Most women know little about one of the most important hormones in their body: progesterone. Working in tandem with the well-known hormone estrogen, progesterone helps to regulate a wide range of bodily functions, from the monthly menstrual cycle to mood, bone health, and sexual function. But what exactly is progesterone and how does it work in the female body? Read on to find out.
Progesterone Basics
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to regulate or "command" all of the body's processes. Progesterone, specifically, is a steroid hormone (meaning it is derived from cholesterol) that is produced and secreted by the adrenal glands, which are located above the kidneys.
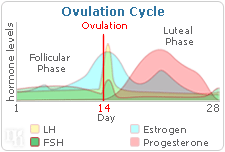
Progesterone's most important role occurs each month during the menstrual cycle. The menstrual cycle is divided into two phases: the follicular phase and the luteal phase. While estrogen primarily acts in the former phase, progesterone makes its debut in the latter phase, when high levels of the hormone are secreted to thicken the lining of the uterus in preparation for a fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, progesterone levels decrease and the uterine lining sheds, triggering the start of the menstrual cycle.
Beyond the menstrual cycle, progesterone influences nearly every cell, organ, and function in the female body. Progesterone's known functions include regulating mood, stimulating the formation of new bones, promoting bone density, bolstering the immune system, converting stored fat into energy, and boosting libido. Therefore, progesterone is essential to numerous everyday functions in the body, not just in reproductive terms. Click here to learn more about the roles and effects of progesterone.
Progesterone and Menopause

During menopause, the female body begins to slow production of essential hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. As a result of these diminished hormone levels, women may experience a variety of uncomfortable symptoms, from irregular periods and low libido to mood swings, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating.
In order to curb these unpleasant symptoms, levels of progesterone and estrogen must be adequately secreted and balanced. This can be achieved in a variety of ways, from making simple lifestyle changes (diet, habits, and exercise) to the use of alternative medicine (herbal remedies and acupuncture) and pharmaceutical options (hormone replacement therapy or bioidentical hormones). It's always best to consult a healthcare professional to find the approach that's right for you. Click here to read more information about treatments for progesterone imbalance.