Getting Pregnant at 40
While women older than 35 are advised to try to conceive naturally for six months before seeking fertility help, those past 40 are instructed to consult with their doctors right away to weigh their options and increase the likelihood of conception.
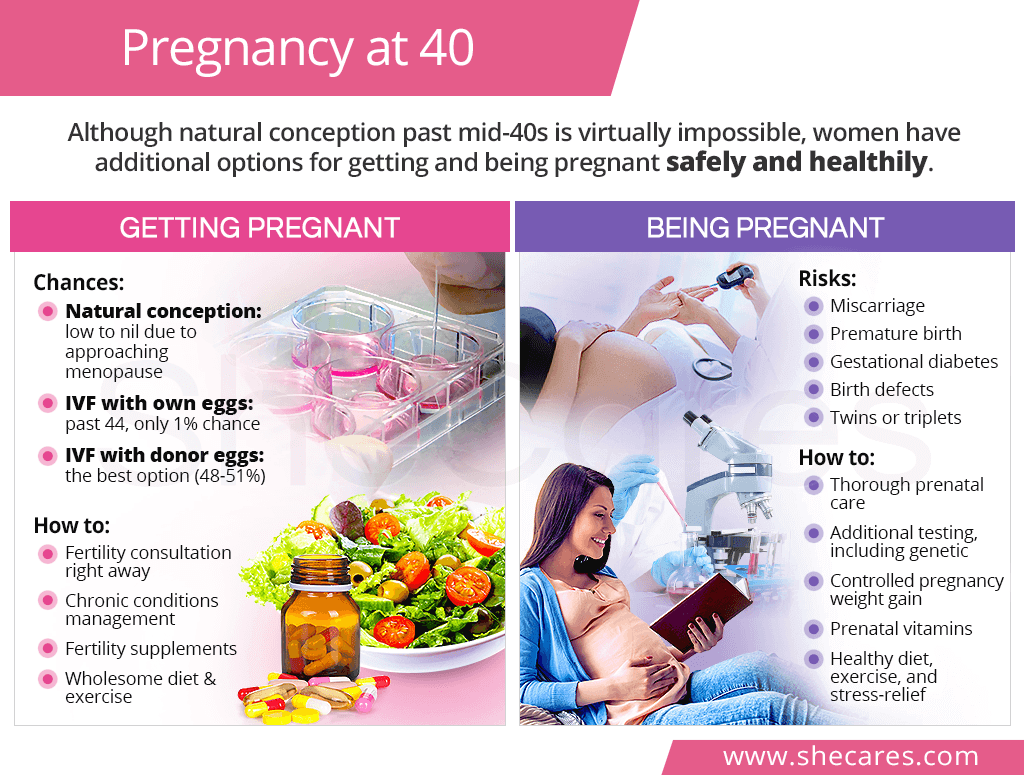
There are two approaches to getting pregnant at 40 and beyond:
Getting Pregnant at 40 Naturally
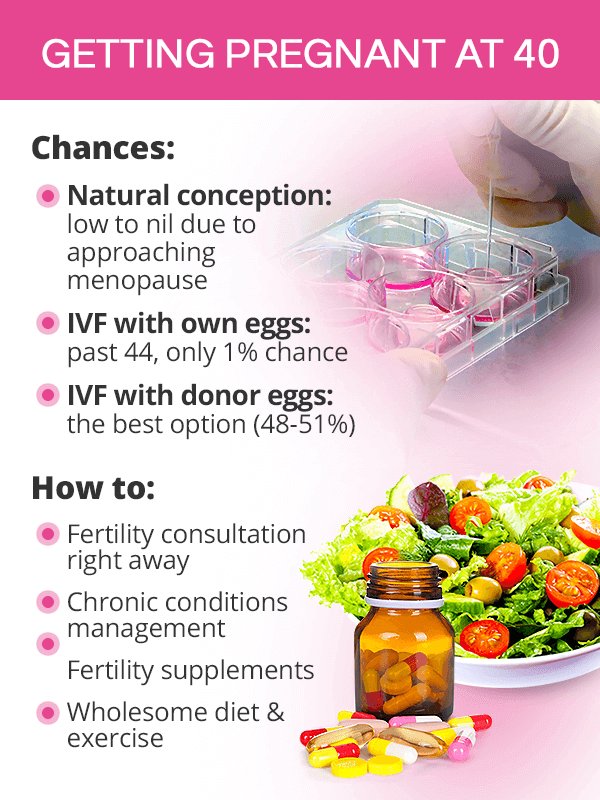
Without a doubt, female fertility past 40 is significantly diminished. Although spontaneous and natural conception is possible for some women, most 40-year-olds face the following reproductive challenges:1,2,3
The supply of eggs in the ovaries, called ovarian reserve, is decreasing more rapidly in the 40s. By menopause, there are no eggs left in the ovaries, and natural pregnancy is not possible.
Up to 80% of the eggs that remain in the ovaries have chromosomal abnormalities, marking them unviable for fertilization or implantation in the uterus. As such, miscarriage rates are high in pregnancies at 40.
Women might be entering perimenopause in their mid-40s with irregular periods or irregular ovulation, including anovulatory cycles, making natural conception less probable.
The biggest challenge for women in their 40s is their egg supply. Since they enter menopause at the age of 51 on average, getting pregnant naturally in those few years prior to that is highly unlikely.4 Once confirmed menopausal, women's ability to conceive is over.
Getting Pregnant after 40 with ARTs
If natural conception is not an option, women can achieve pregnancy at 40 with the help of assisted reproductive technology (ART). There are three possible options available to them:5,6,7
Use their own fresh eggs. Although undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) at 40 with one's own eggs is technically an option, it is not an effective approach as by the age 44, the rates of a successful IVF is only 1%. Specialists often agree that 43 is the cut off age for IVF with one's own eggs.
Use their own, previously frozen eggs. Egg freezing at a younger age as a form of fertility preservation gives women in their 40s and well into their 50s a 48-51% chance of pregnancy.
Use a younger donor's eggs. Because the uterus does not age similarly to the ovaries, women past their 40s and 50s can get pregnant with younger donor eggs since success rates are 48-51%, no matter a woman's age.
No matter which option a woman chooses, it will be beneficial for her to improve her odds of pregnancy by managing her chronic conditions before getting pregnant; maintaining a wholesome fertility diet and regular exercise; and improving her menstrual cycle and ovulation with fertility supplements, like Macafem.
Being Pregnant at 40
Similarly to pregnancies at 35, those to mothers in their 40s are often challenged by the fact that women in that age group are more likely to have pre-existing conditions, including diabetes or hypertension, which may put additional strain on her and her baby's health.
Consequently, a pregnancy over 40 is classified as a high-risk pregnancy.
Risks of Pregnancy after 40
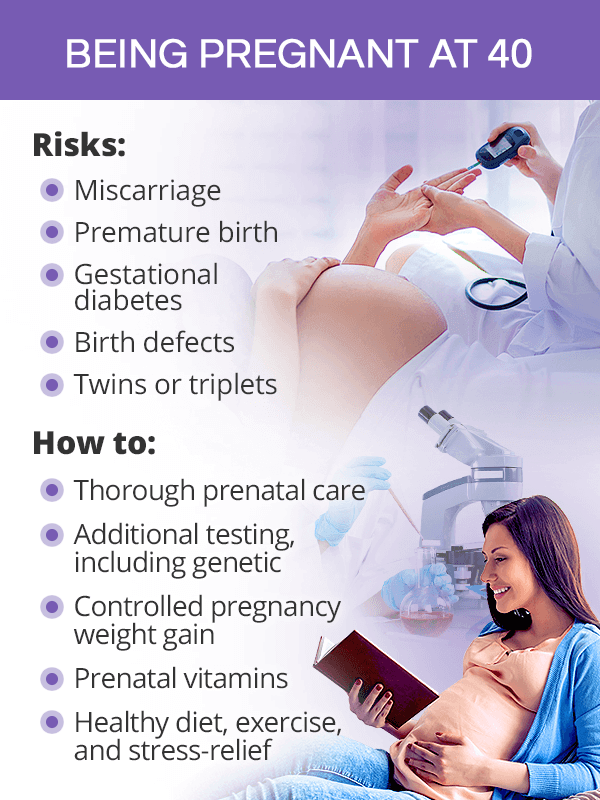
In comparison to younger mothers, those past 40 are faced with higher risks of the following pregnancy complications:8,9,10,11
- Miscarriage (almost 53% past 45 years of age)
- Premature birth
- Preeclampsia
- Gestational diabetes
- Multiple pregnancy (7% of all births to 40-year-old mothers as opposed to 2% in those under 25)
- Cesarean section
- Placenta previa
- Birth defects, particularly Down syndrome (1 in 100 pregnancies by 40; 1 in 10 by 49)
How to Have a Healthy Pregnancy at 40
Despite known risks of being pregnant after 40, women can have healthy and safe pregnancies thanks to additional prenatal care and more caution.
- Regular and frequent prenatal visits, oftentimes in collaboration with several specialists
- Additional prenatal testing, including genetic testing for chromosomal abnormalities
- Prenatal vitamins of at least 400 mcg of folic acid, preferably starting one month before conceiving11
- Healthy weight gain, which for women with normal pre-pregnancy weight equals 25-35 lb. (11-16 kg)12
- Pregnancy diet with complex carbs, lean protein, and healthy fats
- Low- to moderate-level exercise during pregnancy
- Reducing stress during pregnancy with yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises
Key Takeaways
The thought of getting pregnant at 40 can be very stressful before a woman even begins her conception efforts. She is immediately bombarded with data about the dramatic speed of fertility decline after 40, depletion of ovarian reserve, and increased risks of serious pregnancy complications if she does manage to successfully conceive. While all of this is true, and female fertility is time-limited, many women in their early 40s go on to have natural pregnancies, while those who cannot are able to safely and successfully get pregnant with assisted reproduction. Despite associated risks, most women have healthy pregnancies over 40 thanks to more thorough care and attention they and their babies receive from their medical professionals. The key to ultimate fulfillment of one's motherhood dreams is to act quickly and wisely, using one's resources in the most appropriate manner.
Sources
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine. (2013). Volitional determinants and age-related decline in fecundability: a general population prospective cohort study in Denmark. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.fertstert.org/article/S0015-0282(13)00339-7/pdf
- International Federation of Fertility Societies. (2018). Female age and assisted reproductive technology. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://journals.lww.com/grh/Fulltext/2018/06000/Female_age_and_assisted_reproductive_technology.3.aspx
- Human Fertilisation & Embryology Authority. (2014). Fertility treatment. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from http://ifqtesting.blob.core.windows.net/umbraco-website/1783/fertility-treatment-2014-trends-and-figures.pdf
- Fertility & Sterility. (2018). Advanced maternal age may impact placental morphology in IVF pregnancies. Retrieved November 26, 2019from https://www.fertstert.org/article/S0015-0282(18)30168-7/fulltext
- Fertility & Sterility. (2014). The nature of aneuploidy with increasing age of the female partner: a review of 15,169 consecutive trophectoderm biopsies evaluated with comprehensive chromosomal screening. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24355045
- Frontiers in Endocrinology. (2019). Advanced Maternal Age in IVF: Still a Challenge? The Present and the Future of its Treatment. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6391863/
- Reproductive Bio Medicine Online. (2009). Assisted reproduction in women over 40 years of age: how old is too old? Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.rbmojournal.com/article/S1472-6483(09)00024-8/pdf
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2018). Having a Baby After 35: How Aging Affects Fertility and Pregnancy. Retrieved November 26, 2019from https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Having-a-Baby-After-Age-35-How-Aging-Affects-Fertility-and-Pregnancy
- Your Fertility. (2019). Age. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.yourfertility.org.au/everyone/age
Footnotes:
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2014). Female Age-Related Fertility Decline. Retrieved October 16, 2018 from https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Committee-Opinions/Committee-on-Gynecologic-Practice/Female-Age-Related-Fertility-Decline
- Human Reproduction. (2002). Changes with age in the level and duration of fertility in the menstrual cycle. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://academic.oup.com/humrep/article/17/5/1399/845579
- Frontiers in Endocrinology. (2019). The effect of advanced maternal age on embryo morphokinetics. November 26, 2019 from https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2019.00686/full
- Mayo Clinic. (2017). Menopause. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/menopause/symptoms-causes/syc-20353397
- Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics. (2013). Assisted reproduction counseling in women aged 40 and above: a cohort study. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3879927/
- Fertility and Sterility. (2014). Female age-related fertility decline. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.fertstert.org/article/S0015-0282(13)03464-X/pdf
- CDC. (2010). Assisted Reproductive Technology. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.cdc.gov/art/ART2010/PDFs/ART_2010_Clinic_Report-Full.pdf
- Pregnancy, Birth & Birth. (2018). Being pregnant after 40. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/being-pregnant-after-40
- BMJ Clinical Research. (2019). Role of maternal age and pregnancy history in risk of miscarriage: prospective register based study. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.bmj.com/content/364/bmj.l869
- CDC. (2012). Three Decades of Twin Births in the United States, 1980-2009. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db80.pdf
- National Down Syndrome Society. (n.d.). Down Syndrome. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.ndss.org/about-down-syndrome/down-syndrome/
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Folic acid. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/folic-acid
- American Pregnancy Association. (n.d.). Pregnancy Weight Gain. Retrieved November 26, 2019 from https://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/pregnancy-weight-gain/