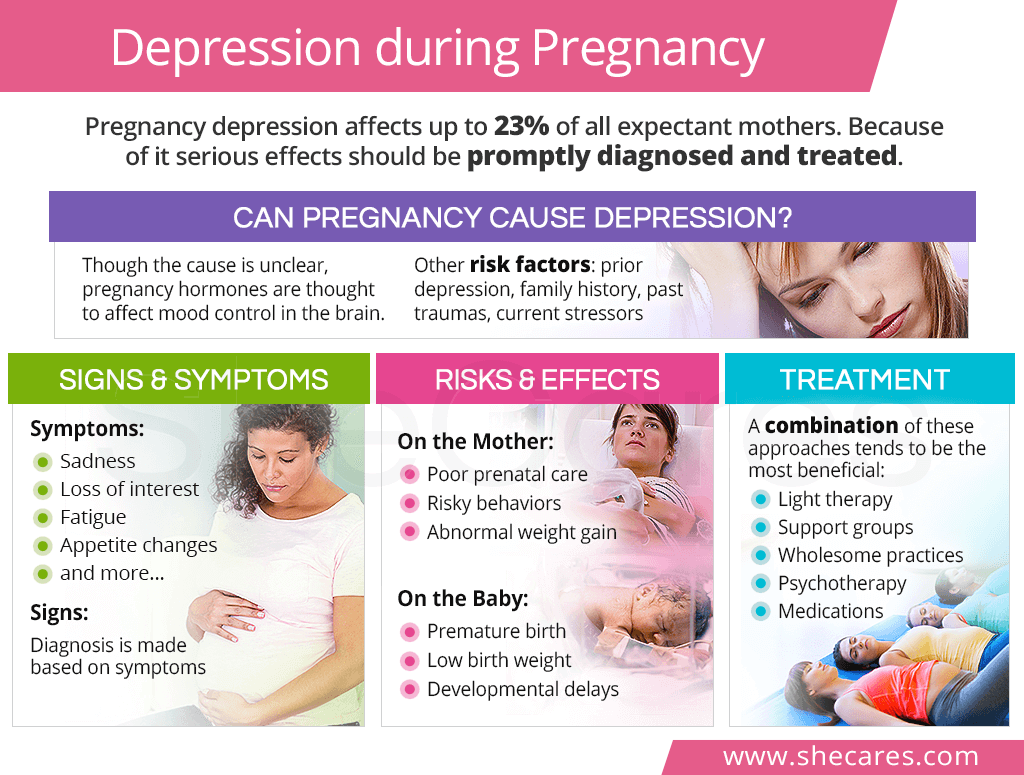
What Is Pregnancy Depression?

Pregnancy depression, or antenatal depression, is a mental health condition that causes feelings of sadness and apathy.
Pregnancy depression is not different from clinical depression that affects non-pregnant women. It is the same exact mood disorder, only called as such because it happens throughout the course of pregnancy.
Understanding that depression is a treatable mood disorder, not a part of occasional mood swings or pregnancy blues, can eliminate unnecessary delays and prompt women to seek proper diagnosis.
Can Pregnancy Cause Depression?
As in the case of clinical depression, it is not well understood what causes depression in pregnancy. Since being pregnant is a time of significant hormonal fluctuations that can affect brain chemicals responsible for mood control and emotions, hormonal imbalance is usually considered the main culprit.
Additionally, various life situations, such as relationship issues or past trauma, as well as previous depression or family history of depression are risk factors, making women more prone to suffering from depression in pregnancy.2
Signs and Symptoms of Depression during Pregnancy

Because a few signs and symptoms of depression during pregnancy might overlap with pregnancy signs and symptoms themselves, women very often wrongly perceive them as a part of being pregnant, without seeking help.
Symptoms of Depression during Pregnancy
In the majority of cases, women feeling depressed during pregnancy report several of the following eight symptoms:
- Persistent sadness most of the day, nearly every day
- Loss of interest or pleasure in previously enjoyed activities
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Feelings of guilt or worthlessness
- A noticeable slowing in physical movement and thinking
- Changes in eating habits and the resulting weight loss or gain
- Thoughts of death, suicide, or hopelessness
Signs of Depression during Pregnancy
There are no medical and laboratory tests that can confirm pregnancy depression. The diagnosis is made based on the symptoms reported by a woman according to the combination of the following criteria:3
- A woman experiences at least five of the aforementioned symptoms
- The symptoms last for at least two consecutive weeks
- At least one of the first two symptoms are experienced
Depression and Pregnancy Risks and Effects

Untreated depression during pregnancy carries a number of serious risks both to maternal and fetal health.4
Depression and Pregnancy: Effects on the Mother
The main influence of pregnancy depression on expectant mothers is that it makes them less likely to take care of themselves and their babies, including:
- Poor adherence to prenatal care
- Poor nutrition
- Abnormal pregnancy weight gain
- Stress and anxiety
- Sleep problems
- Risky behaviors (e.g. unprotected sex, smoking, drinking)
- Suicidal thoughts
All of the aforementioned effects are also major risk factors for pregnancy complications, like cesarean delivery and preeclampsia, putting women and their babies' health and life in danger.
Women with depression in pregnancy are also more likely to be depressed after birth, which can affect the care for their babies, breastfeeding, or bonding.
Depression and Pregnancy: Effects on the Baby
Babies born to mothers who had been feeling depressed during pregnancy are at an increased risk of the following complications:
- Preterm birth
- Having low birth weight
- Being small for gestational age
- Being more agitated, less active, and less attentive
- Having development problems and mental health conditions in the future
Depression In Pregnancy Treatment

Because of the associated risks involved with the use of certain medications in pregnancy, women are encouraged to start with the most natural and least invasive treatment approaches, which might include the following according to the severity of their symptoms:
Light Therapy. Studies of usefulness of light therapy for treating pregnancy depression have shown that it can improve symptoms within several weeks, positioning it as a safe and inexpensive treatment alternative to pharmacological approaches.
Support Groups. Whether it is a support group within one's local community or a circle of family and friends, it is important to have people to talk to and share one's struggles and difficulties. Free depression or suicide hotlines are also available virtually everywhere around the world, where women can find immediate help and support.
Psychotherapy. Expectant mothers with mild or moderate depression usually response well to psychotherapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy (IPT). If depression is severe, a combination of psychotherapy and medications might be recommended.
Medications. Choosing the right depression medication while pregnant can be challenging because there is evidence that some antidepressants might cause adverse reactions in babies, such as heart defects or low birth weight.5 As such, medications like antidepressants in pregnancy are usually reserved for severe depression.
Additional Recommendations
When feeling depressed during pregnant, it might be a challenge to make significant lifestyle changes. Nevertheless, various wholesome practices can be added to the selected treatment to help heal and strengthen the mind and body.
- Moderate-intensity exercise during pregnancy to boost serotonin and endorphin release
- Balanced and nutritious pregnancy diet, especially rich in omega-3 fatty acids and probiotics
- Natural techniques to reduce stress in pregnancy, like a hobby, meditation, or deep breathing
Any regimens of over-the-counter or prescription medications as well as herbal remedies should first be approved by a woman's doctor to ensure they are not harmful to the baby.
Key Takeaways
While pregnancy is a transformative time in women's lives, not everything they experience can be considered a normal part of being pregnant. Such is the case with depression during pregnancy, which affects up to 23% of expectant mothers.
Although its causes are not fully understood, the most probable suspects are the hormones that disrupt the brain's chemistry. As a result, women may report feeling depressed during pregnancy, lose interest in activities that used to be joyful, or observe drastic appetite changes. To lower the risk of serious complications of untreated depression in pregnancy on the mother and baby, women are encouraged to seek help right away. Luckily, for low to moderate symptoms, a combination of light therapy, support groups, psychotherapy, and wholesome practices is usually effective, while women with severe symptoms might need medications.
Sources
- American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. (2016). 658: The impact of prenatal care on pregnancy outcomes in women with depression. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(15)02009-8/fulltext
- Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. (2011). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of light therapy for antepartum depression. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21535997
- BMJ. (2007). Depression during pregnancy. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1867919/
- CDC. (2019). Depression During and After Pregnancy. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/features/maternal-depression/index.html
- Healthy Children. (2018). Depression During and After Pregnancy: You Are Not Alone. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/prenatal/delivery-beyond/Pages/Understanding-Motherhood-and-Mood-Baby-Blues-and-Beyond.aspx
- HRSA. (2006). Depression During and After Pregnancy. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://mchb.hrsa.gov/sites/default/files/mchb/MaternalChildHealthTopics/maternal-womens-health/Depression_During_and_After_Pregnancy_ENGLISH.pdf
- Primary Care. (2009). Depression in Childbearing Women: When Depression Complicates Pregnancy. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2680254/
Footnotes:
- Mayo Clinic. (2016). Depression during pregnancy: You're not alone. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/in-depth/depression-during-pregnancy/art-20237875
- American Pregnancy Association. (2015). Depression in Pregnancy. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://americanpregnancy.org/pregnancy-health/depression-during-pregnancy/
- American Psychiatric Association. (2017). What is Depression? Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/depression/what-is-depression
- American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. (2010). Risk factors for depressive symptoms during pregnancy: a systematic review. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2919747/
- March of Dimes. (2019). Depression during Pregnancy. Retrieved September 12, 2019 from https://www.marchofdimes.org/complications/depression-during-pregnancy.aspx