Did you know?
Nearly all women experience irregular heartbeat during their lives. Whether characterized as a racing heart or a slow heartbeat, heart rhythm irregularities, as well as frequent symptoms associated with a wide range of diseases and triggers. Read below about the risk factors for irregular heartbeat and the symptoms to keep in mind.
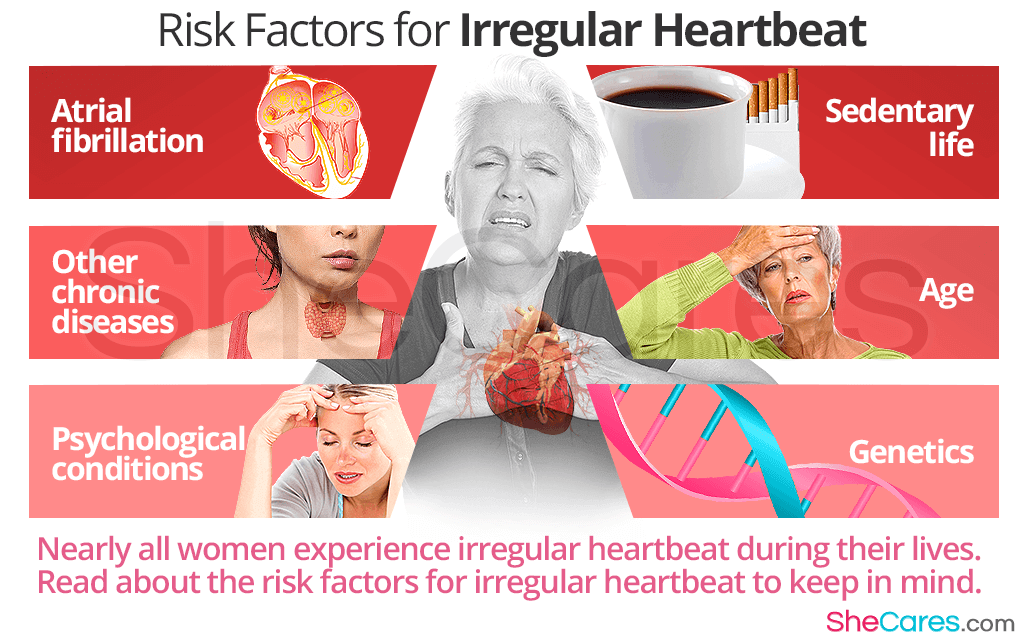
Risk Factors for Irregular Heartbeat
Sometimes identifying the exact cause of irregular heartbeat is a challenge; especially, when it is triggers by a few the following possible risk factors:
Atrial fibrillation. It produces a rapid, irregular heartbeat, or various heart tissues infection slow down the heart rate.
Other chronic diseases. Thyroid dysfunction, dehydration, blood sugar imbalance, fever, anemia are some of the many chronic diseases that can disrupt the normal heart functioning.
Psychological conditions. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), which includes six disorders, such as panic disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder, is the second most common cause of a rapid heartbeat.
Sedentary life. The long of stimulants and triggers of irregular heartbeat is long, and it includes stress, obesity, stationary life, air pollution, caffeine, cigarettes, and illegal drugs.
Age. Prevalence of heart disease and cardiac arrhythmias drastically increase after the age of 65.
Genetics. Some arrhythmias are believed to be inherited from the parents; for example, Brugada syndrome, a condition characterized by an irregular heartbeat.
Signs and Symptoms
Although sometimes asymptomatic, irregular heartbeat usually produces the following symptoms:
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fainting or near fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Sweating
When to See a Doctor
Most of the heart arrhythmias are not dangerous and often go away on their own, but some, if not treated, can cause a substantial damage to the heart and be fatal. Among the arrhythmia types, the most serious ones are atrial fibrillation, because it increases the risk of clot formation and may lead to a stroke, and ventral fibrillation, which often results in death within minutes. If you ever experience extreme pain or pressure in the chest, immediately call your doctor, because you might be experiencing a heart attack.
If you suffer from irregular heartbeat, learning how to measure your heart rate is a helpful skill, enabling you to monitor your heart and notice any alarming irregularities. Symptoms of irregular heartbeat are a signal for sedentary lifestyle. Learn more about irregular heartbeat or palpitations at night.