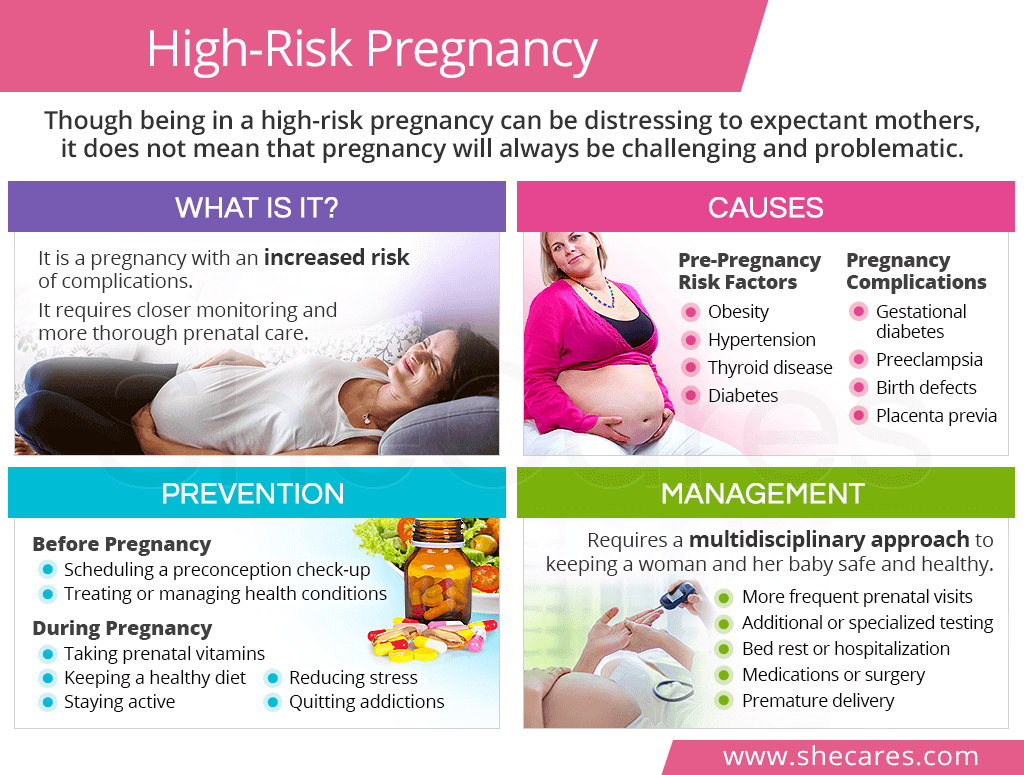
What is a High-Risk Pregnancy?

The term “high-risk pregnancy” means that there is a higher risk of complications, potentially putting the life or health of the mother or her baby in danger.
As such, a high-risk pregnancy necessitates additional monitoring and specialized prenatal care to minimize and prevent further pregnancy complications and improve outcomes. It usually involves a collaboration of a team of multiple medical specialists, including a high-risk pregnancy doctor.
High-Risk Pregnancy Doctor
Many women in high-risk pregnancies can still receive adequate care from their regular obstetrician-gynecologists (OBGYN). Others, however, might be referred to a perinatologist, a maternal-fetal medical specialist with proper training in high-risk pregnancies.
What Makes Pregnancy High-Risk?

There are two scenarios when a woman's pregnancy can be deemed of high risk: if she has pre-existing conditions that put her at risk of complications or when complications occur suddenly in an otherwise healthy pregnancy.
Women with certain risk factors and conditions before getting pregnant might begin their pregnancies already knowing that they are at high risk for complications. These conditions include, but are not limited to, the following:1,2
- Obesity
- Thyroid disease
- Diabetes
- HIV
- Multiple gestation
- Advanced maternal age (35 and older)
- High blood pressure
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Teen pregnancy
- Lupus
- Alcohol, tobacco, or drug addiction
- History of preterm birth
Other women might begin their pregnancies healthily and become high risk at some point during pregnancy as certain complications appear. They include the following:
- Gestational diabetes
- Preeclampsia and its severe form, eclampsia
- Some birth defects
- Placenta previa
Prevention of High Risk Pregnancy

While it is not always possible to prevent complications that make a pregnancy high-risk, there are a number of ways before and during pregnancy to ensure maternal and fetal safety and well-being.
Prevention Before Pregnancy
For women with known pre-pregnancy conditions, taking the time to treat or manage them before conceiving is the best way to significantly reduce the risk of complications.
This can begin by scheduling a thorough preconception check-up with one's doctor to discuss conception plans, undergoing necessary testing, reviewing vaccinations and current medications, and creating a comprehensive pregnancy plan to go through it in the safest way.
During Pregnancy
Although complications can still arise in healthy women at any pregnancy stage, implementing wholesome practices can help women decrease their risk or severity. Some of the best ways to stay healthy during pregnancy can include the following:
- Taking prenatal vitamins as soon as confirmed pregnant
- Undergoing regular doctor's check-ups and recommended prenatal testing
- Maintaining a balanced and nutritious pregnancy diet
- Keeping up with moderate-level pregnancy exercise (Doctor's approval needed)
- Ensuring a safe and healthy pregnancy weight gain
- Practicing various techniques for stress reduction while pregnant
- Quitting addictions to alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drugs
Management of High-Risk Pregnancy

A high-risk pregnancy requires more thorough prenatal care, including medical or surgical interventions; however, the exact regimen will hugely depend on specific circumstances and nature of complications.
Nevertheless, management of a high-risk pregnancy might include the aforementioned practices, like a healthy diet and stress reduction, as well as the following:
More frequent prenatal visits and specialist consultations are a must in high-risk pregnancies in order to closely monitor maternal health and fetal development.
Additional or specialized prenatal testing might include laboratory work and diagnostic tests, like amniocentesis, biophysical profile, and others.
Bed rest or hospitalization might be necessary to help a woman safely carry her baby to term.
Medications or surgery can be used to treat the underlying problem and stop its progression.
A premature delivery might sometimes be the safest way to manage a high-risk pregnancy and prevent further life-threatening complications.
Key Takeaways
For all mothers-to-be, being in a high-risk pregnancy is a significant cause of emotional distress. It is estimated that up to 8% of all pregnancies are deemed high risk, which means that they have an increased risk of complications that can endanger the health of a mother and her baby.3 As such, it requires a multidisciplinary approach and additional prenatal care. Oftentimes, women with pre-existing health conditions or risk factors already know that their pregnancy will be high risk, while others might be considered as such sometime during pregnancy when sudden complications arise. For all women planning to get pregnant, undergoing a preconception check-up is the best way to lower the risk of complications. For expectant mothers, keeping up with regular visits, prenatal vitamins, a healthy diet, and other pregnancy precautions can ensure their own and their little one's well-being.
Sources
- American Pregnancy Association. (n.d.). Understanding a high-risk pregnancy. Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-complications/high-risk-pregnancy/
- CDC. (2018). Pregnancy Complications. Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/pregnancy-complications.html
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2018). What are some factors that make a pregnancy high risk? Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/high-risk/conditioninfo/factors
- John Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.). High-Risk Pregnancy: What You Need to Know. Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/staying-healthy-during-pregnancy/high-risk-pregnancy-what-you-need-to-know
- Minerva Ginecologica. (2014). Management of high-risk pregnancy. Retrieved September 18, 2019 from http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/25020057
- Office on Women's Health. (2019). Prenatal care and tests. Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/prenatal-care-and-tests
Footnotes:
- Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. (2017). What is a high-risk pregnancy? Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancy/conditioninfo/high-risk
- Mayo Clinic. (2018). High-risk pregnancy: Know what to expect. Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/high-risk-pregnancy/art-20047012
- University of California San Francisco. (n.d.). High-Risk Pregnancy. Retrieved September 18, 2019 from https://www.ucsfhealth.org/conditions/high-risk_pregnancy/