Because the signs and symptoms of having too much testosterone are similar to those of various other conditions, it is not uncommon of the hormonal imbalance to gradually exacerbate before being correctly diagnosed.
Accordingly, in attempt to prevent the onset of more serious conditions, continue reading to discover more about signs and symptoms of high testosterone levels.
Symptoms of High Testosterone Levels

High testosterone symptoms - many of which are listed below - can occur at any age and affect more than just the reproductive system.
Physical Symptoms
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Increased muscle bulk
- Female-patterned hair loss
- Hirsutism
- Oily skin
- Enlarged clitoris
- Changes in body shape
- Decreased breast size
- Weight gain
- Acne
- Deepening of voice or hoarseness
Psychological Symptoms
- Depression
- Aggression
- Lack of well-being
Signs of High Testosterone Levels
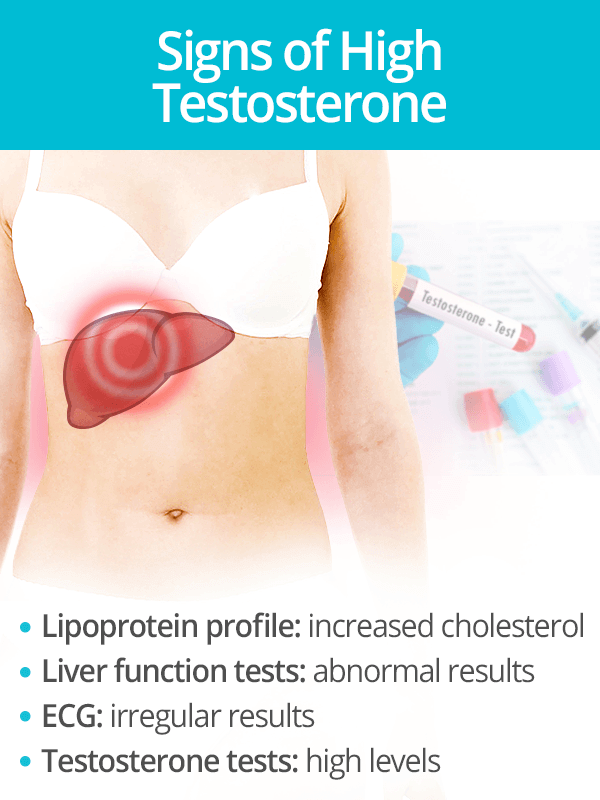
While many of the symptoms aforementioned are self-examinable, there are certain health complications that can arise in women due to too much testosterone. Confirming signs for these conditions can help a physician work backwards to pinpoint the original cause.
The following are medical signs, results from quantifiable tests, that can help a doctor diagnose a woman with excess testosterone in the body if paired with appropriate symptoms.
- Increased cholesterol levels (as determined by lipoprotein profile)
- Abnormal results of liver function tests
- Irregular electrocardiogram (ECG) results, showing risk of heart disease
- Testosterone tests proving the presence of excess testosterone
Discover more valuable information about lowering testosterone levels and evade the future onset of high testosterone-related health conditions.
Sources
- Berman, J. & Berman, L. (2001). For Women Only: A Revolutionary Guide to Reclaiming Your Sex Life. London: Hachette Digital. Available from Google Books.
- Glaser, R. & Dimitrakakis, C. (2013). Testosterone therapy in women: Myths and misconceptions. Maturitas, 74(3), 230-234. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.01.003
- Rohr, U.D. (2002). The impact of testosterone imbalance on depression and women's health. Maturitas, 41(Suppl 1), S25-S46. Retrieved August 2, 2018, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11955793
