Much is known about the benefits of estrogen production during menopause, but little is known about the effects of its “sidekick”- progesterone. This hormone is vital to the female human body for regulation of ovulation and menstruation. But how does progesterone affect menopause? Read on to find out about the effects of progesterone.
What Is Progesterone?
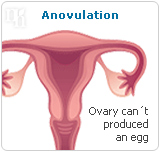
Progesterone is a female hormone produced by the ovaries. It has several roles within a woman's body, which include preparing the uterus lining for fertilization. Among premenopausal women, progesterone is used to cause menstruation. If fertilization does not occur, progesterone levels drop and the uterine lining sheds, resulting in menstruation. An absence of this hormone can result in anovulation, no menstrual bleeding or heavy menstrual bleeding.
Progesterone also acts to naturally balance estrogen and is necessary for optimum estrogen utilization. Its presence within the body sensitizes both estrogen and thyroid hormone receptor sites, which allow the body to use these hormones more effectively.
How Does Progesterone Affect My Hot Flashes?
Although progesterone therapy has been proven effective at treating hot flashes, it is not clear if progesterone is safe to take for breast cancer patients.
Studies indicate strong evidence that synthetic cousins like medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera), progesterone creams and megestrol acetate (Megace) have proven to be effective at controlling hot flashes.
In women with breast cancer, there is concern that progesterone may increase the risk of cancer reappearance, especially in women with hormone-repetitive tumors. Additional research is needed to evaluate the safety of progesterone therapy in alleviating hot flashes for women who have had breast cancer.
For sufferers of debilitating hot flashes, it might be helpful to consult with your doctor or a healthcare professional to discuss the use of progesterone therapy. Read on to learn about the side effects of progesterone.
What Are the Side Effects of Taking Progesterone?
In contrast to some forms of progesterone such as medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera), natural progesterone seems to suppress high density lipoprotein or “good” cholesterol. However, progesterone has no effect on mood, blood pressure, or enhancing characteristically male hormone effects such as facial hair growth.
Too much progesterone can cause fatigue and sedation; however, this side effect can be beneficial for women suffering from uterine irritability because in high doses it can help to decrease uterine activity.
Although there continues to be relatively few studies on this hormone, progesterone is vital to a woman's well being. Click here to find out more information on treating progesterone imbalance properly.