Women who are searching for ways to restore healthy progesterone levels have a variety of options available. Each progesterone treatment involves an extensive list of benefits and side effects as well as instructions for use.
Discover more about one of the most ubiquitous options available, progesterone pills, including what they are; how, when, and why they are used; and their side effects; to be one step closer to a healthy, happy you.
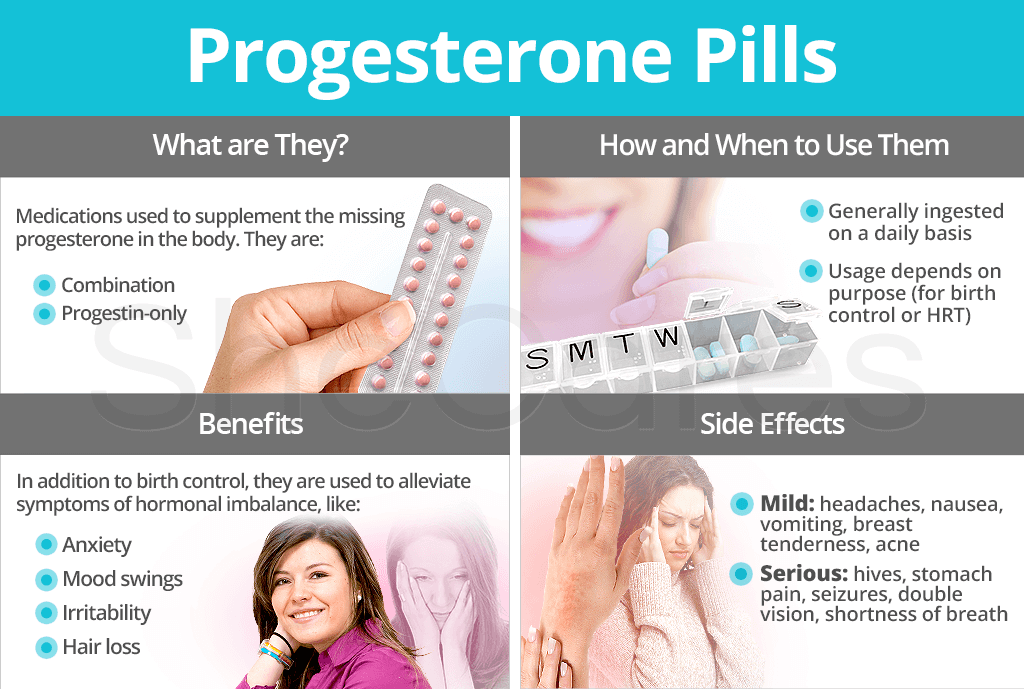
What are Progesterone Pills?

Progesterone pills - also known as progesterone tablets - are drugs used to supplement the amount of natural progesterone produced in a woman's body. There are two kinds.
Combination pills. Combination pills are progesterone tablets composed of estrogen and progestin, a synthetic form of progesterone.
Progestin-only pills. The progestin-only pill, also referred to as the progestogen-only pill (POP) or “mini pill,” does not contain estrogen. It is often prescribed to women who have adverse side effects from the combination pill or have health issues restricting them from taking supplemental estrogen.
What do Progesterone Pills Do?
Combination pills and progestin-only pills are generally used as oral contraceptives. They help thicken cervical mucus to stop sperm from reaching the egg and can also stop ovulation.
Moreover, there are non-contraceptive uses of both pills. Certain brands are used to treat symptoms of hormonal imbalances, such as premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), premenstrual syndrome (PMS), and the menopausal transition.
Benefits of Progesterone Pills
Additionally to being a good birth control measure, progesterone pills are often used to alleviate the following symptoms associated with hormonal disorders:

- Depression
- Anxiety
- Mood swings
- Irritability
- Hair loss
- Difficulty concentrating
- Bloating
- Excessive hair (or hirsutism)
- Acne
- Breast tenderness
- Insomnia
- Food cravings
- Decreased energy levels
- And many more
Also, progesterone pills are used to reduce the risk of developing certain diseases before and after hormone replacement therapy (HRT), such as cancers of the uterus, breasts, and endometrium. They are often prescribed to treat endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and other hormonal disruptions.
How and When to Use Progesterone Pills
How Do I Take Progesterone Pills?
Generally, progesterone tablets are ingested orally on a daily basis. Women's medication regimens vary and depend upon various factors, such as length of the treatment and strength of the progesterone tablet.
When Do I Use Progesterone Pills?
For women who use progesterone pills as birth control, they are prescribed for daily use and should be taken at the same time each day to remain effective. Generally, when a woman finishes a packet, she should begin the next pack the following day.
For women who use progesterone tablets for HRT, the pills are often taken on a rotating schedule that alternates 10 to 12 days on and 16 to 18 days off.
Progesterone Pills Side Effects

Some minor progesterone pill side effects include headaches, nausea, spotty skin, vomiting, breast tenderness, acne, and mood swings. Even so, progestin-only pills are generally well-tolerated, and side effects mostly occur during the first few months of consumption.
For specific use, the progestin-only pill is safe to use when breastfeeding. However, it should not be used without proper clearance from a doctor in women with a history of heart disease, stroke, breast cancer, or liver disease and tumors.
Serious side effects are uncommon, but they might include hives, stomach pain, seizures, bulging eyes, double vision, coughing up blood, fast heartbeat, shortness of breath, severe dizziness, ovarian cysts, depression, numbness of extremities, and more.
Where Do I Buy Progesterone Pills?
Micronized progesterone pills can only be acquired with a doctor's prescription. The standard doses are generally progesterone 300 mg, progesterone 200 mg, or progesterone 100 mg.1 The dosage will depend upon each woman's purpose for taking the hormone.
Key Takeaways
In sum, progesterone pills can be used to supplement missing progesterone in a woman's body. By doing so, consumption of progesterone tablets helps treat hormonal disorders and their symptoms while also allaying the possible onset of estrogen dominance. The pill is generally consumed on a daily or rotational basis. Minor side effects of oral progesterone may evolve, although it is generally well tolerated. Progesterone pills can be attained with a doctor's prescription.
Even though pharmaceutical treatments may bring quick results, they are not always the most beneficial choice for overall well-being. Learn more about natural progesterone supplements before electing the path favoring the use of synthetic hormones.
Sources
- Cleveland Clinic. (2017). Hormone Therapy. Retrieved November 11, 2019, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/15245-hormone-therapy
- Harvard Health Publishing: Harvard Medical School. (2009). Treating premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Retrieved November 11, 2019, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/treating-premenstrual-dysphoric-disorder
- Mayo Clinic. (2017). Progestin (Oral Route, Parenteral Route, Vaginal Route). Retrieved November 11, 2019, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/progestin-oral-route-parenteral-route-vaginal-route/proper-use/drg-20069443
- NHS. (2018). The progestogen-only pill. Retrieved November 11, 2019, from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/the-pill-progestogen-only/
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2017). Progesterone | Estrogen and Progestin (Oral Contraceptives). Retrieved November 11, 2019, from https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a604017.html | https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a601050.html
Footnotes:
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2018). PROGESTERONE - progesterone capsule. Retrieved November 18, 2019, from https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=efded380-02ff-68c9-13e4-47a561ede440&type=display