Hormones, which are chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands, travel through the body's fluids and regulate the function of tissues in the body. Essentially, these "chemical messengers" affect growth and behavior. In women, two key hormones - estrogen and testosterone - are involved in the growth, maintenance, and repair of reproductive organs and other tissues. Read on to learn about estrogen versus testosterone and the effects of these hormones on your health.
Estrogen: What Is it?
Comprised of three main compounds - estrone, estradiol, and estriol - estrogen is essential to maintain female development and reproduction. Normally found in higher amounts in women, estrogen helps in the maturity of secondary sex characteristics. These characteristics include increased fat in the buttocks, hips, and thigh, enlargement of the breasts, and widening of the pelvis.
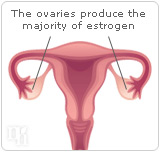
Estrogen also plays an essential role in the reproductive process by helping to regulate the menstrual cycle and to enrich and thicken the endometrium to prepare the uterus for pregnancy. In women who ovulate, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and lutenizing hormone (LH) also help regulate the levels of estrogen production. Although the ovaries produce the majority of estrogen, the breasts, liver, and adrenal glands also produce estrogen in smaller quantities.
During menopause, estrogen levels decline. As a result, many women begin to experience familiar symptoms such as mood swings, hot flashes, memory problems, fatigue, and decreased bone density. Despite being controversial, estrogen replacement therapy is widely used to help combat the effects of menopause.
Testosterone: A Female Hormone?
Not just a male hormone, testosterone helps increase sex drive and muscle mass, and it also contributes to the general well-being of the female body. [http://www.natural-hormones.net/pics/estrogen-versus-testosterone-2.jpg*|*Osteoporosis]
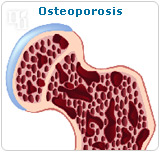
During menopause, testosterone levels decrease, leading to weakened bones, muscle tone loss, and reduced libido. For women suffering from osteoporosis, doctors may prescribe testosterone therapy as an alternative to help boost physical fitness and increase body strength. For women with breast or uterine cancer, testosterone therapy is not recommended since it may increase the risk of cardiovascular or liver disease.
Estrogen and Testosterone: Working in Tandem
Often, testosterone and estrogen work together. Testosterone works to aid estrogen by converting into estradiol and boosting the effects of estrogen. This produces a cascade effect and helps to relieve hot flashes, improve libido, and ward off fatigue. Specifically during treatment for hot flashes, it has been shown that estrogen levels can be increased if testosterone is added, confirming an additive effect of estrogen with testosterone.
Click here to learn more about hormones and menopause.


