Women can find natural estrogen in foods and supplements, which may help them correct hormonal imbalances without having to worry about health risks involved with pharmaceutical options.
Continue reading to learn more about estrogen foods and supplements and how they can help restore estrogen balance naturally.
Natural Sources of Estrogen
Natural sources of estrogen consist of foods and supplements rich in phytoestrogens.
What are phytoestrogens?
Phytoestrogens are substances found in plants that have estrogenic activity in animals. They are similar to endogenous estrogens and are distinguished by their capacity to prompt specific responses from estrogen-sensitive glands and receptors.
How do phytoestrogens compare to normal estrogens?
Phytoestrogens' chemical structure closely resembles that of endogenous estrogens. However, because they have lower estrogenic activity, from 1/400 to 1/1,000 the strength of natural estrogen, they behave like weak, natural estrogens in cell receptor sites.
How do phytoestrogens react in the body?
Phytoestrogens' effectiveness depends on many factors, including the amount of estrogen produced by the body, saturation of estrogen receptor sites, and a woman's age. When estrogen levels are low, phytoestrogens help raise them by occupying empty receptor sites. Inversely, when estrogen levels are high, phytoestrogens attach themselves to estrogen receptor sites to block endogenous estrogen from entering the cells.
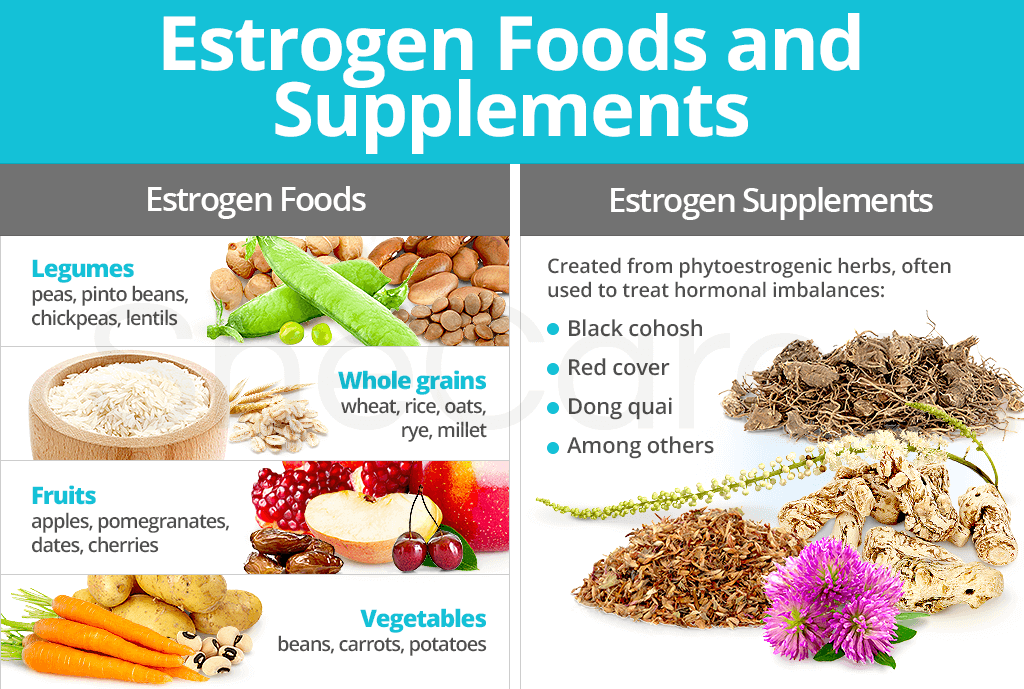
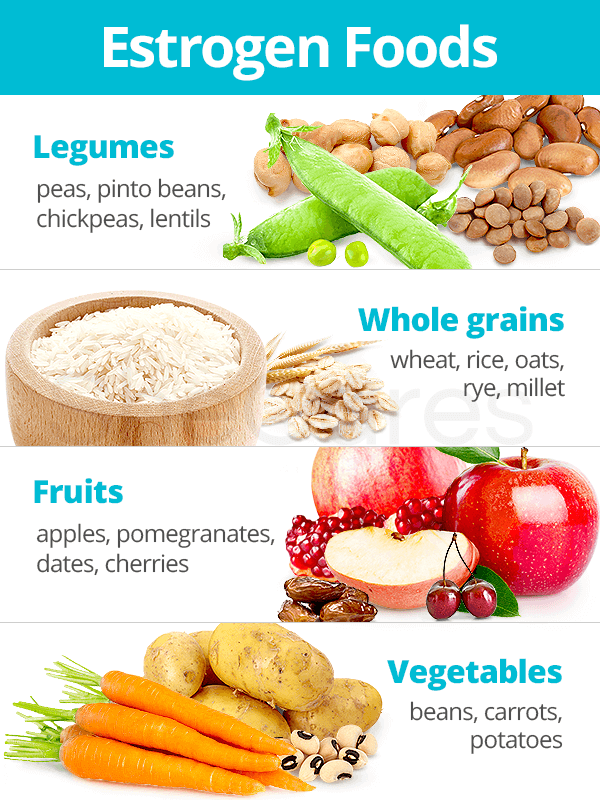
Estrogen Foods
The two most studied phytoestrogen groups in foods are lignans and isoflavones. Lignans are products of intestinal microbial breakdown of compounds found in whole grains, flaxseed, and many fruits and vegetables. On the other hand, isoflavones, such as genistein and daidzein, are present in soybeans and other legumes.
As aforementioned, since these phytoestrogens are similar in chemical composition to endogenous estrogens, they balance levels in the body by increasing low levels or decreasing high levels. Studies have shown that the following estrogen foods are among those with the most potent hormone-like effects:
- Legumes: peas, pinto beans, chickpeas, lentils
- Whole grains: wheat, rice, oats, rye, millet
- Fruits: apples, pomegranates, dates, cherries
- Vegetables: beans, carrots, potatoes
- Seeds: flaxseed, sesame seeds
- Alfalfa sprouts
- Clover
- Among others
Soy - the best estrogen food
Research indicates that soy contains the most potent isoflavones. Because of their structural similarity to estradiol, soy isoflavones have estrogenic and anti-estrogenic effects by mimicking the effects of estrogen in some tissues and blocking the effects of estrogen in others. Both serve as beneficial behaviors.
Studies indicate that consuming higher intakes of soy foods early in life may decrease the risk of breast cancer later. At the same time, isoflavones could also build up estrogen levels to help maintain bone mineral density. The most potent soy isoflavone content is found in soy protein, miso, soybeans, tempeh, soy milk, and tofu.
Estrogen diet
Women often choose to start consuming an estrogen diet for its benefit of being able to relieve symptoms of hormonal abnormalities, such as hot flashes, vaginal dryness, mood swings, night sweats, and more.
Keep in mind that phytoestrogen absorption depends on many factors, including the amount of time the food takes to pass through the intestines, one's gut bacteria, chemicals in the food product, etc. As with any change in diet, moderation is key.
Estrogen Supplements

Phytoestrogens occur in medicinal herbs and spices as well. The following are examples of some herbs high in phytoestrogens that are commonly used as supplements:
- Black cohosh
- Red clover
- Dong quai
- Evening primrose
- Ginkgo
- Ginseng
- Licorice
- Garlic
- Parsley
Also, there are non-estrogenic supplements, such as Macafem, that support natural estrogen production and increase levels by stimulating the endocrine glands to, thus, promote hormonal balance. They do not contain phytoestrogens nor exogenous hormones.
Women find that it may take a few months until they start experiencing benefits from a natural estrogen diet consisting of estrogen foods or supplements. Keep in mind that compromising time for the diet's overall effectiveness can be less of a burden compared to possible long-term financial and health risks associated with estrogen medications and products like HRT.
All in all, phytoestrogens found in a variety of foods and supplements can be easily implemented into one's plan to improve hormonal balance. Continue reading to find out more about how to increase estrogen levels through other lifestyle changes, alternative medicines, and more.
Sources
- Liew, L. (2003). The Natural Estrogen Diet and Recipe Books: Delicious Recipes for a Healthy Lifestyle. California: Hunter House Publishers. Available from Google Books.
- Murray, M.T. et al. (2010). The Encyclopedia of Healing Foods. New York: Atria Books. Available from Google Books.
- National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). NCI Drug Dictionary: soy isoflavones. Retrieved July 19, 2017, from https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-drug?cdrid=466602
- National Woman's Health Network. (n.d.). Herbs and Phytoestrogens. Retrieved July 12, 2017, from https://www.nwhn.org/herbs-and-phytoestrogens/
- Oregon State University. (2016). Soy Isoflavones. Retrieved July 19, 2017, from http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/phytochemicals/soy-isoflavones
- Rigden, S. & Schiltz, B. (2009). The Ultimate Metabolism Diet: Eat Right for Your Metabolic Type. California: Hunter House Publishers. Available from Google Books.
- Tulane University. (2014). Phytoestrogens. Retrieved July 19, 2017, from http://e.hormone.tulane.edu/learning/phytoestrogens.html
- Watson, R.R. (Ed.). (2003). Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals in Cancer Prevention. Iowa: Iowa State Press. Available from Google Books.