All the best things in life have a complement, and the female endocrine system is no different. Two female hormones - estrogen and progesterone - work in harmony to influence almost every cell, organ, and function in the human body. But how exactly do these two hormones differ? Read on to find out.
In the Spotlight: Estrogen
Estrogen is probably the most-well known hormone in the female body. It is a compound hormone produced in the ovaries and is comprised of the hormones estrone, estradiol, and estriol. These hormones send messages that travel through the bloodstream and regulate or "command" many bodily processes.
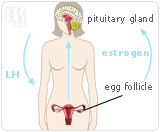
One of estrogen's most important roles is to help regulate the menstrual cycle. During the first days of the cycle, estrogen is produced in the egg follicle and secreted into the bloodstream. Then it travels to the pituitary gland and sends a message to the female body to begin ovulation by producing the luteinizing hormone (LH), which is responsible for releasing the egg. From there, the hormone progesterone takes over.
No Small Part: Progesterone
Progesterone is a steroid hormone (derived from cholesterol) produced and secreted from the ovaries and adrenal grand. Progesterone gives its performance in the second act of the menstrual cycle, when it is secreted at high levels to help thicken the lining of the uterus and prepare the body for a fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, progesterone levels drop drastically. The uterine lining sheds, causing a woman to begin menstruation. Read on to learn more about the important roles of estrogen and progesterone in the female body.
It Takes Two

Estrogen and progesterone do more than just prepare a woman's body for pregnancy or menstruation. In fact, they play supporting roles in almost every one of the body's processes, from mood and memory to bone health, body temperature, and vaginal moisture. Thus, when a woman's body begins to slow production of these essential hormones during menopause, she often experiences a range of uncomfortable physical and emotional symptoms, from hot flashes and night sweats to vaginal dryness, mood swings, and loss of libido.
In order to curb these symptoms and prevent the onset of postmenopausal threats like osteoporosis, a woman must take steps to ensure that her hormone levels - particularly estrogen and progesterone - are properly balanced. A variety of treatment options are available for hormone imbalance and include making simple lifestyle changes, taking herbal supplements, or using prescription medications.