurance companies.
When calculating the out-of-pocket cost of the egg freezing process, several components have to be taken into account.
Medications used for ovulation stimulation can cost between $2,000 up to $6,000 per cycle.
Egg retrieval and freezing processes, including optional fertilization, typically range between $6,000 - 10,000 per cycle.
Egg storage fees might range from $300 to $500 annually.
In sum, an average cost to freeze eggs can fall between $8,000 and $16,000 per cycle. However, it is important to remember that once pregnancy is desired, they have to be thawed, fertilized (if frozen unfertilized), and then transferred to the uterus. The cost of these procedures can easily exceed $10,000.
Key Takeaways
Egg freezing is increasingly popular among women who want to delay getting pregnant for later due to their health status or personal choice. It allows them to prevent the age-related fertility decline from affecting their chances of motherhood. A woman's eggs can be frozen in two forms, either unfertilized (oocyte cryopreservation) or fertilized (embryo cryopreservation), and the steps before and after freezing resemble those involved with in vitro fertilization (IVF). Egg and embryo freezing have the highest rates of success of all fertility preservation methods. Accordingly, they also come with the highest financial costs.
Sources
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2014). Oocyte Cryopreservation. Retrieved November 6, 2018 from https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Committee-Opinions/Committee-on-Gynecologic-Practice/Oocyte-Cryopreservation
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Embryo Cryopreservation. Retrieved November 6, 2018 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/15464-embryo-cryopreservation
- Human Reproduction Update. (2016). Oocyte cryopreservation: where are we now? Retrieved November 6, 2018 from https://academic.oup.com/humupd/article/22/4/440/2573626
- Mayo Clinic. (2017). Egg Freezing. Retrieved November 6, 2018 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/egg-freezing/about/pac-20384556
- Northwestern University. (2013). Chance of Pregnancy after Oocyte Cryopreservation. Retrieved November 6, 2018 from http://oncofertility.northwestern.edu/resources/chance-pregnancy-after-oocyte-cryopreservation
- University of California. (n.d.). Egg Freezing. Retrieved November 6, 2018 from http://obgyn.ucla.edu/egg-freezing