When a progesterone imbalance occurs, a plethora of signs and symptoms ensue, negatively affecting a woman's well-being. Before a more serious progesterone deficiency occurs, there are various treatment options that increase progesterone women can choose to pursue.
Continue reading to learn more about how to alleviate a hormonal imbalance by increasing progesterone levels naturally and pharmaceutically.
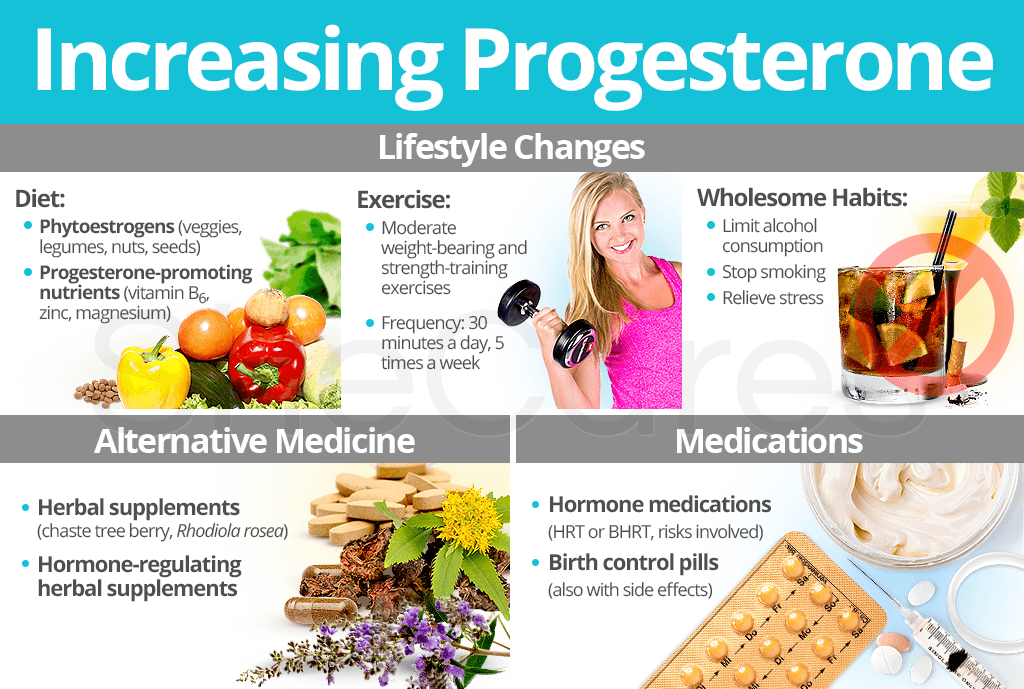
Lifestyle Changes to Increase Progesterone

Lifestyle changes can greatly improve endocrine system functions, especially in regards to increasing progesterone. When proper initiative is taken, a variety of positive effects in the body will begin to take place for months to come, not solely in regard to hormones.
Diet
The best diet plan to increase progesterone levels naturally is to consume a colorful mix of whole foods in balanced amounts. Although there is no set plan that will mutually benefit every woman, it is worth keeping the following tips in mind.
- Foods with phytoestrogens. Phytoestrogens are weaker, plant-based estrogens that compete with stronger estrogens that attach to body receptors. By consuming them, women may potentially resolve a state of estrogen dominance to ultimately help stabilize progesterone levels. Phytoestrogenic foods consist of:
- Foods with progesterone-promoting nutrients. Several vitamins and minerals are noted for helping maintain healthy progesterone levels or improving the health of the corpus luteum, a temporary structure created after ovulation that produces mass amounts of progesterone:
- Foods that inhibit estrogen production. Some foods are acclaimed for inhibiting estrogen production, thus increasing progesterone levels naturally. They include various fruits - such as melons, pineapples, figs, and grapes - as well as several vegetables, like green beans, corn, and broccoli.
- Non-inflammatory foods. Reducing the consumption of inflammatory foods such as sugar, wheat, and cow's milk will help increase progesterone naturally by lessening inflammation, which impedes ovulation. Non-inflammatory foods also assist in improving the functioning of hormone receptors for progesterone and GABA, the calming neurotransmitter.
Exercise
Women attempting to increase progesterone levels with exercise should do so in moderation. Prolonged and high intensity exercises have an adverse effect on female reproductive hormones by possibly leading to luteal phase deficiency, anovulation, or secondary amenorrhea.
To naturally increase progesterone levels, choose moderate, weight-bearing and strength-training exercises at least 30 minutes a day, five times a week to sustain an ideal body weight and fat percentage of at least 17 percent. Hiking, dancing, jogging, and running are all viable options.
Wholesome habits
Maintaining healthy habits is also important to be able to increase progesterone levels naturally.
- Limit alcohol consumption. Research studies commonly show that extreme consumption of alcohol increases levels of estrogen. Also, moderate consumption has been linked to decreased progesterone levels in pre-menopausal women.1
- Stop smoking. Perimenopausal women who smoke have lower progesterone levels than do nonsmokers. Moreover, smoking seems to increase androgen and adrenal hormone levels - such as cortisol - in the process, worsening symptoms of hormonal imbalance.2,3
- Relieve stress. During periods of chronic stress, progesterone is converted into cortisol, which can lead to a progesterone deficiency, thus translating into worsened PMS symptoms and menstrual problems. Yoga, tai chi, deep breathing techniques, or a favorite hobby can all promote relaxation.
All of these lifestyle changes may have a positive outcome on balancing hormones holistically by giving the body a healthy boost. However, they do not directly increase progesterone levels.
Alternative Medicine to Increase Progesterone

Using alternative approaches involves little to no risk and can be an extremely effective way in treating hormonal imbalances. Two of the most common alternative medicines are:
Herbal supplements
There are various herbal supplements that help aid in the formation of the corpus luteum as well as the overall production of progesterone.
For example, chaste tree berry inhibits the pituitary hormone prolactin, thereby enhancing ovulation and progesterone production. Also, Rhodiola rosea regulates cortisol and prevents the unwanted conversion of progesterone to cortisol during stressful situations.
Hormone-regulating herbal supplements
These supplements, including Macafem, stimulate the body's natural hormone production by nourishing the endocrine glands, helping the body produce its own hormones more efficiently.
They can be considered one of the safest natural ways to treat underlying hormonal imbalances and can be taken throughout a woman's life as they support endogenous hormone production.
Read about natural progesterone treatments to learn more about supplements and products used to combat low progesterone symptoms naturally to resolve the underlying imbalance.
Medications to Increase Progesterone
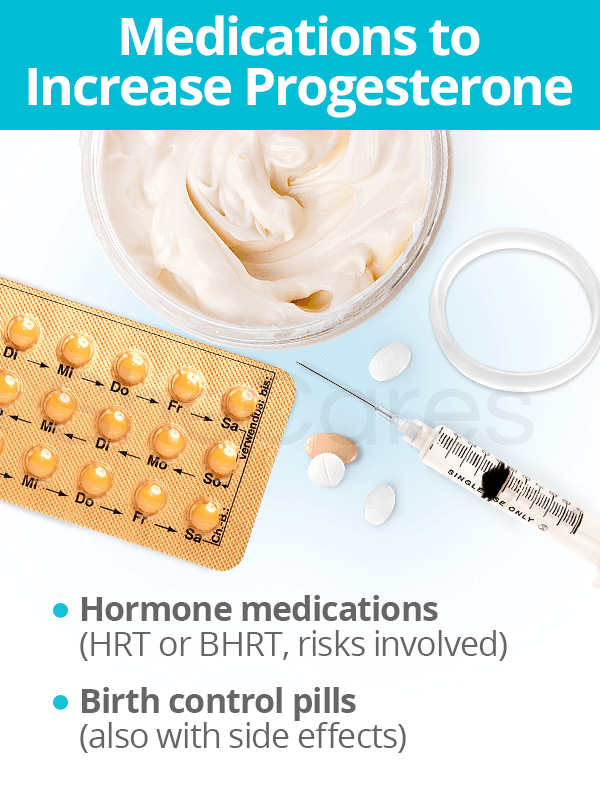
Interventions involving medical treatments often involve the highest risk at the highest costs. Most common therapies to increase progesterone levels include:
Conventional hormone medications
Women in the menopausal transition will sometimes take hormone replacement therapy (HRT), even knowing the risks involved. They may also opt for bioidentical hormone therapy, or “natural hormone therapy,” in which plant chemicals are made into molecularly-identical, endogenous progesterone.
Although bioidentical hormone therapy is considered safer than HRT, more research is needed to further understand its risks and benefits.
Birth control pills
Other prescription medications, such as birth control pills, can help progesterone increase in the body and ultimately regulate hormones. Just like HRT, birth control pills carry certain side effects, which sometimes may not arise until after discontinuing use.
For more extensive information on increasing progesterone levels or combatting progesterone symptoms with pharmaceutical options, read more about progesterone medications.
Sources
- Briden, L. (2015). Period Repair Manual: Natural Treatments for Better Hormones and Better Periods. Publisher: Author.
- Colbert, D. (2008). Stress Less. Florida: Siloam. Available from Google Books.
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2006). What are bioidentical hormones? Retrieved September 30, 2019, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/what-are-bioidentical-hormones
- Meraglia, T. (2015). The Hormone Secret. New York: Atria Paperback. Available from Google Books.
- National Institutes of Health. (2018). Exercise for Your Bone Health. Retrieved September 30, 2019, from https://www.bones.nih.gov/health-info/bone/bone-health/exercise/exercise-your-bone-health
- Nyberg, S. et al. (2005). The effect of a low dose of alcohol on allopregnanolone serum concentrations across the menstrual cycle in women with severe premenstrual syndrome and controls. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 30(9), 892-901. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2005.04.016
- Warren, M. (1999). Health Issues for Women Athletes: Exercise- Induced Amenorrhea. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 84(6), 1892-1896. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.6.5806
Footnotes:
- Gill, J. (2000). The Effects of Moderate Alcohol Consumption on Female Hormone Levels and Reproductive Function. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 35(5), 417-423. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/35.5.417
- Natural University of Natural Medicine. (n.d.). Cigarettes Can Sabotage Hormone Balance. Retrieved September 30, 2019, from https://womeninbalance.org/2012/10/26/cigarettes-can-sabotage-hormone-balance/
- Kapoor, D. & Jones, T.H. (2005). Smoking and hormones in health and endocrine disorders. European Journal of Endocrinology, 152(4), 491-499. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.01867