What Is Tubal Ligation?
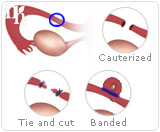
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that cuts, blocks, or ties a woman's fallopian tubes, which in turn makes her sexually sterile. This process means that eggs can no longer travel from the ovaries to her uterus and it also obstructs sperm from being able to travel along the fallopian tube to meet the egg. The fertilization process is prevented completely.
How Is it Done?
The most common way that tubal ligation is done is by a procedure known as laparoscopic surgery. This involves making a small incision under the navel and inserting instruments through a tiny tube to complete the process. It is done under general or local anesthetic. The most common method of tubal ligation is the Pomeroy technique, also known as “getting your tubes tied”. It involves tying a loop in the fallopian tube and surgically removing the tied section.
Why Do Women Have it Done?

The main reason for woman choosing to have a tubal ligation is as a permanent form of birth control. It is almost 100% effective in preventing unwanted pregnancy. Some choose sterilization because they do not want to have any more children, or some do it because getting pregnant could be potentially harmful to them. A much smaller percentage of women have it done for medical reasons, although usually a hysterectomy will be the preferred option for these women.
Can You Reverse This Surgical Procedure?
Tubal ligation can be reversed, but it requires major surgery which might not be successful. In order for your fallopian tubes to function again, the doctor has to unclamp, reattach, or remove any devices that are blocking it, or place an implant into your fallopian tubes. If part of your fallopian tube was removed then it will depend on the amount that was removed as to whether the procedure is reversible. Side effects are possible with any form of ligation reversal. You are more likely to encounter bleeding, infections, damage to the surrounding organs, and complications in pregnancy.
How Does it Affect Your Hormones?
Typically, tubal ligation doesn't affect the hormones in your body because your ovaries are still intact and will therefore still produce an egg each month. They also still produce all the essential hormones that a woman requires to function normally. This means that menstruation will continue, you shouldn't suffer with symptoms of hormone imbalance, and your sex drive will remain. However, many women have suffered with a decline in estrogen and progesterone after surgery. This complication is referred to as post tubal ligation syndrome, or PTLS or PTS, and is reportedly becoming more common.
Most women who experience PTS will encounter one of two things: either very heavy bleeding and irregular periods due to estrogen dominance, or the onset of perimenopausal symptoms due to the sudden decline of estrogen and progesterone. Hormone creams are sometimes suggested as a treatment for these various problems.
Recommendation
Always talk to your doctor before opting for this procedure and consider the negative effects it could have as well as the positive. Click on the following link to find out more about hormones roles and effects.


