For some couples, conceiving may take several attempts. If the woman does not become pregnant within 6 - 12 months, the couple is likely experiencing fertility problems, which can be diagnosed by a physician of fertility specialist. This guide will help you understand fertility, conception, and pregnancy, as well as how you can increase your chances of getting pregnant.
About the Reproductive System
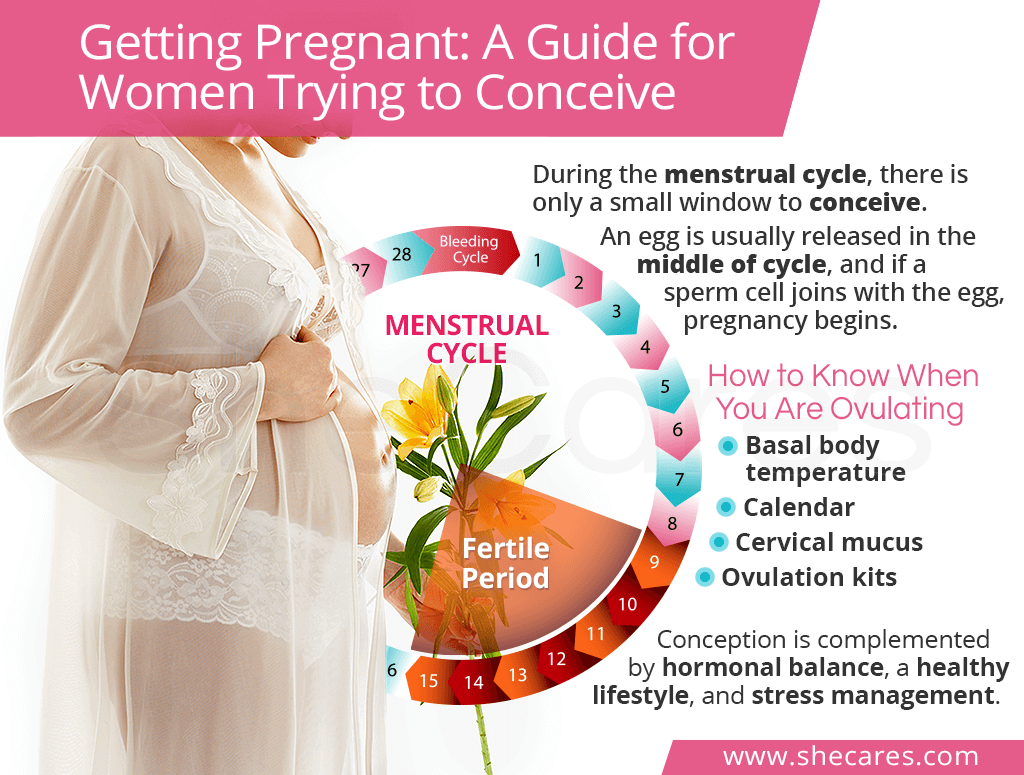
The menstrual cycle dictates when a woman can become pregnant. A typical cycle consists of 28 days, and it starts with a period, which usually lasts for 3 – 5 days or up to 7. After the bleeding has finished, a rise in estrogen and luteinizing hormone causes the lining of the uterus to thicken in preparation for a fertilized egg to implant there.
About halfway through the cycle, around day 14, an egg is released and ovulation begins. A woman's fertile window typically starts three to five days before her ovulation day and closes within 24 hours after she ovulates. This means that she has the highest chances of getting pregnant on days 10 to 15. If a sperm cell joins with the egg, it will implant on the uterine lining, beginning the pregnancy.
Ovulation and Fertility
Although, it is ideal for couples trying to get pregnant to have intercourse regularly even when the woman is not ovulating, a woman can detect her ovulation - and therefore, her fertile window - with certain home methods.
Basal body temperature method
When a woman ovulates, her body temperature increases slightly. This can be measured with a basal body thermometer, which is more sensitive than the typical household thermometer. A woman should take her temperature every day and record it, ideally for several months to get a sense of what her body temperature is at different points of her menstrual cycle. Typically, body temperature ranges from 96 - 98°F (35.6 - 36.7°C) before ovulation and 97 - 99°F (36.1 - 37.2°C) during ovulation. A woman's temperature increases by only about 0.4 - 0.8°F when she is ovulating, but many women can detect this rise to know when they are fertile.
Calendar method
In general, it is helpful for a woman to make a written record of her menstrual cycles when she is trying to get pregnant. For the calendar method, a woman needs to keep track of the length of her cycles over the course of 8 - 12 months. To calculate your fertile window, subtract 18 from the total number of days in your shortest cycle. Take this difference and count ahead from the first day of your period; this is the beginning of your fertile window. Then, subtract 11 from the total number of days of your longest cycle. Again, take this difference and count ahead from the first day of your period. This marks the end of your fertile window.
Cervical mucus method
Hormone levels affect the characteristics of cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle. A woman can keep track of these changes to detect another sign of ovulation. In the days directly following a period, there is typically little to no mucus production. Then, as the egg matures, cloudy and sticky mucus is produced. Then, a few days later, the mucus becomes clear and stretchy for a span of about four days. This is when a woman is most fertile.
It should be noted that this method is not reliable for women who are breastfeeding, taking hormonal birth control, or using douches, as well as those who have had sexually-transmitted infections or surgery on the cervix.
Ovulation kits
These kits are available at pharmacies and can be used at home. They detect surges in luteinizing hormone, the hormone that triggers ovulation.
Prenatal Vitamins and Preconception Health
The most important vitamin a woman can take before becoming pregnant is vitamin B9 (i,e; folic acid). Taking 400 - 800 mcg of folic acid lowers the risk of some severe birth defects.
It may not be appropriate; however, to take per-formulated prenatal vitamins before you actually become pregnant. These products may contain amounts of nutrients like iron that are higher than the recommended amount for an adult woman who is not pregnant. It is always best to consult your physician about what prenatal vitamin supplements would be helpful in your case.
Other health tips
Leading a healthy lifestyle not only helps with fertility, but it is also essential for the health of the baby when a woman does become pregnant. Keep the following health factors in mind when you are trying to conceive:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Women who are underweight or overweight tend to have a harder time becoming pregnant than those with the healthy BMI of 18.5 - 25.
- Eliminate alcohol and tobacco use. Not only do these substances reduce fertility, but they also harm the fetus.
- Manage chronic health problems. Visit your physician to be sure that any ongoing health problems - like diabetes, gum disease, or thyroid issues - are resolved or under control.
Intercourse for Conception
Couples should have intercourse every day, if it is not too stressful for them - when the woman is ovulating. Sperm cells can live inside the vagina for 3 – 5 days, so a woman can still become pregnant from intercourse that took place even prior to ovulation.
Although there has not been extensive study on position, it is suggested that the missionary position is ideal for conception, and it is recommended that the woman remain on her back for 10 - 15 minutes after intercourse.
Oil-based lubricants are recommended over water-based lubricants, as the last ones can reduce sperm motility and thereby prevent fertilization.
Infertility
A couple is considered infertile when they have not been able to conceive after one year of unprotected sex on a regular basis. In about one-third of cases, the infertility is attributable to a female problem; in the other two-thirds of cases, the infertility is caused by a male problem or both male and female problems. In a small percentage of these cases, no cause can be found.
Often, hormonal imbalance halts ovulation or otherwise interrupts the menstrual cycle, thereby lowering fertility. It could also make the fertilized egg unable to implant on the uterus lining. Other causes of infertility can be genetic or anatomical.
Pregnancy After 35
A woman's chances of becoming pregnant decrease around her mid-thirties, but it is still possible to have a healthy pregnancy, and about 20% of U.S. women do not have their first child until after age 35. However, about a third of women over 35 have infertility problems, and the risk of miscarriage increases after this age. Couples over 35 - or at least if the woman is over 35 - should only try to conceive on their own for about six months, and then seek medical advice if they are unable to conceive.
Assisted Reproduction
Medical technology can now help some couples conceive when all other methods have failed. Assisted reproductive technologies facilitate fertilization in different ways when it does not happen naturally through regular intercourse. They may use fresh sperm and eggs, previously-frozen sperm and eggs, or donor sperm, eggs, or embryos. The most common techniques are:
- In vitro fertilization
- Zygote intrafallopian transfer (also known as tubal embryo transfer)
- Gamete intrafallopian transfer
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
In extreme cases, these techniques may be applied to surrogates or gestational carriers for women who cannot carry a pregnancy.
An Action Plan for Getting Pregnant
A woman and her partner can take steps to improve their chances of getting pregnant before they even see a healthcare professional.
Track fertility and ovulation
This takes some preparation, as a woman should track her periods, basal body temperature, and the characteristics of her cervical mucus for several months or even a year. A woman can look for signs of ovulation using the above mentioned methods to help know when she is most fertile.
Make appropriate lifestyle adjustments
Sometimes, a woman and her partner may need to make changes in habit to promote fertility and have a healthy pregnancy. Women should aim to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, though they should not exercise so vigorously that it induces rapid weight loss. Both men and women should quit smoking and reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption to increase their chances of conceiving.
Manage stress
Intense stress can stop ovulation, making a woman unable to become pregnant for a time. Each woman relaxes in her own way, but popular ways of releasing stress and tension are yoga, meditation, and aromatherapy because they are inherently calming. Other women partake in a hobby, socialize with friends, or spend time with a pet, as long as they are not undermining their healthy lifestyle changes. No matter your relaxing activity, the important thing is that you carve time out of your week to do it so that stress does not build up.
Balance hormone levels
If a woman's menstrual cycle is irregular, she will have a harder time predicting when she is fertile. In fact, in some cases, she may not even be ovulating at all. The menstrual cycle can be regulated with certain herbal supplements, thereby promoting fertility as well.
- Phytoestrogenic herbal supplements. These products include supplements that contain herbs like black cohosh, soy, red clover, and dong quai, among others. These plants are rich in phytoestrogens, which are botanical compounds that act similarly to estrogen in the body. Therefore, they can help increase estrogen levels when they are low. However, they should not be used for more than six straight months at a time, as the body can grow accustomed to external estrogenic compounds and reduce production of its own estrogen.
- Hormone-regulating herbal supplements. These products, such as Macafem, contain essential nutrients that support the glands of the hormonal system. With this help, the glands naturally produce hormones at balanced levels. Because of this unique mechanism, hormone-regulating supplements balance not only estrogen levels, but also progesterone and other hormones that influence the menstrual cycle and fertility.
The different aspects of this action plan can be combined to suit each individual woman's lifestyle and preference and lead her to healthy pregnancy. Hormone-regulating herbal supplements coupled with a healthy lifestyle can maximize a woman's fertility, and ovulation tracking methods can help her know at what point in the month she is most fertile.