Estrogen is the most commonly prescribed component of bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT), yet not much is known about bioidentical estrogen. Continue reading through the following sections to learn more about bioidentical estrogen and bioidentical estrogen replacement therapy, including its types, products available on the market, potential benefits, and much more.
What Is Bioidentical Estrogen?
Bioidentical estrogen is an animal- or plant-derived hormone - often synthesized from yams, soy, or pregnant mare's urine - that functions identically to endogenous estrogen produced by the body.
Although commonly referred to as more natural, bioidentical estrogen hormones are still man-made as the plant precursors are chemically modified in laboratories to be molecularly identical to endogenous estrogens.
What Is Bioidentical Estrogen Replacement Therapy?
Bioidentical estrogen replacement therapy refers to a hormone therapy that uses bioidentical estrogen in place of the synthetically-created hormones normally used in traditional hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
Bioidentical estrogen replacement therapy is commonly used by perimenopausal and postmenopausal women whose fluctuating hormone levels drastically affect their well-being, causing symptoms such as mood swings, vaginal dryness, loss of libido, hot flashes, and more.
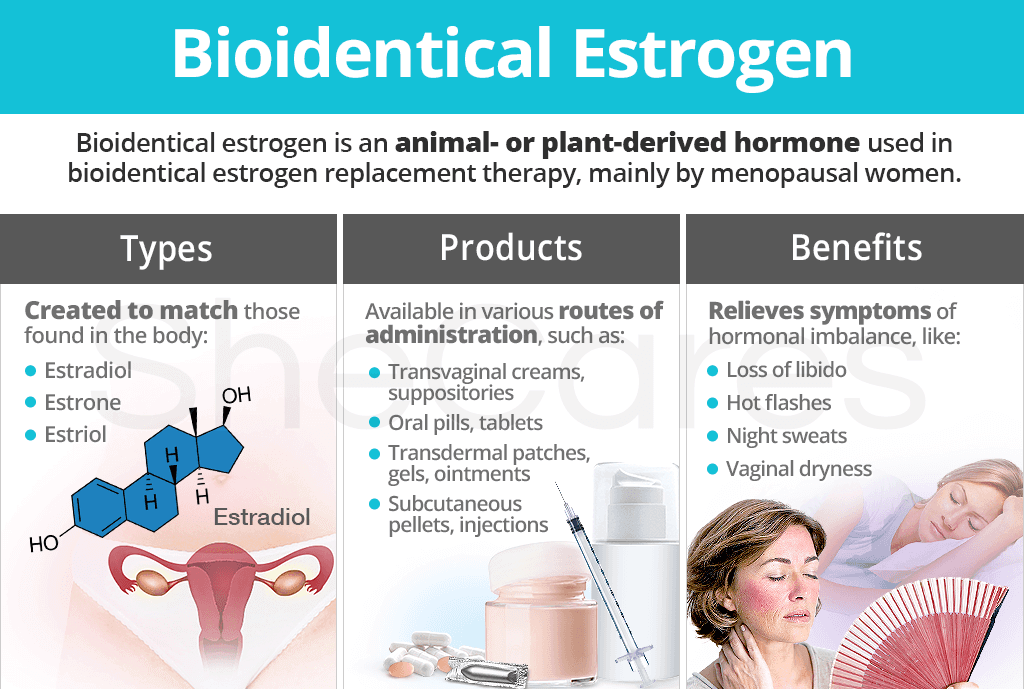
Types of Bioidentical Estrogen Hormones
Hormones used in bioidentical estrogen replacement therapy are created to match the types of estrogen found in the female body, which are estradiol, estrone, and estriol:
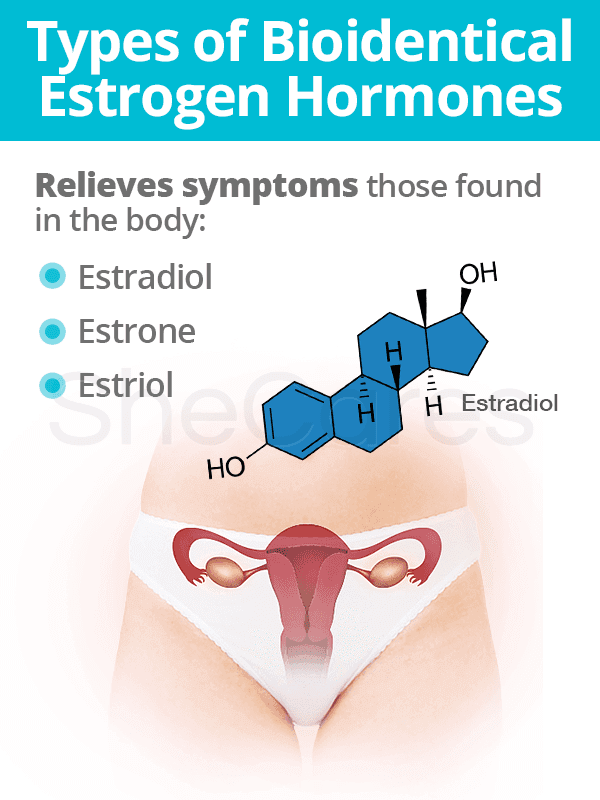
- Estradiol. Throughout women's reproductive lives, estradiol makes up the majority of the body's estrogen stores. Since it is mainly produced in the ovaries during the first half of the menstrual cycle, estradiol levels decrease drastically with the onset of perimenopause.
- Estrone. Estrone is the primary circulating estrogen hormone once a woman begins transitioning into perimenopause and postmenopause. When ovarian function halts, small amounts of estrogens are produced by converting adrenal precursors into estrone.
- Estriol. This type of estrogen is the least active of the endogenous estrogens as it plays its principal role during pregnancy.
All bioidentical estrogens are available in one of two preparations: prescription-regulated preparations or customized compounded preparations.
Prescription-regulated bioidentical estrogen preparations are FDA-approved. They contain doses that are exactly reproducible with proven efficacy through scientific research studies. They are not customized according to a woman's specific hormonal needs.
On the other hand, customized compounded bioidentical estrogen preparations are not FDA-regulated since they are personalized to each woman's needs. Doses may be inexact, and as such, efficacy and safety cannot be proven in controlled studies.
Bioidentical Estrogen Products
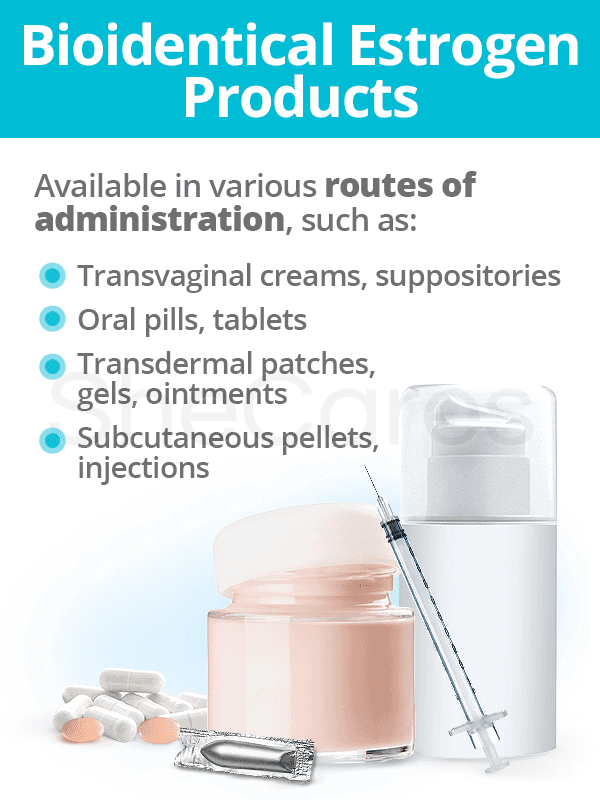
Bioidentical estrogen is available in various routes of administration, including:
- Transvaginal route, like creams, tablets, suppositories, or rings
- Oral route, including pills and sublingual tablets
- Transdermal route, such as patches, gels, ointments, and creams
- Subcutaneous route via pellets or injections
Depending upon the product used, bioidentical estrogen can be combined with other hormones - such as progesterone - to maximize treatment effectiveness depending upon a woman's needs.
Throughout the bioidentical estrogen replacement therapy, it is important to work with your doctor to decide which method is best for you and your specific needs. You may be encouraged to try more than one method.
Potential Benefits of Bioidentical Estrogen Replacement Therapy
Below is a list of hormonal imbalance symptoms that could be improved with bioidentical estrogen replacement therapy:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Low libido
- Dyspareunia
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Loss of energy
- Sleep problems
- Memory lapses
- Vaginal dryness
- Mood changes, including irritability and anxiety
- And more
Nevertheless, to fully understand the breadth of taking bioidentical estrogen hormones, continue reading about bioidentical estrogen side effects before deciding if it's right for you.
Sources
- Cleveland Clinic. (2014). Bioidentical Hormones. Retrieved April 22, 2019, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15660-bioidentical-hormones |
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2006). What are bioidentical hormones? | Bioidentical hormones: Help or hype? Retrieved April 22, 2019, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/what-are-bioidentical-hormones | https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/bioidentical-hormones-help-or-hype
- Mayo Clinic. (2018). Bioidentical hormones: Are they safer? Retrieved April 22, 2019, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/menopause/expert-answers/bioidentical-hormones/faq-20058460