The prescription of bioidentical testosterone for women is a controversial topic among healthcare providers, with some encouraging its short-term use and others promoting other methods to balance hormonal imbalance symptoms during times of drastic changes, such as menopause.
Continue reading below to learn more about bioidentical testosterone and bioidentical testosterone replacement therapy, including what they are, products available on the market, potential benefits, and much more.
What Is Bioidentical Testosterone?

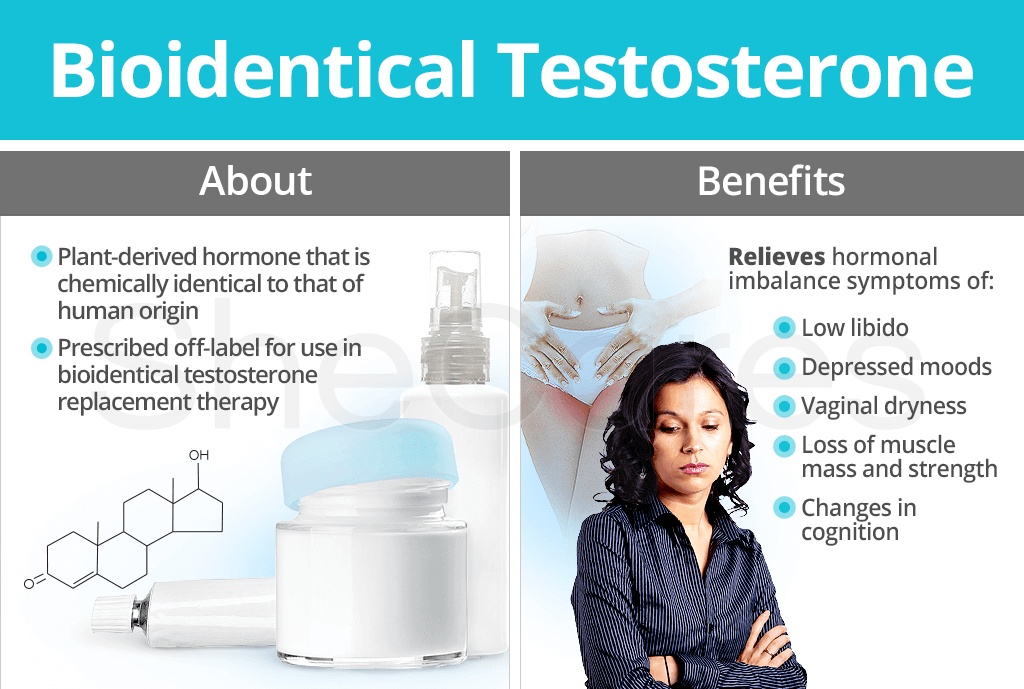
Bioidentical testosterone is a plant-derived hormone that is chemically identical to that of human origin. Bioidentical testosterone originates from diosgenin from Mexican wild yams or stigmasterol from soybeans.
A chemical conversion of both plant compounds is then needed to produce progesterone, the precursor to androgens, and then testosterone.
As such, because its plant precursors are synthetically altered to be molecularly equal to endogenous testosterone, bioidentical testosterone is considered comparable to its synthetic alternative.
What Is Bioidentical Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
As such, bioidentical testosterone replacement therapy refers to a hormone treatment that uses bioidentical testosterone in place of synthetic androgens traditionally used in normal hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
Usually, bioidentical testosterone replacement therapy is prescribed off-label to perimenopausal and postmenopausal women who are suffering from symptoms of hormonal imbalance, particularly sexual dysfunction, such as low libido.
It is worth noting that bioidentical testosterone replacement therapy is generally only prescribed for women who have sufficient estrogen levels.
Bioidentical Testosterone Products
Bioidentical testosterone is available in a few routes of administration for women, including:
- Oral route, with capsules or tablets
- Transdermal route, such as creams, pellets, and gels
- Sublingual/ buccal route, through dissolvable tablets or patches placed under the tongue or between the gums and the cheek
Keep in mind that there are no FDA-approved testosterone preparations for women. Because of this, healthcare providers often prescribe bioidentical testosterone products used in men at considerably reduced doses.
It is important to remember that as a woman partaking in bioidentical testosterone replacement therapy, you should coordinate with your doctor to decide which route of administration is best for your needs. Your blood testosterone levels will be closely monitored throughout treatment.
Potential Benefits of Bioidentical Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Below is a list of symptoms that could be relieved by taking bioidentical testosterone:

- Low libido
- Vaginal dryness
- Sleep disturbances
- Depressed moods
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Changes in cognition
- Incontinence
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Lack of well-being
- Loss of muscle mass and strength
- Decreased energy levels
- And more
Nevertheless, women who are suffering from a loss of libido are encouraged to investigate other reasons behind sexual dysfunction - chronic pain, fatigue, depression, relationship issues, lack of adequate stimulation, thyroid problems, other menopause symptoms, etc. - before running to bioidentical testosterone.
To completely understand the complications involved with taking bioidentical testosterone as a woman, continue reading about bioidentical testosterone side effects before embarking on this treatment regimen.
Sources
- Bolour, S. & Braunstein, G. (2005). Testosterone therapy in women: a review. International Journal of Impotence Research, 17(5), 399-408. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3901334
- Cleveland Clinic. (2014). Bioidentical Hormone. Retrieved May 13, 2019, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15660-bioidentical-hormones
- Files, J.A. et al. (2011). Bioidentical Hormone Therapy. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 86(7), 673-680. doi: 10.4065/mcp.2010.0714
- Fugh-Berman, A. & Bythrow, J. (2007). Bioidentical Hormones for Menopausal Hormone Therapy: Variation on a Theme. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 22(7), 1030-1034. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0141-4
- Glaser, R. & Dimitrakakis, C. (2013). Testosterone therapy in women: Myths and misconceptions. Maturitas, 74(3), 230-234. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.01.003
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2013). Testosterone therapy: Is it for women? Retrieved May 13, 2019, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/testosterone-therapy-is-it-for-women
- Healthy Women. (n.d.). The Reality behind Testosterone Therapy. Retrieved May 13, 2019, from https://forevher.healthywomen.org/treatment/the-reality-behind-testosterone-therapy/
- Hudson's FTM Resource Guide. (n.d.). Bioidentical Testosterone. Retrieved May 13, 2019, from http://www.ftmguide.org/bioidenticalt.html
- Mayo Clinic. (2016). Testosterone therapy in women: Does it boost sex drive? Retrieved May 13, 2019, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/menopause/expert-answers/testosterone-therapy/faq-20057935
- Pattimakiel, L. & Thacker, H.L. (2011). Bioidentical hormone therapy: Clarifying the misconceptions. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, 78(12), 829-836. Retrieved May 13, 2019, from https://www.mdedge.com/ccjm/article/95466/womens-health/bioidentical-hormone-therapy-clarifying-misconceptions
- Victoria State Government. (2019). Androgen deficiency in women. Retrieved May 13, 2019, from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/androgen-deficiency-in-women