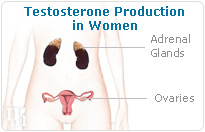
Women produce testosterone in their body. This androgen is secreted by the ovaries, and it is responsible for functions like libido and muscle mass maintenance. Menopause is a time in a woman's life when her hormones are fluctuating wildly, and sometimes too much or too little of one hormone can throw the entire body off of its natural balance.
If women do not have enough testosterone, they can experience uncomfortable symptoms. On the other hand, if too much testosterone is produced, symptoms of another sort could appear. Keep reading to discover more about high or low levels of testosterone.
Too Much Testosterone during Menopause
During menopause, if a woman is experiencing an overabundance of testosterone, she may experience several symptoms like:
- Deepening of the voice
- Increased muscle mass
- Male pattern baldness
- Excess body hair
- Enlarged clitoris
- Irregular periods
- Acne
Excessive amounts of testosterone have been linked to infertility and other conditions, such as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), a disorder that sometimes appears during the menopausal transition. Therefore, it is important to consult your doctor if you are experiencing this kind of symptoms, especially if you're pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
Not Enough Testosterone during Menopause
If your body does not have enough testosterone, your sex life could be greatly affected, as well as your confidence level and body shape. You may also experience one or a combination of the following symptoms, which can also have emotional effects:

- Anorgasmia (the inability to have an orgasm)
- Fattened area around the abdomen
- Sudden absence of menstruation
- Loss of libido, or interest in sex
- Loss of muscle mass
- Vaginal dryness
- Depression
- Hot flashes
- Fatigue
Controlling testosterone levels are a serious matter, and if you think you are experiencing a surplus or shortage of this or any other hormone, you should talk with your doctor to consider your options. The least invasive measures, which are becoming more popular with the advent of the organic movement, are to control imbalances with lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular exercise. However, some cases are more severe than others and may need alternative medicines or, if nothing else works, consideration of hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Click on the link below to read more about controlling testosterone imbalance.
