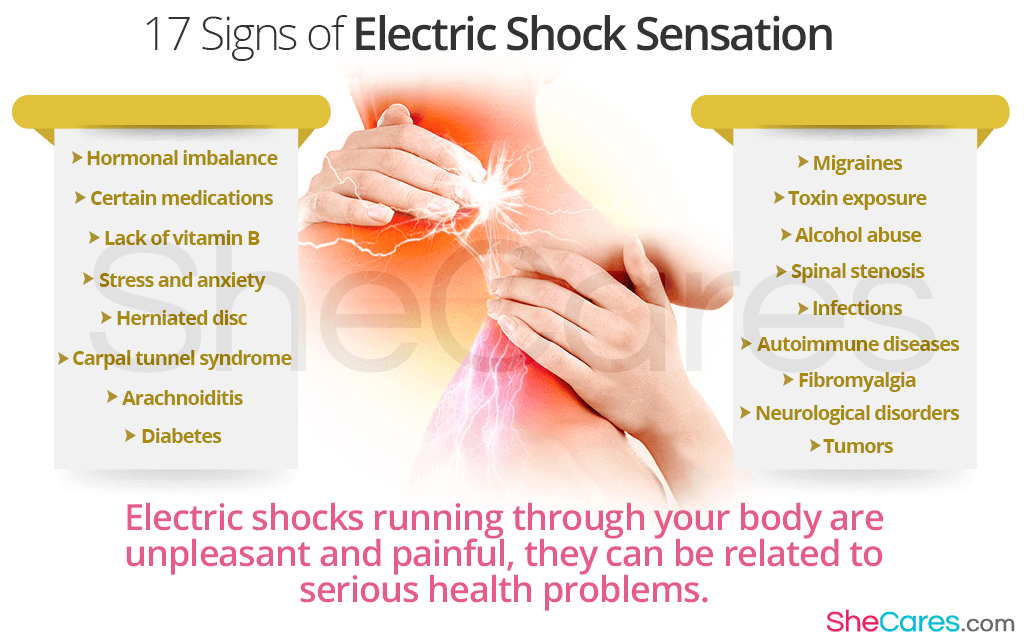
The sensation of electric shocks running through your body is unpleasant, often painful, and, understandably, a source of fear and stress. It can be a sign of numerous conditions, but their causes continue to be poorly understood by science. Continue reading to discover the most common signs of electric shock sensations.
Signs vs. Symptoms
Hormonal Imbalance
Shifting hormones during pregnancy, menopause, or other stages of women's life can bring about a wide range of symptoms, including an electric shock sensation all over the body.
Certain Medications
Medications to treat anxiety and depression commonly cause electric shocks in various body parts. Studies have shown that they can also be a sign of antidepressant withdrawal.1
Lack of vitamin B
Low vitamin B12 can cause an electric-like sensation, which usually shoots down the arms and legs, especially while bending. It can also be accompanied by difficulty walking, tingling, muscle cramps, and other symptoms.
Stress and Anxiety
Prolonged stress and anxiety are believed to exaggerate brain's response to various stimuli, often producing electric-like shocks and stabs in the head. They are sometimes referred to as brain zaps.
Herniated Disc
Commonly known as slipped disc, it produces pain, weakness, and electric-like shocks in lower extremities. It can also cause sciatica, which is characterized by pain radiating down the leg.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
It is caused by putting extensive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, producing tingling and electric-like sensations, numbness, and weakness in the hand and arm.
Arachnoiditis
It is an inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord, which is characterized by neurological symptoms, severe stinging, and electric-like shocks, mainly in the lower back and legs.
Diabetes
Poorly controlled diabetes can cause diabetic peripheral neuropathy, characterized by pain and a radiating sensation of electric shock-like throbbing, especially in the feet and hands.
Migraines
Migraine is a debilitating condition, characterized by severe headaches, throbbing and electric-like shocks on the sides of the head, nausea, and sensitivity to light.
Toxin Exposure
Exposure to harsh substances, like arsenic, has been associated with painful shock-like throbs in the head as well as other life-threatening complications.
Alcohol Abuse
Excessive alcohol consumption can cause irreversible damage to the peripheral nerves, resulting in various neurological symptoms, such as electric shock sensations.
Spinal Stenosis
It is an age-related condition of narrowing of the the spinal canal opening. It can affect lower back regions and extend to limbs, head, and neck, producing pain with electric shock feelings.
Infections
Several microorganisms can cause various infections, such as shingles or HIV, which can result in painful electric shocks in all parts of the body. There is also a link of Toxoplasmosis gondii infection with several menopause symptoms, including electric shock sensations.2
Autoimmune Diseases
Certain diseases, such as celiac disease or lupus, might cause a wide range of symptoms, including pain, tingling, and electric shocks anywhere in the body.
Fibromyalgia
It is characterized by widespread muscoskeletal pain, often with electric-shock throbs, fatigue, mood swings, and cognitive disturbances.
Neurological Disorders
Epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and other neurological diseases often produce electric-like shock sensations all over the body.
Tumors
Tumors in various body regions might compress the nerves, causing them to misfire and produce sharp electric-like shocks stabs.
Many women suffering from electric shock sensations undergo numerous tests in efforts to find the underlying cause, often without reaching a definite diagnosis. Although electric shocks cannot always be explained by science, they should be adequately monitored and managed by your doctor to ensure they do not progress into a more serious condition.
Sources
- Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology. (2015). Lhermitte's Sign: The Current Status. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4445188/
- Cleveland Clinic. (2019). Arachnoiditis. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12062-arachnoiditis
- ClinMed International LIbrary. (n.d.). Selected symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency and/or hyperhomocysteinemia. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://clinmedjournals.org/articles/jfmdp/jfmdp-3-057table2.html
- Journal of Psychopharmacology. (2010). Lhermitte's sign, electric shock sensations and high dose exactas consumption: preliminary findings. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19240087/
- Multiple Sclerosis Trust. (2018). Lhermitte's Sign. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://mstrust.org.uk/a-z/lhermittes-sign
- World Journal of Diabetes. (2015). Diabetic neuropathic pain: Physiopathology and treatment. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4398900/
Footnotes:
- The Primary Care Compasion for CNS Disorders. (2018). Brain Zaps: An Underappreciated Symptom of Antidepressant Discontinuation. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30605268/
- European Journal of Microbiology & Immunology. (2016). Influence of Toxoplasma Gondii Infection on Symptoms and Menopause. Retrieved May 11, 2021 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4838985/